The Union Minister for Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying is set to inaugurate India’s first commercial-scale tropical Recirculatory Aquaculture System (RAS) based Rainbow Trout Aquaculture Farm & Research Institute in Hyderabad, Telangana.
About Recirculatory Aquaculture System (RAS)
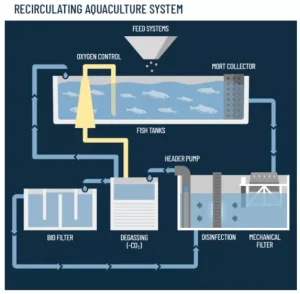
- A Recirculatory Aquaculture System (RAS) is a land-based, closed-loop aquaculture system in which water from culture tanks is continuously treated and reused, allowing intensive fish farming with minimal freshwater use and controlled environmental conditions.
- RAS is different from flow-through systems, where water is used once and discharged. In RAS, water is treated and reused multiple times.
- Species Cultured:
- Food fish: Tilapia, Catfish, Salmon, Trout, Barramundi
- Others: Shrimp, Prawns, Ornamental fish
Core Components
- Culture Tanks – Where fish/shrimp are reared.
- Mechanical Filter – Removes solid wastes (uneaten feed, feces).
- Biofilter – Houses nitrifying bacteria that convert toxic ammonia → nitrite → nitrate.
- Oxygenation/Aeration Unit – Maintains dissolved oxygen levels.
- Disinfection Unit – UV or ozone to control pathogens.
- Pumps & Pipes – Circulate water through the system.
- Temperature & pH Control – Ensures species-specific conditions.
|
Key Features of Recirculatory Aquaculture Systems
- Closed-Loop Water Reuse The system continuously recycles water after treatment, resulting in 90–99% water reuse and significantly reducing dependence on freshwater resources.
- Mechanical Waste Removal Mechanical filtration units remove solid wastes such as fish excreta and uneaten feed, thereby preventing deterioration of water quality.
- Biological Filtration Process Biofilters containing nitrifying bacteria convert toxic ammonia into nitrite and then into relatively harmless nitrate, ensuring a safe environment for aquatic organisms.
- High Stocking Density RAS supports high stocking densities by maintaining optimal water quality, which leads to higher productivity per unit area.
- Controlled Environmental Conditions The system allows precise regulation of temperature, pH, dissolved oxygen and salinity, enabling consistent and year-round aquaculture production.
Limitations of RAS
- High initial capital investment
- Requires skilled manpower and uninterrupted power supply
RAS vs Traditional Aquaculture
| Aspect |
RAS |
Traditional Pond Culture |
| Water use |
Very low |
High |
| Land requirement |
Low |
High |
| Control over environment |
Very high |
Limited |
| Pollution |
Minimal |
Often high |
| Initial Cost |
High |
Low |
About Trout farming
- Trout farming is the practice of raising trout in controlled freshwater systems for food, restocking rivers, or sport fishing.
- It is common in cool regions because trout need clean, cold, oxygen-rich water.
- Environmental Requirements:
- Temperature: Generally 10–18°C
- Water quality: High dissolved oxygen, low turbidity
- Common trout species
- Rainbow trout: Most widely farmed. Fast growth and adaptable.
- Brown trout: Slower growth, higher market value in some regions.
- Brook trout: Sensitive to water quality, usually small scale.
Government Initiatives Supporting Recirculatory Aquaculture System (RAS)
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY): It is the flagship government scheme promoting sustainable aquaculture in India, under which Recirculatory Aquaculture System (RAS) technology is actively supported to modernise the fisheries sector and enhance productivity.
- Financial Assistance: Under PMMSY, the Government offers central financial assistance for establishing RAS units, with up to 40% of the unit cost subsidised for general category beneficiaries and 60% for Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes and women beneficiaries.
Cold Water Fisheries in India
- Emerging High-Potential Segment: Cold water fisheries are gaining importance due to rising demand for premium species, export potential, and adoption of sustainable technologies.
- Traditional Geographical Concentration: Trout farming has historically been concentrated in Himalayan and hill states such as Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Jammu & Kashmir, Arunachal Pradesh, and Sikkim, utilising snow-fed streams.
- Seed Production Expansion: The Department of Fisheries has achieved annual production of 14 lakh trout seeds through the establishment of new hatcheries.
- Institutional Collaboration: Uttarakhand signed an MoU with the ITBP under the Vibrant Villages Programme to support trout supply and livelihoods.
![]() 5 Jan 2026
5 Jan 2026



