The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) revised the guidelines for Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs) through the updated Master Direction -Reserve Bank of India (Asset Reconstruction Companies) Directions, 2024.
Key Highlights of the Modified Guidelines
- Settlement Policies: ARCs must adopt a board-approved policy covering eligibility criteria for one-time settlements (OTS), permissible sacrifices, and methodologies for determining the realizable value of securities.
- Settlements are to be considered only when all recovery options are exhausted and deemed the best available choice.
- Settlement Amount: Preferably, settlements should be paid in lump sums.
- For staggered payments, ARCs must evaluate the borrower’s business plans, projected earnings, and cash flows.
- Independent Advisory Committee (IAC): For accounts with dues exceeding ₹1 crore, the proposal must be examined by an IAC comprising professionals from technical, financial, and legal backgrounds.
- Fraud or Wilful Default Accounts: ARCs can settle dues in cases involving fraud or wilful defaulters, provided legal proceedings remain unaffected.
- Revised Valuation Norms: ARCs must record reasons for variations between the original valuation of acquired securities and their realizable value during settlement.
- Legal Oversight: Settlements for accounts under judicial proceedings must secure consent decrees from the relevant authorities.
- Net Owned Fund Requirement: ARCs are required to maintain a minimum net owned fund of ₹300 crore by FY26.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARCs)
- ARCs are financial institutions specializing in acquiring and resolving non-performing assets (NPAs) or distressed loans.
- Established: Introduced in India under the Securitization and Reconstruction of Financial Assets and Enforcement of Security Interest (SARFAESI) Act, 2002.
- Regulation: Governed by the RBI to ensure adherence to fair practices and systemic stability.
- Operational Scope: ARCs can restructure loans, enforce security interests, or sell assets to recover dues.
- Examples of ARC:
- ARCIL (2002): India’s first Asset Reconstruction Company successfully resolved several high-value NPAs, including debts of large corporations like Essar Steel.
- Edelweiss ARC (2008): Known for managing distressed assets worth over ₹45,000 crore, Edelweiss ARC has been instrumental in corporate debt restructuring
Working of ARC
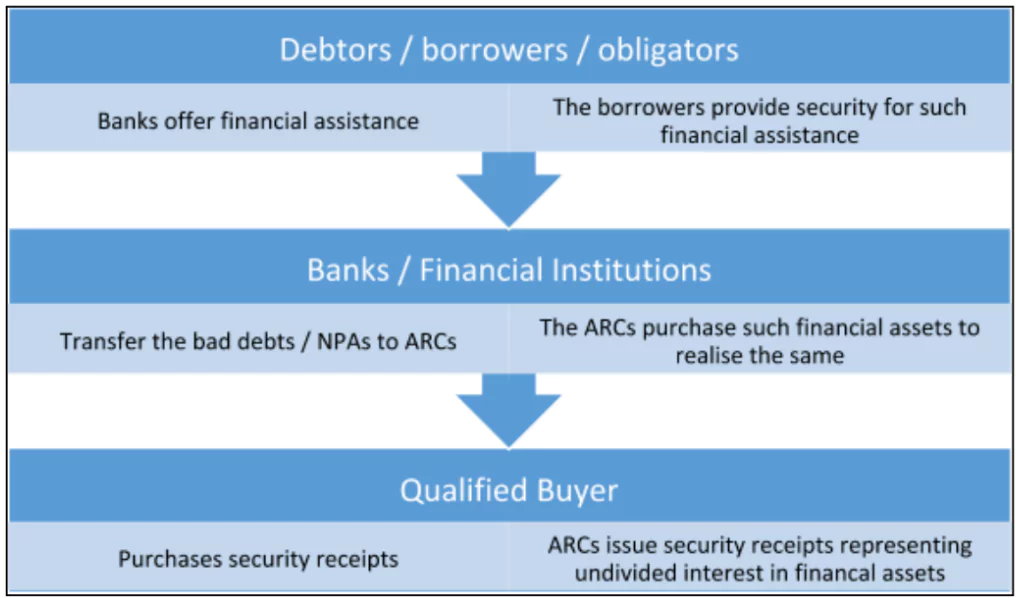
Role of ARCs
- NPA Resolution: Acquire bad loans from banks to help clean their balance sheets.
- Recovery Strategies: Employ debt restructuring, asset sales, and legal actions to recover maximum value.
- Economic Stability: Enable banks to refocus on core lending activities by managing distressed assets.
- Investor Confidence: Facilitate market-based resolutions, encouraging investor participation in stressed assets.
Types of Debt ARC can take over
- The ARC can take over only secured debts which have been classified as a non-performing asset (NPA).
- In case debentures / bonds remain unpaid, the beneficiary of the securities is required to give a notice of 90 days before it qualifies to be taken over.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Significance of ARCs
- ARCs act as a buffer for the banking system, ensuring that NPAs do not erode profitability or capital adequacy.
- The revised guidelines by the RBI aim to enhance operational efficiency, strengthen governance, and ensure ARCs contribute effectively to financial stability.
![]() 21 Jan 2025
21 Jan 2025


