India is set to become the top global labor supplier due to its growing working-age population, which will continue to rise until 2048.
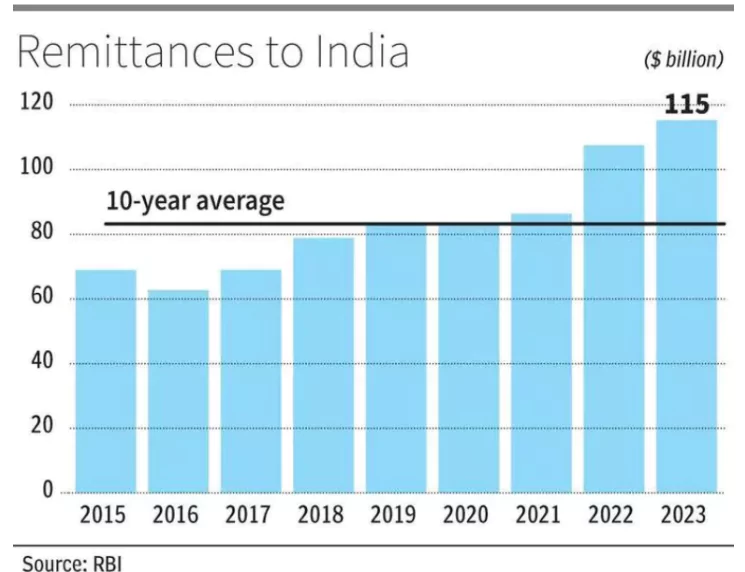
It will drive remittances up to about $160 billion by 2029, compared to $115 billion in 2023, according to the RBI’s latest Report on Currency and Finance.
Current Status
- India is the top recipient of remittances globally, making up 13.5% of the world total.
-
Increasing Importance of Remittances
- GDP Ratio: The ratio of remittances to India’s GDP has risen from 2.8% in 2000 to 3.2% in 2023.
- Comparison: This ratio is higher than the ratio of foreign direct investment (FDI) inflows to GDP, which is 1.9% in 2023.
- This indicates a strengthening of India’s external sector.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Remittance
- A remittance is money sent home by workers abroad, members of diaspora communities, or citizens with family ties overseas.
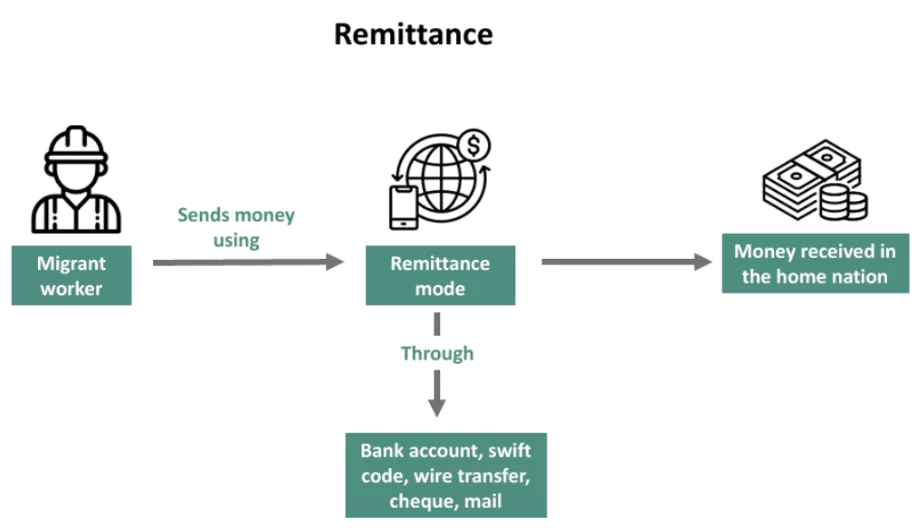 This money is used to support household income in the sender’s home country and is a major financial inflow for developing nations.
This money is used to support household income in the sender’s home country and is a major financial inflow for developing nations.
- Importance: Remittances are a significant source of international capital, often rivaling international aid in financial importance for labor-exporting countries.
- India’s Position: India consistently tops the list of remittance-receiving countries due to its large diaspora.
- Annual Remittances: In FY21, remittances to India totaled $87 billion, which was 2.75% of India’s GDP.
- Top Sources: The UAE, USA, and Saudi Arabia are the leading sources of remittances to India.
- Top Destinations: Bangladesh, Nepal, and Sri Lanka are the primary countries receiving remittances from India.
Challenges and Considerations
- Cost of Remittances: Sending money internationally can be costly. It can be even higher for remote destinations.
- Security and Regulation: There are concerns about remittances being used for illegal activities such as terrorism or money laundering.
- Despite advancements in digital transfers, some funds still move through less transparent channels.
- Technological Advances: Fintech companies like Payoneer and Wise are lowering remittance fees.
- Modernizing infrastructure and implementing regulations can improve financial inclusion and safety.
Factors Affecting Remittance Cost
- Digitalization: Using technology for money transfers can make the process faster, more transparent, and cheaper.
- Transfer Method: How the money is sent (cash, bank transfer, etc.) and where it’s sent from (bank, online, agent) affects the cost.
- Competition: Having many companies offering money transfer services can help keep costs low.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Liberalized Remittance Scheme (LRS)
- LRS is a foreign exchange policy.
- It was introduced by the RBI in 2004.
- Objective: It aims to simplify and ease the process of transfer of funds from India to other countries.
-
- Under this scheme, individuals can remit funds up to a certain specified limit for a range of permissible transitions.
|
- Benefits of Digital Remittances
- Faster Transfers: Online systems allow money to be sent quickly.
- More Transparency: Digital transactions are easier to track and understand.
- Lower Costs: Online services often have lower fees than traditional methods.
Status and Contribution of Indian workers
- Large Migrant Workforce: India has a significant number of people living and working in other countries.
- Gulf Dominates: Most of the money sent back to India comes from countries in the Middle East.
- North America : The United States and Canada also contribute a significant amount to India’s remittances.
- Key Factors Impacting Demand for Indian Migrant Workers
- High Global Demand: There’s a continued strong international need for Indian workers across various sectors.
- Skill Upgradation: Improving the skills of Indian workers is further boosting their appeal to foreign employers.
Ways to Enhance Remittance Inflow in India
- Boost financial inclusion:
- Expansion of banking services: By increasing the bank branches, ATMs, and digital platforms in rural areas can make remittance transfer more easy.
- Promote mobile banking: There should be encouragement for using mobile banking and digital wallets to ease the sending and receiving the remittance.
- Transaction cost:
- Low fee: By decreasing the fee imposed by banks and money transfer operators, the formal remittance channel can be more attractive.
- Rise in competition: Foster competition in service providers to decrease cost and enhance quality of services.
- Enhance security measures:
- Fraud prevention: Implement various measures to prevent fraud and security of remittance transactions.
- Customer support: Offer reliable customer support services to address issues and various concerns.
- Encourage Investment in Home countries:
- Investment opportunities: Offer various attractive investment opportunities for diaspora to invest in their home nation including bonds, real estate, and local business.
- Incentive program: Develop incentive programs for diaspora investors such as tax benefits and special investment schemes.
- Strengthen ties with financial Institutions:
- Partnership with banks: Forge partnership between Indian banks and international financial institutions to facilitate smooth remittance process.
- Remittance service: Establish remittance service within banks to cater the needs of remittance sender and receiver.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Working-Age Population
- The working-age population includes everyone in a specific age range who is considered capable of working.
- This typically includes people from late teens to retirement age, often between 15 and 64 years old.
- Estimate of Potential Workers: This measure helps estimate the number of people who could potentially work in an economy, providing insight into various economic indicators.
-
Purpose of the Measurement
-
- Analyzing Potential Workforce: It helps analyze how many people are available and able to work but does not account for those currently employed or those seeking employment.
- Employment Dynamics: This measurement does not distinguish between those who are working and those who are not within the working-age range, giving a broader view of potential labor availability.
India’s Position
- India working- age population is increasing and it is expected to reach until 2048.
- In contrast, the working-age population in major advanced economies is declining.
|
![]() 31 Jul 2024
31 Jul 2024

 This money is used to support household income in the sender’s home country and is a major financial inflow for developing nations.
This money is used to support household income in the sender’s home country and is a major financial inflow for developing nations.