![]() 6 Feb 2024
6 Feb 2024
English
हिन्दी

This article is based on the news “Government introduced Public Examinations Bill 2024 in Lok Sabha” which was published in the All India Radio. The Government has recently introduced the Public Examinations (Prevention of Unfair Means) Bill, 2024 in the Lok Sabha.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Parliament Budget Session 2024 Live Updates, Union Budget 2024-25, Interim Budget 2024-2025, and Parliament Passes Three Criminal Law Reform Bills.
Relevancy for Mains: Public Examinations Bill 2024: Background, Need, Highlights, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
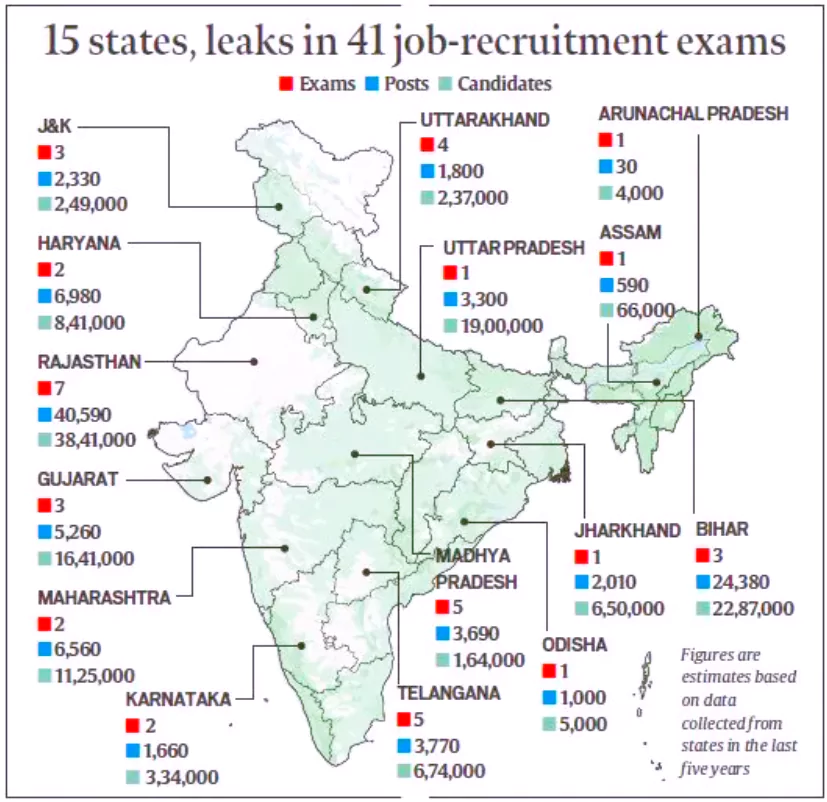 Constable recruitment examination in Bihar following question paper leaks.
Constable recruitment examination in Bihar following question paper leaks.
Anti Cheating Laws in States
|
|---|
Challenges Associated with Public Exams
|
|---|
Government Initiatives to Enhance Transparency in Examinations
|
|---|
News Source: NOA
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>