Recently, the Reserve Bank of India released the 29th issue of the Financial Stability Report (FSR).
- The Indian Fintech industry is estimated to be at US$ 150 billion by 2025. India has the 3rd largest FinTech ecosystem globally. Boston Consulting Group (BCG) predicts that the proportion of digital payments will grow to 65% by 2026.
About Financial Stability Report (FSR)
The FSR is published by the RBI, once every six months (a biannual report).
- Mandate: It evaluates the banks, NBFCs and other financial intermediaries based on the progress in terms of:
- Operating margins
- Net Interest Income (NII)
- Net Interest Margins (NIMs)
- Gross Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)
- Net Non-Performing Assets (NPAs)
- The outcome of the various stress tests conducted by the RBI
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Highlights of the 29th Financial Stability Report (FSR)
The FSR reflects the collective assessment of the Sub-Committee of the Financial Stability and Development Council (FSDC) on the resilience of the Indian financial system and risks to financial stability.
- Stable Global Economy: Despite the various challenges in the global economy- facing heightened risks from prolonged geopolitical tensions, elevated public debt, and the slow progress in disinflation, the global financial system has remained resilient, and financial conditions stable.
- Resilient and Robust Indian Economy: The Indian economy and the financial system remain robust and resilient, anchored by macroeconomic and financial stability.
- With improved balance sheets, banks and financial institutions are supporting economic activity through sustained credit expansion.
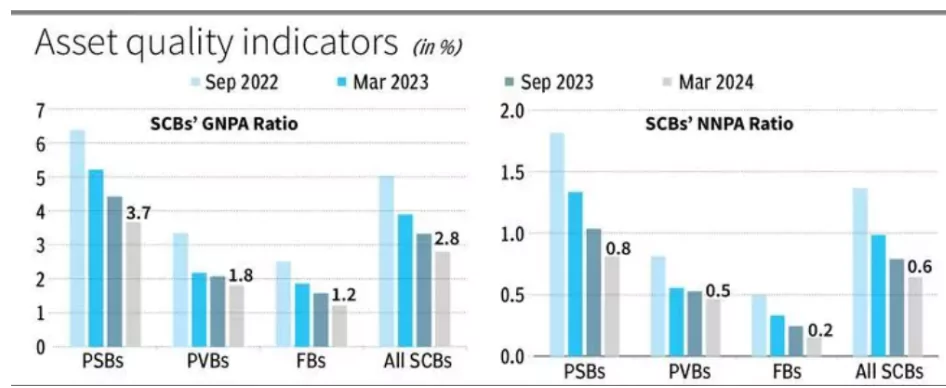
 Financial Statistics for Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) at end-March 2024:
Financial Statistics for Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) at end-March 2024:-
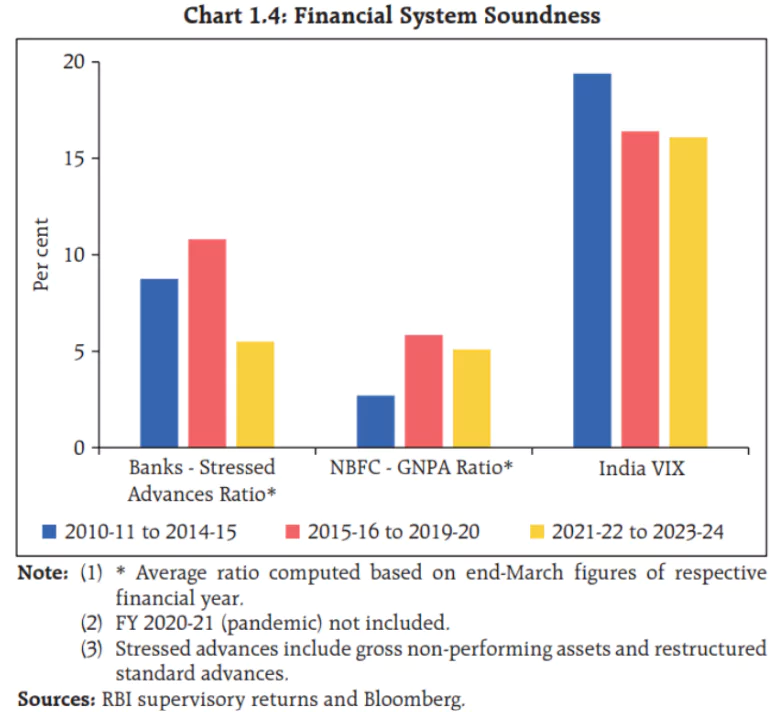
- Capital to Risk-Weighted Assets Ratio (CRAR): it is 16.8%, which means that for every 100 units of risk, the bank has 16.8 units of capital to cover potential losses.
- Common Equity Tier 1 (CET1) Ratio: It is 13.9%, which means the bank has a strong base of high-quality capital.
- Gross Non-Performing Assets (GNPA) Ratio: It fell to a multi-year low of 2.8%, which means that 2.8% of the total loans are in trouble.
- Net Non-Performing Assets (NNPA) Ratio: It is 0.6%, which means that 0.6% of the total loans, after accounting for provisions, are in trouble.
- Macro Stress Tests for Credit Risk: It revealed that SCBs would be able to comply with minimum capital requirements, with the system-level CRAR in March 2025 projected at 16.1%, 14.4% and 13.0% respectively, under baseline, medium and severe stress scenarios.
- These scenarios are stringent conservative assessments under hypothetical shocks and the results should not be interpreted as forecasts.
- Stress test results revealed that banks are well capitalised and capable of absorbing macroeconomic shocks even in the absence of any further capital infusion by stakeholders.
- Stress tests are conducted covering credit risk, interest rate risk and liquidity risk and the resilience of commercial banks in response to these shocks is studied.
- Using the stress tests, the RBI projects impairment or bad loans and capital ratios over a one-year horizon under above mentioned scenarios.
- Health of Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs): It is healthy, with CRAR at 26.6% (financially strong), GNPA ratio at 4.0% (meaning 4% of their loans are not being repaid) and return on assets (RoA) at 3.3% (making good profits from their assets), respectively.
Indian Banking Sector
Banks are Financial Intermediaries between borrowers and lenders. It accepts deposits from the public and lends money to businesses and consumers. Its primary liabilities are deposits and primary assets are loans and bonds.
- Statistics: The Indian banking system consists of 12 public sector banks, 21 private sector banks, 44 foreign banks, 12 Small finance banks. As of December 2023, the total number of micro-ATMs in India reached 16,88,558. Moreover, there are 1,26,205 on-site ATMs and Cash Recycling Machines (CRMs) and 93,671 off-site ATMs and CRMs.
- Classification: Banks, forming part of the Banking System in India, can be divided into two categories – Scheduled Banks and Non-Scheduled Banks.
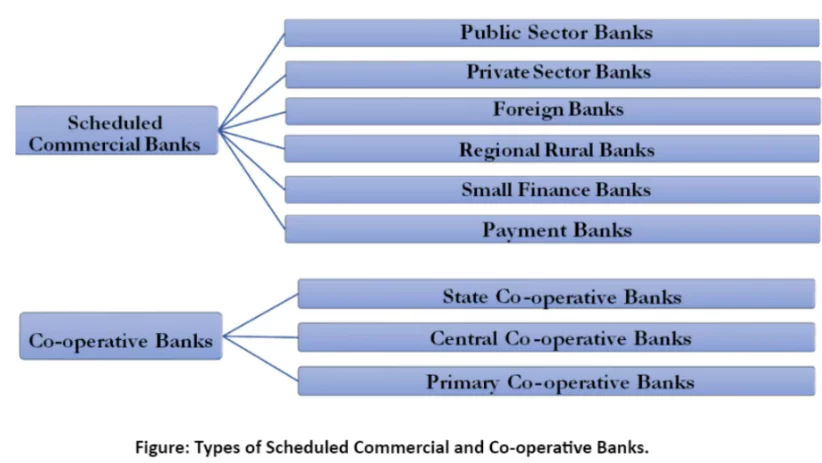 Scheduled Banks: Those financial institutions that are listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. This inclusion signifies that they meet specific criteria set by the RBI and are subject to its stricter regulations.
Scheduled Banks: Those financial institutions that are listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. This inclusion signifies that they meet specific criteria set by the RBI and are subject to its stricter regulations.
- Under the Second Schedule of RBI Act, 1934, these banks should raise at least Rs 5 lakhs and capital.
- Non-Scheduled Banks: Those financial institutions that do not meet the criteria to be included in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934.
- They operate under a different set of regulations as compared to Scheduled Banks.
 Structure of Banking System: The RBI is at the top of the structure of the Banking System in India and acts as the central bank of India. Beneath the central bank operates various types of following banks:
Structure of Banking System: The RBI is at the top of the structure of the Banking System in India and acts as the central bank of India. Beneath the central bank operates various types of following banks:-
- Commercial Banks: State Bank of India (SBI), Housing Development Finance Corporation (HDFC) Bank, Industrial Credit and Investment Corporation of India (ICICI) Bank, etc.
- Cooperative Banks: Bharat Co-operative Bank, Saraswat Co-operative Bank, Cosmos Co-operative Bank, etc.
- Development Banks: Industrial Finance Corporation of India (IFCI), Industrial Development Bank of India (IDBI), Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI), etc.
- Differentiated Banks: Small Finance Banks and Payment Banks are examples of differentiated banks in India such as Custodian Banks and Wholesale and Long-Term Finance banks (WLTF)
- Basel Norms in the Banking Industry:
- It encompasses international regulatory standards designed to ensure stability by offering guidelines on capital adequacy, risk management, and liquidity.
- These norms play a crucial role in regulating banks worldwide, promoting a safer and more resilient banking sector.
Achievements as per 29th Financial Stability Report (FSR)
- Robust Performance: The Indian banking system has continued to register a robust performance across various metrics.
- Not only have banks seen a sustained improvement in their asset quality, but their profitability has remained high, and their capital position also remains healthy.
- This improvement is being observed across both public and private sector banks.
- This has, in turn, improved their attractiveness — the Nifty Bank index is up more than 16% over the past year, with PSU banks registering handsome gains.
- Decline in Gross Non-Performing Loans: According to the report, the gross non-performing loans of the Indian banking system have declined to a 12-year low of 2.8% in March, with declines observed across public, private and foreign banks.
- Sector wise data shows that bad loans have fallen across agriculture, industry, services and the personal loans category.
- This broad decline in bad loans has been driven by a combination of write-offs and fall in fresh bad loans.
- Improvement in Provision Coverage Ratios: Net interest income of banks have risen, and their capital position remains healthy.
- Further, banks may well see bad loans fall further to 2.5% by March 2025 under usual business conditions.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Concerns Raised by the 29th Financial Stability Report (FSR)
Despite having many positive impacts, the FSR has disquieting stuff on many fronts.
- Decline in Savings:
- Gross Savings Rate: Decline in Gross Savings Rate to 29.7% of gross net disposable income.
- Household Savings: Fell household savings from 20% during the period 2013-22 to 18.4% in 2022-23.
- Net Financial Saving: Dropped From an average of 39.8% during 2013-2022, this share is now down to 28.5% in 2022-23.
- While a rise in financial liabilities has resulted in net financial savings falling to 5.3% of GDP during 2022-23, down from an average of 8% during 2013-2022.
- Decline in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI):
- FDI Flows: Dropped from $28 billion in 2022-23 to $9.8 billion in 2023-24.
- Foreign direct investment (FDI): A category of cross-border investment in which an investor resident in one economy establishes a lasting interest in and a significant degree of influence over an enterprise resident in another economy.
 Reason for FDI Decline: It may be partly due to higher repatriations, but its magnitude is a cause for concern. Especially since the inclusion of government securities in the JPMorgan global bond index will likely attract more debt inflows, further skewing the balance against FDI.
Reason for FDI Decline: It may be partly due to higher repatriations, but its magnitude is a cause for concern. Especially since the inclusion of government securities in the JPMorgan global bond index will likely attract more debt inflows, further skewing the balance against FDI.- For Foreign Portfolio Investment (FPI): In the same period, FPI flows shot up from minus $4.8 billion to $44.6 billion, a difference of nearly $50 billion.
- FDI inflows are preferred over easy-come-easy-go FPI inflows or ‘hot money.’
- Assets Valuation Concerns:
- Stretched Valuation: The FSR warns that some asset valuations could be stretched, and there has been seen a “sharp increase in prices of relatively riskier assets”.
- Correlated Effects: In stretched valuation, “sudden shocks could precipitate stress that spreads contagiously across financial market segments through correlated sell-offs and band-wagon effects.”
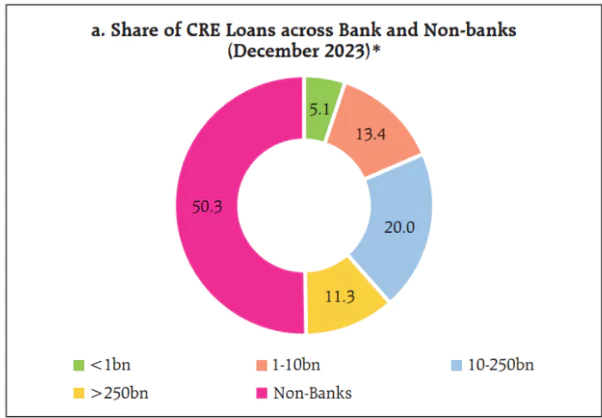
- Non-Bank Institution: The growing importance of the role of non-bank institutions in financial intermediation and higher and hidden leverage could amplify stress even further in the face of large shocks.
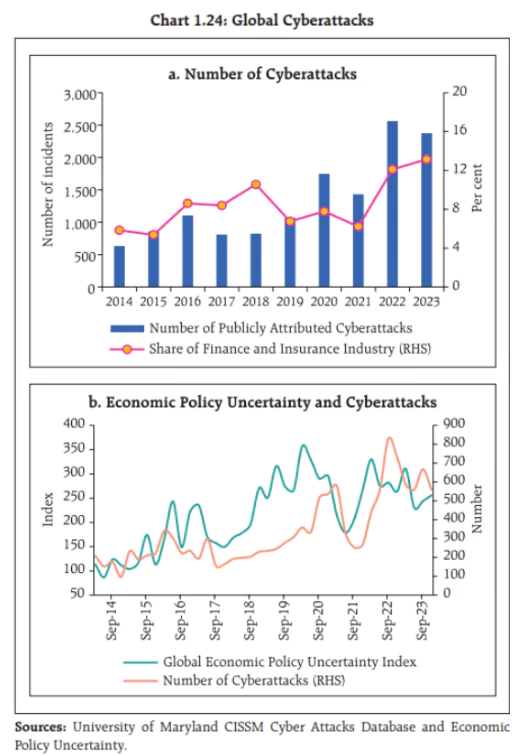
 Others: Emerging risks, including those from cyber hazards, climate change and global spillovers.
Others: Emerging risks, including those from cyber hazards, climate change and global spillovers. -
- Domestic Risks: Somewhat newer concerns are beginning to make themselves felt in the financial system. Two domestic risks were perceived to have increased.
- Lower Consumption and Demand: This reflects broader concerns about wage and employment growth in the Indian economy.
- Climate Change along with Cyber Risks: These are viewed as the greatest macro-financial risk at the moment.
Way Forward
Following actions are required to be taken to counter the arising challenges and achieve the best of the potential of Indian Banking System:
- Tackle Climate Risks: The FSR contains a review of global trends when it comes to regulating climate risk. Both the Indian financial system and financial-sector regulators, including the RBI, need to start preparing to deal with increasing climate risk.
- Climate change will also have implications for monetary policy, which could increase risks for the financial system.
- Focus on Governance: The highest priority must be assigned to governance – strong governance is at the core of resilience of stakeholders in the financial system.
- Google India Digital Services (P) Limited and NPCI International Payments Ltd (NIPL), have signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) to expand the transformative impact of UPI to countries beyond India.
- The digital payments system in India has evolved the most among 25 countries with India’s Immediate Payment Service being the only system at level five in the Faster Payments Innovation Index (FPII).
- India’s Unified Payments Interface (UPI) has also revolutionized real-time payments and strived to increase its global reach in recent years.
- Monitoring: As per latest FSR, decline in saving is a matter of concern and deserves monitoring.
- Even as the asset quality of retail loans has improved in the case of private sector banks (bad loans have fallen from 2.1% in June 2022 to 1.2% in March 2024), 40% fresh additions to bad loans is a concerning issue, which requires continuous supervision.
- Advancement in Technology: It has brought mobile and internet banking services to the fore. AI and automation are demonstrating unprecedented value while Blockchain has sparked innovation throughout the business landscape and is poised to continue in doing so.
- Others: Enhanced spending on infrastructure, speedy implementation of projects and continuation of reforms are expected to provide further impetus to growth in the banking sector.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Key Government & Regulatory Initiatives:
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana: The world’s largest financial inclusion initiative, “Jan Dhan Yojna”, has helped in new bank account enrollment of 486+ mn beneficiaries, with 265+ mn being women.
- Scheme for Setting up of Wholly Owned Subsidiaries (WOS) by foreign banks in India: In 2013, the RBI published guidelines for setting up of WOS by foreign banks in India to promote foreign investments into the sector.
- Introduction of Kisan Credit Card (KCC) loans in a fully digital and hassle-free manner.
- Aadhaar e-KYC authentication for NBFC/Non-Banking Entities: All NBFCs, payment system providers and payment system participants can now obtain Aadhaar Authentication Licence (KUA/sub-KUA)
- Establishment of Digital Banking Units: In 2022, 75 DBUs were announced in 75 districts of the country to commemorate 75 years of India’s independence.
|
![]() 3 Jul 2024
3 Jul 2024


 Financial Statistics for Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) at end-March 2024:
Financial Statistics for Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs) at end-March 2024:
 Scheduled Banks: Those financial institutions that are listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. This inclusion signifies that they meet specific criteria set by the RBI and are subject to its stricter regulations.
Scheduled Banks: Those financial institutions that are listed in the 2nd Schedule of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. This inclusion signifies that they meet specific criteria set by the RBI and are subject to its stricter regulations.
 Structure of Banking System: The RBI is at the top of the structure of the Banking System in India and acts as the central bank of India. Beneath the central bank operates various types of following banks:
Structure of Banking System: The RBI is at the top of the structure of the Banking System in India and acts as the central bank of India. Beneath the central bank operates various types of following banks: Reason for FDI Decline: It may be partly due to higher repatriations, but its magnitude is a cause for concern. Especially since the inclusion of government securities in the JPMorgan global bond index will likely attract more debt inflows, further skewing the balance against FDI.
Reason for FDI Decline: It may be partly due to higher repatriations, but its magnitude is a cause for concern. Especially since the inclusion of government securities in the JPMorgan global bond index will likely attract more debt inflows, further skewing the balance against FDI. Others: Emerging risks, including those from cyber hazards, climate change and global spillovers.
Others: Emerging risks, including those from cyber hazards, climate change and global spillovers.