Context: Plants can listen to damage to other plants because plants release a group of compounds called green leaf volatiles (GLVs) into the air when injured, warning other plants about the proximity of danger.
Plants Can Listen Damage to Other Plants
- A Professor from Saitama University, known for his work on microscopes, has found a way to ‘watch’ plants responding to these warning signals.
- The study was published in Nature Communications in October 2023.
Green leaf volatiles (GLVs):
- They consist of six carbon (C6) compounds including alcohols, aldehydes and esters and are released from almost every plant.
- They can repel or attract herbivores and their natural enemies; and
- They can induce plant defences or against herbivores and pathogens and can have direct toxic effects on bacteria and fungi.
|
How Plants Communicate?
- Plants employ through a series of molecular reactions.
- These reactions activate when a plant sustains damage, leading to the release of green leaf volatiles (GLVs) as by-products.
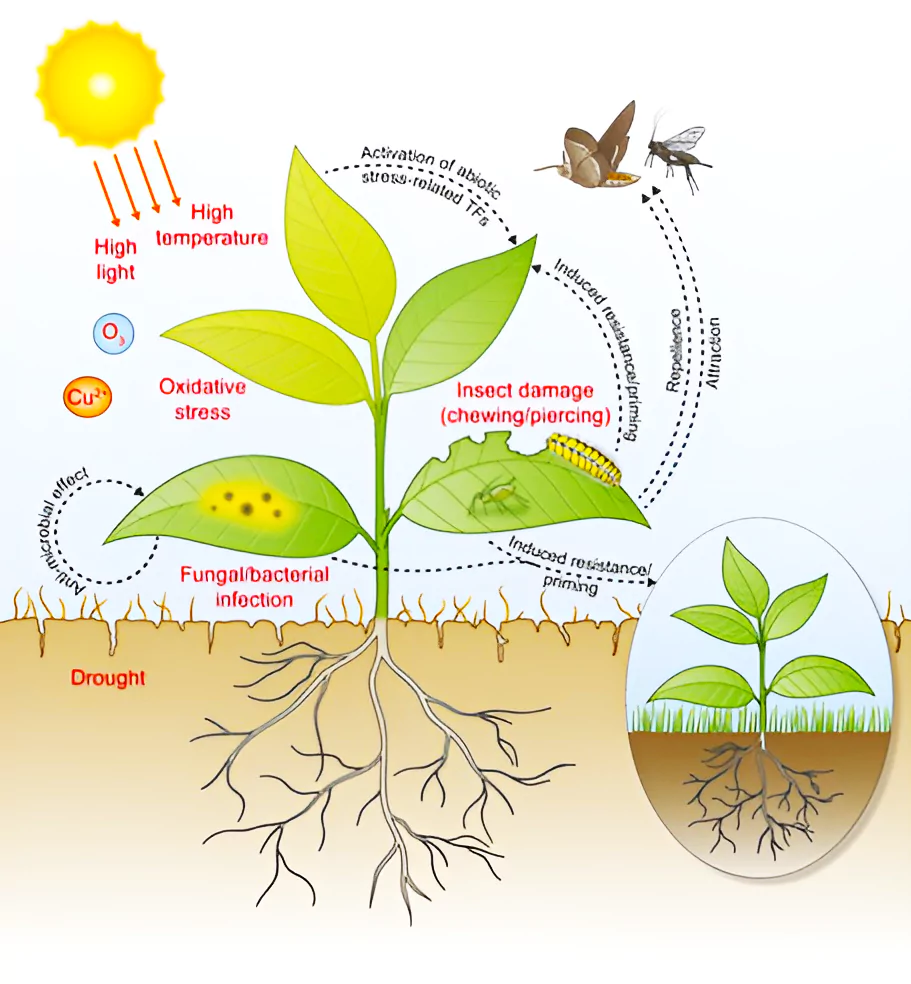
- Plants, by initiating a defense response, can render themselves less palatable or even indigestible to insect attackers.
- The molecular reaction is mediated by calcium, a common mediator of chemical and electrical signals found throughout biology.
Experimental Setup:
- Scientist inserted a gene into mustard plants, causing them to glow when flooded with calcium.
- Under a special microscope, the mutant plants lit up in response to touch, cutting, or being eaten by a caterpillar.
Significance of Findings:
- Potential Applications:
- Consideration for pesticide-free pest control by leveraging plants’ internal defense responses.
- GLVs could activate plants’ defenses, protecting crops naturally.
- Implications for Agriculture:
- GLVs may play a role in mitigating pest damage to crops.
- Understanding specific compounds inducing defenses against particular pests is crucial.
| Related Terms
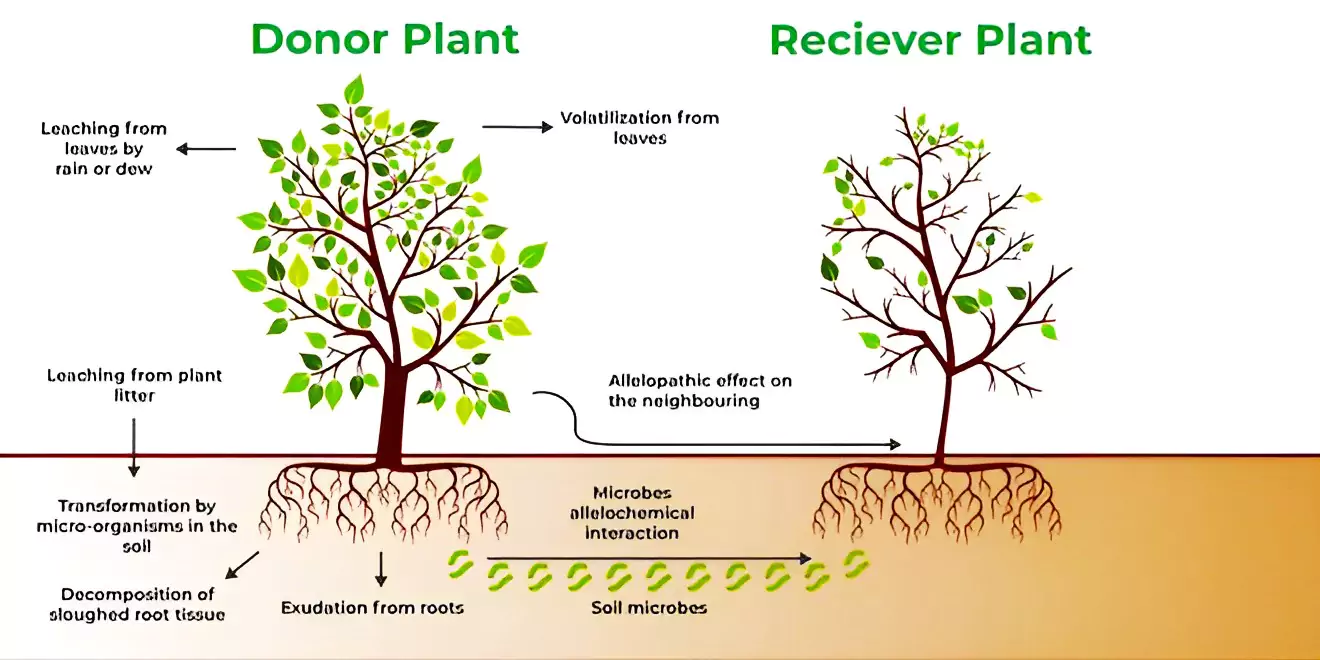
What is Allelopathy?
- It explains how certain plants emit dangerous substances known as allelochemicals, which have the ability to kill nearby plants.
- Allelochemicals produced by allelopathic plants might be concealed in their stems, leaves, flowers, or even roots. But the best sites for allelopathic plants to store their allelochemicals are in their leaves.
|
News Source: The Hindu
![]() 27 Nov 2023
27 Nov 2023
