The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has announced the list of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in the Upper Layer (UL) under Scale Based Regulation (SBR) for the year 2024-25
Highlights of Recent RBI Release
The NBFC Upper Layer (UL) list for 2024-25 includes Tata Sons Private Ltd, Bajaj Finance Ltd, LIC Housing Finance Ltd, and Aditya Birla Finance Ltd, among others.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About NBFC Regulation
- Regulatory Powers: RBI regulates NBFCs under the RBI Act, 1934, with powers to register, inspect, and supervise NBFCs meeting the 50-50 principal business criteria.
- 50-50 Principal Business Criteria: Financial activity constitutes over 50% of total assets and gross income.
- Requirements for NBFC Registration
-
- Must be a company registered under Section 3 of the Companies Act, 1956.
- Minimum Net Owned Fund (NOF) of ₹200 lakh.
About Scale-Based Regulation (SBR) Framework
- The Scale-Based Regulation (SBR) framework, introduced by the Reserve Bank of India in 2021, is a regulatory framework designed to classify Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) based on their asset size and scoring criteria.
- The aim is to strengthen risk management, apply proportional regulation, and address systemic risks in the NBFC sector.
- Objectives of the SBR Framework
- Mitigation of Systemic Risks: To reduce the impact of financial contagion and safeguard the overall financial ecosystem.
- Proportional Regulation: To ensure that regulatory intensity corresponds to the scale and complexity of NBFC operations.
- Enhanced Risk Management: To improve the operational resilience and governance standards of NBFCs.
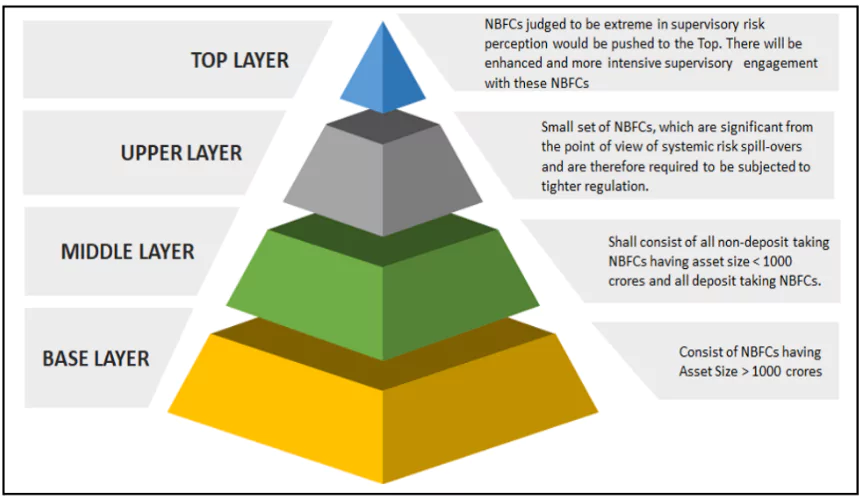 Categorization of NBFCs
Categorization of NBFCs
- Base Layer (NBFC-BL): Includes smaller NBFCs with limited risk to the system.
- Middle Layer (NBFC-ML): Comprises larger entities with moderate systemic importance.
- Upper Layer (NBFC-UL): High-risk NBFCs based on scoring methodology and systemic importance.
- Top Layer (NBFC-TL): Rarely occupied, for entities posing exceptional risks.
- Features of Enhanced Regulations
- NBFC-ULs are subjected to stricter regulatory requirements for at least five years.
- This includes increased compliance, monitoring, and governance norms
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Difference Between Banks and NBFCs
| Parameter |
Banks |
NBFCs |
| Demand Deposits |
Can accept demand deposits |
Cannot accept demand deposits |
| Payment and Settlement System (PSS) |
Part of PSS; can issue cheques |
Not part of PSS; cannot issue cheques |
| Deposit Insurance |
Deposits insured by Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation |
No deposit insurance facility available |
| Reserve Ratios (CRR, SLR) |
Must maintain Reserve Ratios prescribed by RBI |
Not required to maintain Reserve Ratios |
| Regulation Act |
Regulated under Banking Regulation Act, 1949 |
Regulated under Companies Act, 1956 |
| Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) |
Up to 74% FDI allowed for private sector banks (49% under automatic route) |
100% FDI allowed |
![]() 18 Jan 2025
18 Jan 2025

 Categorization of NBFCs
Categorization of NBFCs