Context
Recently, Norway, Ireland and Spain announced that they will formally recognise the state of Palestine.
Norway, Ireland, and Spain Recognize Palestine; Steps Towards Peace in West Asia
- The European countries’ announcements come weeks after 143 of 193 countries in the United Nations General Assembly voted for full membership to the U.N. for the State of Palestine.
- Norway: It has been involved in peace talks between Israel and Palestine for decades, including by hosting the beginning of the Oslo process, which culminated in the Oslo Peace Accords in the early-mid 1990s, agreements that were meant to usher in a resolution to the conflict and a two state solution.
- Ireland: It believed that recognizing a Palestinian state would lead to peace and reconciliation in West Asia.
- Spain: It announced that its recognition of Palestine was not against the Israelis, but a step in favor of “peace, justice and moral consistency.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Oslo Peace Accord:
- Israel accepted the Palestine Liberation Organization (PLO) as the representative of Palestine, and the PLO renounce terrorism and recognized Israel’s right to exist in peace.
- Both sides agreed that a Palestinian Authority (PA) would be established and assume governing responsibilities in the West Bank and Gaza Strip over a five-year period.
|
Implications of Recognition
- Unclear to Say: While dozens of countries have recognized Palestine, none of the major Western powers has done so, and it is unclear how much of a difference the move by the three countries might make.
- International Legitimacy: This recognition would mark a significant accomplishment for the Palestinians, who believe it confers international legitimacy on their struggle.
- Negligible Short Term Change: Little would likely change on the ground in the short term. Peace talks are stalled, and Israel’s hardline government has dug its heels in against Palestinian statehood.
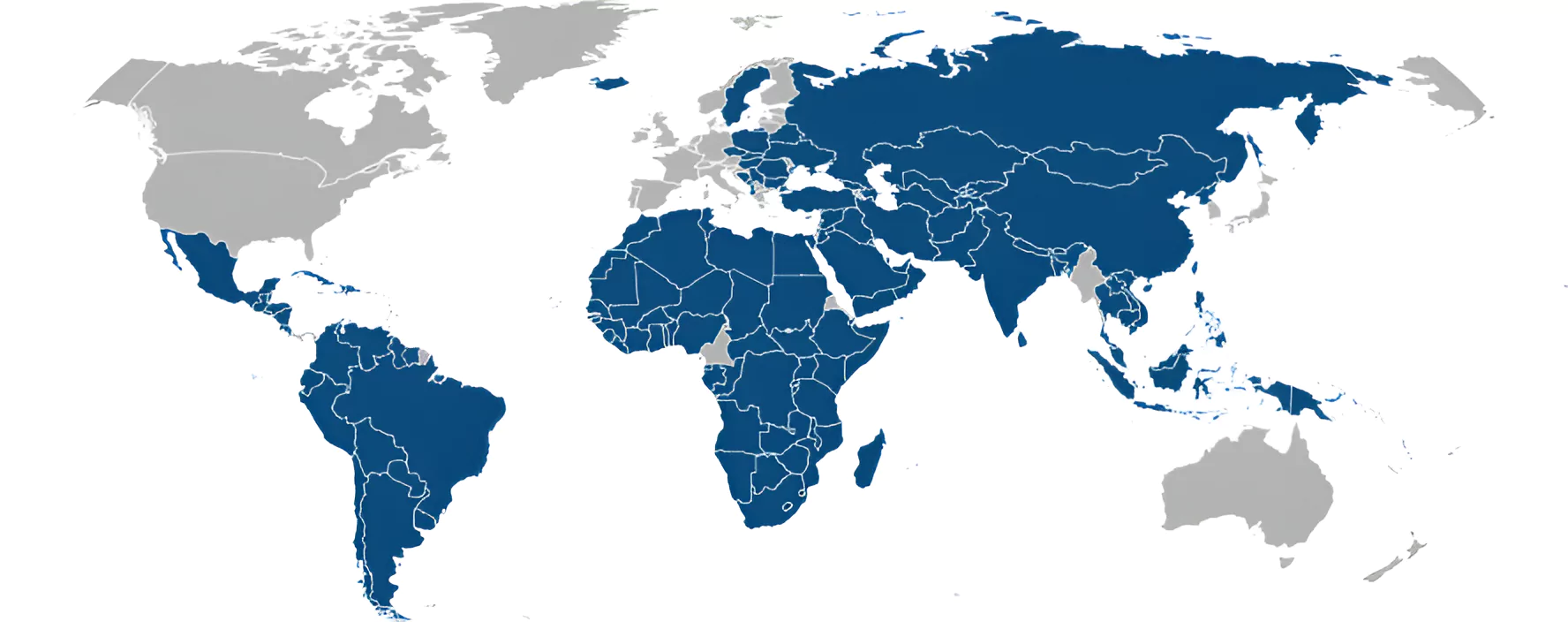
Recognition to Palestine as a State
- Some 140 countries have already recognized Palestine, more than two-thirds of the United Nations’ membership.
- Some major powers have indicated their stance may be evolving amid the outcry over the consequences of Israel’s offensive in Gaza, which has killed more than 35,000 Palestinians according to Gaza’s Health Ministry.
A Timeline Israel Palestine Conflict
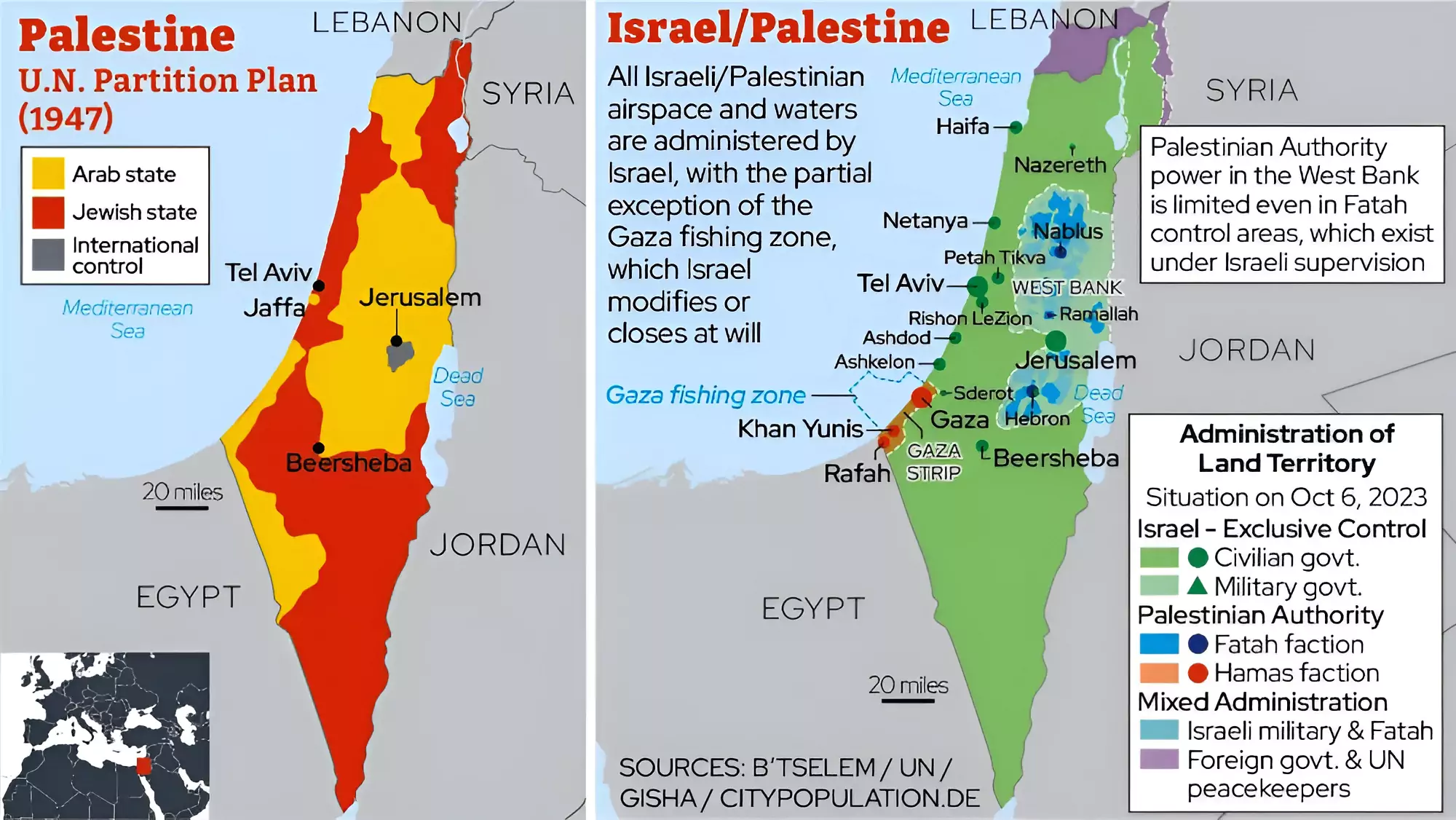
- 1949: Israel signs truces with Arab countries, and the Gaza Strip was under Egypt’s control.
- 1956: Israel invades the Sinai Peninsula and the Gaza Strip in response to Egypt’s nationalization of the Suez Canal.
- 1957: Israel withdrew from Egyptian land, except from the Gaza Strip and the area of the Gulf of Aqaba, arguing that the Gaza Strip never belonged to Egypt.
- 1967: During the Six-Day War, Israel gains control of the Gaza Strip and the Sinai Peninsula.
- 1987: Palestine initiated the first intifada against Israel.
- 1993: Arafat signs the Oslo Accords with Israel, committing to negotiating a two-state solution; Hamas launches suicide bombings in Israel.
- 2021: Israeli police raid Al-Aqsa Mosque, leading to an 11-day war between Israel and Hamas; casualties on both sides.
- 2023: Recent attacks by Hamas on Israel
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
![]() 23 May 2024
23 May 2024

