Context:
Recently, the Supreme Court made public the report of the Committee on Prison Reforms.
More on News:
- In September 2018, the Supreme Court established a three-member committee led by former Supreme Court Justice Amitava Roy to investigate prison conditions in India.
- Prisons in the country and ‘persons detained therein’ are a State subject.
Status in India:
- Prison: The 1,319 prisons in the country consist of 564 Sub Jails, 424 District Jails, 148 Central Jails, 88 Open Jails, 41 Special Jails, 32 Women Jails, 19 Borstal Schools and 3 Other than the above Jails.
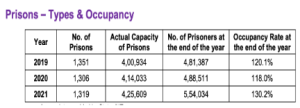 Prisoners: As per the NCRB, a total of (5,54,034) prisoners were confined as on 31st December, 2021 in various jails across the country.
Prisoners: As per the NCRB, a total of (5,54,034) prisoners were confined as on 31st December, 2021 in various jails across the country. -
- The number of Convicts, Undertrial inmates and Detenues were reported as 1,22,852, 4,27,165 and 3,470 respectively accounting for 22.2%, 77.1% and 0.6% respectively at the end of 2021.
Key Findings of the Report:
| Women Prisoners: |
- Rise in Female Prison Population in India (2014-2019): Between 2014 and 2019, Indian prisons witnessed an increase in the population of female prisoners by 11.7%, and by 2019, women accounted for 4.2% of the total prison population.
- Gender Disparities: Women in incarceration face more significant challenges compared to male prisoners, particularly in terms of access to basic facilities and services.
- Ex: Medical care, legal aid, paid labor opportunities, and recreational facilities.
- Lack of Exclusive Facilities: Only 18% of women prisoners in India are allocated exclusive women’s prison facilities, as only 15 states and UTs have functional women’s prisons
- Inadequate Sanitary Facilities: Less than 40% of prisons in the country provide sanitary napkins for female inmates.
- Shared Facilities: About 75% of female wards in prisons have to share kitchens and common facilities with male wards.
- Limited Complaint Mechanisms: In only 10 states and 1 union territory, women inmates are allowed to file complaints against jail staff for any form of abuse or harassment.
- Medical Challenges: There is a lack of separate medical and psychiatric wards, basic facilities for child delivery, and healthcare professionals who can address gender-specific health needs.
- Additionally, prisons in 19 states and 6 UTs lack psychiatric wards for women inmates.
|
| Overcrowding Concerns |
- The occupancy rate in Indian prisons, as of November 30, 2018, stood at 122 percent across 1,341 jails, including sub-jails, district jails, and others.
- High Overcrowding Rates: The highest overcrowding rates were observed in district prisons (148 percent), followed by central prisons (129 percent) and sub-prisons (106 percent).
|
| Transgender Prisoner |
- There is a lack of welfare schemes for transgender prisoners in most states and Union Territories.
- Only 13 states and 2 UT’s have designated a “complaint officer” to address rights violations of transgender inmates, as mandated by the Transgender Persons (Protection of Rights) Act, 2019.
|
| Suicide |
- Suicide was a major cause of the 817 unnatural deaths reported in jails across India during 2017-21.
|
Model Prisons Act 2023:
- About: The Ministry of Home Affairs has introduced the ‘Model Prisons Act 2023’ to replace a British-era law, the Prisons Act of 1894.
- Aim: To overhaul prison administration with a focus on the reformation and rehabilitation of inmates.
- Key features of the Model Prisons Act 2023:
- Punishment for Prohibited Items: The act includes provisions for punishing prisoners and jail staff for the use of prohibited items such as mobile phones within jails.
- Establishment of High-Security Jails: It outlines the establishment and management of high-security jails, as well as open and semi-open jails.
Factors Contributing to Overcrowding in Jails:
- Stagnancy of prison infrastructure against steady increase in inmate flow,
- Lack of initiative and drive of expansion or improvement in prison infrastructure,
- Avoidable arrests and incarceration for petty offences,
- Delay in investigation and trial.
|
-
- Parole, Furlough, and Premature Release: The act includes provisions for granting parole, furlough, and premature release to incentivize good conduct among prisoners.
- Modernization: It encourages the use of technology in prison management to enhance transparency and efficiency in prison administration. It also allows for video conferencing with courts and technological interventions.
- Special Provisions: The act includes special provisions for women prisoners and transgender inmates, taking into account their unique needs.
Committee’s Recommendations:

- Strengthening Undertrial Review Committee (UTRC) Mechanism: It assesses the release of undertrial prisoners and convicts eligible for release.
- Focus on Speedy Trials: Establishment of special fast-track courts to deal with petty offenses and long-pending cases.
- Monitoring by High Courts: High courts are urged to direct District & Sessions Judges to monitor the progress of cases involving prisoners in custody for extended periods, both in session triable and magistrate triable cases.
- Addressing Staff Shortages: Need to address staff shortages in the prison department across the country by filling existing vacancies.
- The Prison Department has a perennial average of 30%-40% vacancies.
- Alternative Sentencing: There are legal provisions for alternative sentences, such as fines, probation, and admonition, which are underutilized by the courts.
- Encouraging their use could help alleviate overcrowding and aid prisoner reintegration into society.
- Suicide-Proof Barracks with collapsible materials to prevent suicide in Prison.
- Suicide comprised 6·24% of all deaths reported in Indian prisons between Jan 1, 2015, and Dec 31, 2019.
- Transgender Welfare:
- Specific rules should be outlined regarding documentation, search procedures, placement, medical facilities, and recreational, welfare, and educational activities for transgender inmates.
- Separate bathing and toilet areas should be provided exclusively for transgender prisoners.
- A comprehensive health check-up should be conducted for every transgender prisoner upon admission to the jail.
- Encouraging Vocational Training and Skill Development
United Nations Environment Assembly
- The UNEA was created in June 2012, during the United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development, also referred to as RIO+20.
- It was the culmination of decades of international efforts, initiated at the UN Conference on the Human Environment in Stockholm in 1972.
- It is the world’s highest-level decision-making body on the environment.
- Assembly meets biennially to set priorities for global environmental policies and develop international environmental law.
- Understanding critical environmental challenges and preserving and rehabilitating our environment is at the heart of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
|
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 6 Sep 2023
6 Sep 2023
 Prisoners: As per the NCRB, a total of (5,54,034) prisoners were confined as on 31st December, 2021 in various jails across the country.
Prisoners: As per the NCRB, a total of (5,54,034) prisoners were confined as on 31st December, 2021 in various jails across the country. 