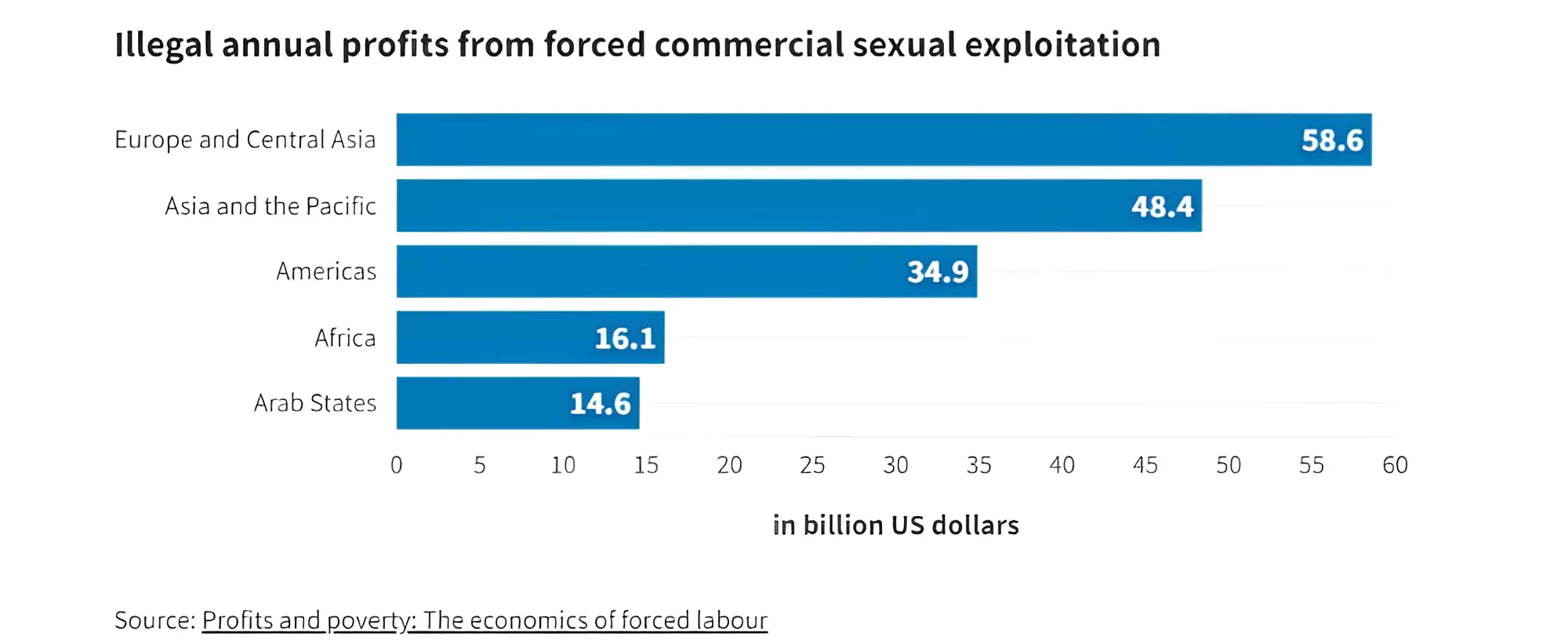
According to a research paper, titled ‘Profits and Poverty: The Economics of Forced Labour’, released by the International Labour Organisation (ILO), forced labor earns illegal earnings of $36 billion each year.
About International Labour Organization (ILO)
|
|---|
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.

<div class="new-fform">
</div>