Context:
This editorial is based on the news “Iran-backed Houthis warn of ‘serious consequences’ after US, UK strikes hit Yemen” which was published in Indian Express. The United States-backed coalition including the United Kingdom launched airstrikes in Yemen, targeting Houthi rebels.
US-UK Airstrikes in Yemen and the Unfolding Humanitarian Crisis
- Airstrike Targeted: According to reports, the airstrikes by the US and UK on Yemen targeted an airbase, airports, and a military camp.
- The Red Sea Crisis: It is part of the violent regional spillover of Israel’s war with Hamas in the Palestinian enclave of Gaza.
- Hamas militants attacked southern Israel, killing 1,200 people and seizing 240 hostages.
- Israel has responded byq attacking large sections of Gaza to annihilate Hamas, leading to the death of more than 23,000 Palestinians.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Operation Prosperity Guardian: Multinational Response to Houthi Threats Lead the Red Sea Crisis
- Reason for Genesis: In response to the Houthi attacks on ships in the Red Sea, the U.S. Secretary of Defense announced the formation of Operation Prosperity Guardian in December 2023.
- About: It is a multinational security mission to ensure safe transit through the Red Sea region, under the aegis of the existing Combined Maritime Forces’ Task Force 153.
- Allies Participation: A united effort made up of 20 nations, with almost half preferring to remain unnamed.
- The Netherlands, Australia, Canada, and Bahrain provided logistical and intelligence support.
- While it is expected that the coalition will grow over time, the group lacks named participation from several key allies, including Turkey, Germany, Egypt, South Korea and Japan.
- India’s Decision: Countries like India, Italy and France have sent ships to the region on their own initiative, distancing themselves from the U.S. umbrella.
|
Houthis: Roots, Movement, and Regional Alliances in Yemen’s Civil War
- Houthis: The Houthis are a large clan belonging to the Zaidi Shia sect, with roots in Yemen’s northwestern Sa’dah province. They are a militant group that has been fighting the civil war in Yemen for a decade.
- Houthi Movement: It began in the 1990s against the dictatorship of Yemeni President Ali Abdullah Saleh. They now control northern Yemen, and have a presence in most regions of the country.
- Iran’s backing: The Houthis are Shia, and are backed with arms and finances by the Shia regime in Iran.
- Support for Hamas: Though Hamas is a Sunni organisation, it is backed by Iran because of their mutual opposition to the US and Israel. The Houthis’ support for Palestine and the Yemen conflict are a manifestation of existing regional rivalries.
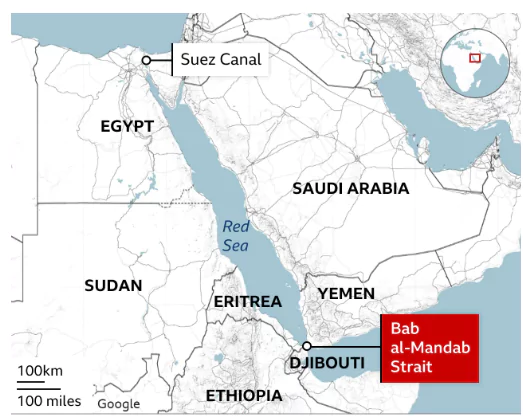
Red Sea and Bab el-Mandeb: Strategic Maritime Passages in Global Trade
- Red Sea: A vital waterway for global commerce and energy shipping lanes.
- Bab el-Mandeb: It is a narrow strait between Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. It is located between Yemen on the Arabian Peninsula, Djibouti, and Eritrea on the African coast. It is also known as the Gate of Tears.
- Significance: It is the route by which ships can reach the Suez Canal from the south, itself a major shipping lane.
Red Sea Crisis: Escalating Concerns for Global Security, Economy, and Human Lives
- Security Concerns: Due to the importance of the Red Sea shipping channel, the Red Sea crisis has risen to a global security threat, causing a serious impact on international shipping and global supply chain security.
- Further, Yemeni authorities have vowed vendetta against America and Britain for the air strike which has increased concerns about a potential escalation of the Israeli-Palestinian conflict spilling over into the crucial waterway.
- Economic Concerns: The Red Sea crisis will lead to higher energy prices and higher inflation, which will have a greater negative impact on world economic growth, drag down the economic recovery of Asian and European countries, and cause huge losses to Egypt and other Red Sea shipping stakeholders.
- For instance, around 12% of the world’s trade passes through the Red Sea and the Suez Canal and after the Houthi attacks began, several major shipping and oil companies have announced they were pausing movement on this East-West passage.
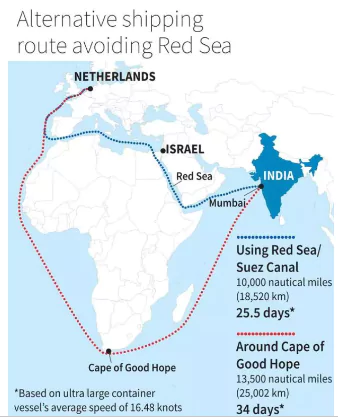
- The Houthi attacks have forced more than 2,000 ships to divert from the Red Sea since November 2023, leading ships to sail around the Cape of Good Hope in South Africa which takes much longer and leads to higher fuel costs.
- Violation of International Laws: The attack by the US and UK is seen as a violation of Yemen’s sovereignty and international laws. Russia and China accused the Western allies of raising regional tensions and charged that the U.S. and British strikes violated international law and raised regional tensions.
- Russia has requested an urgent UN Security Council meeting in connection with US and UK strikes on Yemen.
- However, the US and UK defended the legality of strikes they launched against Yemen’s Houthis in the U.N. Security Council.
- Increasing Threat to Human Lives due to Red Sea Crisis: In addition to existing Israel-Palestine challenges, the continued Houthi threats to maritime navigation coupled with the risk of further military escalation could potentially impact millions in Yemen, the Red Sea region and the world at large.
 For instance, the ship Galaxy Leader and its crew were seized by the Houthis.
For instance, the ship Galaxy Leader and its crew were seized by the Houthis.
- Aggravating Yemen Issue: Yemen has just gotten rid of external intervention with the reconciliation between Saudi Arabia and Iran, and the mediation of Oman and other countries are all factors that have improved the situation in Yemen. The situation will be more complicated if it is subject to military intervention again.
- Impact on Asian Economies due to the Red Sea Crisis: Beyond the regional crisis points, the depletion of security in the Red Sea will have a global impact, specifically for Asian economies such as India, Japan, South Korea, and China, drawing in their interests as well.
Red Sea Crisis: Impact on India’s Trade, Energy Security, and Overseas Citizens
- Impacts on Exports: The longer route is being used when exporting to Europe, the U.S. East Coast or even to countries in North Africa.
- According to the Federation of Indian Export Organisations, almost 90% of western hemisphere cargo, both inbound or shipped from India, that used to go through the Red Sea is now getting re-routed through the Cape of Good Hope.
- Impact on Imports: Besides the extra time taken on account of the longer route, the developments could make imports costlier and call for better inventory management.
- Energy Security: The instability in the Middle East could lead to a spike in global oil prices. India heavily depends on oil imports, and any significant price increase could adversely affect its economy.
- For instance, the Red Sea crisis could come in the way of any plans to reduce pump prices of petrol and diesel as India’s import dependence (based on consumption) in the April-September 2023 period was 87.6%, according to the government’s Petroleum Planning and Analysis Cell.
- Impact on Security of Merchant Vessels: Houthis are attacking international shipping vessels with drone and missile attacks in the area.
- For instance, in December 2023, a Liberia-flagged merchant vessel (MV Chem Pluto) carrying a crew of 22 (of which 21 were Indians), came under a drone attack around 220 nautical miles southwest of Porbandar, Gujarat, while it was on its way to New Mangalore.
- Security of Indian Diaspora: The safety of the Indian diaspora residing in the conflict zone becomes a priority. India may need to undertake evacuation operations to ensure the well-being of its citizens.
- For instance, as of March 2022, of the estimated 1.34 crore Non-Resident Indians, more than 66% are in the Gulf countries of UAE, Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, Qatar, Oman and Bahrain, according to the External Affairs Ministry.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Charting a Path Forward: Global Strategies for Resolving the Red Sea Crisis and Ensuring Regional Stability
- Achieving Peace Through Mediation: The escalating Red Sea crisis is evolving into a global security challenge that requires a joint response from the international community.
- At present, the US and Western countries should restrain from further using military means to resolve the Red Sea crisis and the Yemen issue.
- Strengthening international coordination and seeking a political solution should become the international consensus to resolve the Red Sea crisis.
- India needs a Balanced Approach: In response to the escalating Middle East crisis, India should proactively engage with all stakeholders, including Iran, the USA, and regional powers.
- Through diplomatic channels, India must advocate for de-escalation, dialogue, and a collective effort to address the root causes.
- Role of International Organisation: According to the UN, no cause or grievance could justify Houthi attacks against freedom of navigation in the Red Sea.
- The Secretary-General of the International Maritime Organization (IMO) underlined the importance of ensuring the safety of seafarers, the freedom of navigation and the stability of supply chains.
- Resolving Israel-Palestine Issue: The Red Sea Crisis is a chain reaction to the Palestinian-Israeli conflict. The international community should promote a comprehensive ceasefire between Palestine and Israel as soon as possible.
- Strengthen Security Governance in the Middle East: Many security problems in the Middle East have their roots in development and governance.
- Favorably using the tide of reconciliation to promote security governance and economic development is a direction that requires greater efforts by countries in the region and the international community.
- Learn from Anti-Piracy Efforts: Draw lessons from successful anti-piracy efforts, such as coordinated patrols in the Gulf of Aden.
- For instance, the global community did rally to address the issue of piracy off coastal eastern Africa, specifically around the waters of Somalia.
- In 2012, India joined China, Japan, and South Korea for coordinated joint patrols in the Gulf of Aden..
- Non-State Actor Consideration: Acknowledge the rising influence of non-state militant actors in the geopolitical landscape. Develop strategies that account for the evolving role of non-state actors and their impact on regional stability.
![]() 13 Jan 2024
13 Jan 2024


 For instance, the ship Galaxy Leader and its crew were seized by the Houthis.
For instance, the ship Galaxy Leader and its crew were seized by the Houthis.