Context:
The Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raised the repo rate by 25 basis points in an effort to bring inflation back to the target level of 4%.
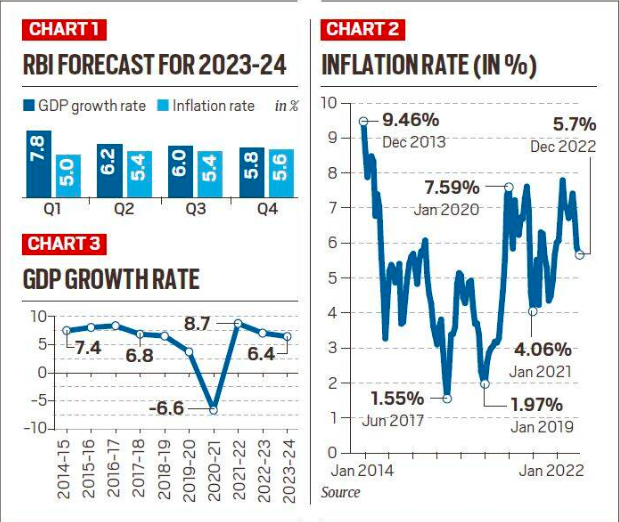
Image Source: The Indian Express
Key Points:
About Repo Rate:
- The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends to commercial banks.
- It can be adjusted by the MPC to reduce price fluctuations in the economy while keeping the inflation rate at a reasonable level.
RBI Monetary Policy:
- The RBI’s monetary policy aims to control the supply and cost of money in the economy.
- If the RBI is more concerned about containing inflation, it raises interest rates to curb economic activity, and if it wants to stimulate growth, it lowers interest rates.
- The decision to raise the repo rate was made by a 4-2 majority in the MPC.
- The RBI’s stance was more “hawkish” than expected, as it was more concerned about high inflation than the moderation in economic growth.
- A hawkish stance is a monetary policy stance taken by the central bank, that is characterized by a strong focus on controlling inflation and maintaining price stability.
What will be the impact?
- Lending rates of banks are expected to go up as the cost of funds is expected to rise further.
- EMIs on vehicles, home and personal loans will also rise.
- The external benchmark linked lending rate (EBLR) of banks will rise by 25 bps, as such loans are linked to the Repo rate.
- The EBLR is a type of lending rate adopted by banks, in which the interest rate on loans is linked to an external benchmark instead of being determined by the bank itself.
- Marginal cost of funds-based lending rates (MCLR) are also expected to move up. The hike will help in moderating inflation in the country.
- The MCLR is calculated based on the marginal cost of funds, which takes into account the cost of the latest deposit obtained by the bank and the cost of borrowing funds from the RBI’s repo rate.
- This means that changes in the repo rate will be reflected in the MCLR and, in turn, the interest rates offered on loans by the bank.
GDP Growth Projection:
- The RBI expects India’s GDP to grow by 6.4% in the next financial year, but the growth rate is expected to slow down in each quarter of the year.
Inflation Forecast:
- The RBI has lowered the inflation target for FY23 from 6.7 per cent to 6.5 per cent – which is still above the RBI’s comfort level of four per cent.
- Inflation is expected to be 5.3 per cent in FY24.
News Source: The Indian Express
![]() 9 Feb 2023
9 Feb 2023
