The Remote Sensing technology has revolutionised monitoring of vegetation, water resources, and subsurface minerals, making exploration faster, cheaper, and more environmentally friendly.
About Remote Sensing Technology
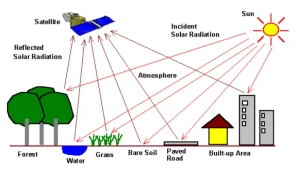
- Remote sensing is the science of acquiring information about Earth’s surface, atmosphere, or objects without physical contact.
- How It Works: It works primarily by measuring reflected or emitted electromagnetic radiation from satellites, aircraft, drones, or ground-based platforms.
Types of Remote Sensing
- Passive: Sensors detect natural energy, usually reflected sunlight (e.g., visible light cameras) or emitted thermal radiation.
- Active: Sensors emit their own energy (e.g., radar or LiDAR) and measure the return signal, enabling operation day/night and through clouds.
Applications of Remote Sensing
- Environmental Monitoring: Tracks deforestation, climate change, glaciers, and biodiversity.
- Agriculture: Precision farming: crop health , soil moisture, pest detection.
- Chlorophyll content in the vegetation of a specific location; Land surface temperatures of a specific location; Greenhouse gas emissions from rice paddies of a specific location (PYQ:2019)
- Disaster Management: Monitors floods, wildfires, earthquakes.
- Urban Planning & Defense: Land use mapping, infrastructure, surveillance.
- Ocean & Atmosphere: Sea levels, weather forecasting, pollution.
Monitoring Plants and Forests
- Satellites assess plant health using spectral signatures, particularly in visible and near-infrared bands.
- Healthy plants absorb red light for photosynthesis and reflect near-infrared to prevent overheating.
- Normalized Difference Vegetation Index: NDVI quantifies vegetation health, high NDVI indicates vigorous growth; low values signal stress, drought, or disease.
- Applications in India: Forest Survey of India (FSI) uses NDVI for biennial forest cover assessment and monitoring deforestation.
Mapping Water Bodies and Quality
- Remote sensing detects water using optical and radar techniques.
- Normalized Difference Water Index (NDWI) and Modified NDWI (MNDWI) exploit water’s strong absorption in near-infrared and shortwave infrared.
- Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) identifies water as dark areas due to smooth reflection of radio waves; ideal for flood mapping during clouds or storms.
- Recent advancement: NASA-ISRO NISAR satellite (launched July 2025) uses dual-frequency SAR (L-band and S-band).
- Satellites also assess water quality by detecting muddy water or algal blooms via spectral differences.
Mineral Exploration and Subsurface Mapping
- Remote sensing provides surface clues to underground resources.
- Hyperspectral imaging splits light into hundreds of bands, identifying minerals like copper, gold, and lithium via detailed spectral signatures.
- In India: Used in Rajasthan (e.g., Alwar basin for Cu-mineralization), Jahajpur, and Gadag Schist Belt.
![]() 6 Jan 2026
6 Jan 2026



