A new study by Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) has revealed that Ground-level ozone pollution is on the rise across India’s major cities.
Ozone
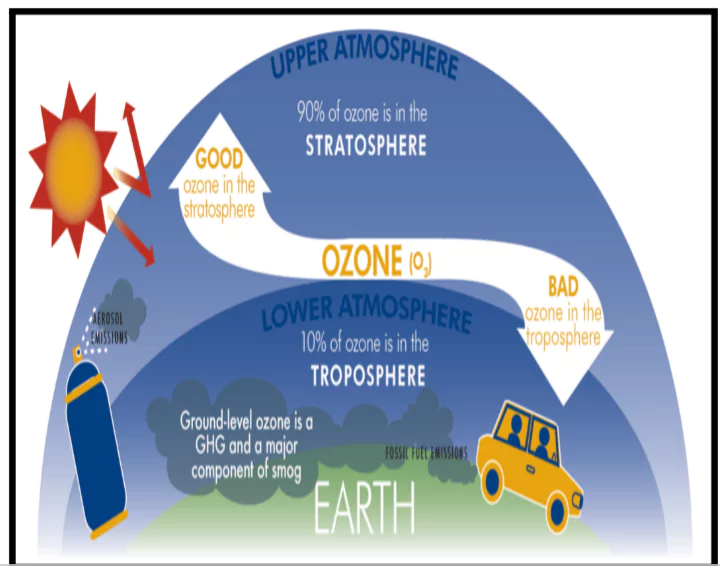
- About: Ozone is a variant of oxygen composed of three oxygen atoms.
- Location: It occurs both in the Earth’s upper atmosphere and at ground level.
- Good or Bad Ozone: Ozone can be good or bad, depending on where it is found.
- Stratospheric Ozone: In the stratosphere, it forms a layer that protects us from the sun’s ultraviolet rays.
Ground Level Ozone
- Definition: Ground-level ozone is a colourless and highly irritating gas that forms near the Earth’s surface, typically within two miles above the ground.
- It is also known as surface-level ozone or tropospheric ozone.
- It is a secondary, short-lived pollutant.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
| Centre for Science and Environment (CSE):
About: The Centre for Science and Environment (CSE) is a not-for-profit public interest research and advocacy think tank based in New Delhi, India.
- It was established in 1980 and it focuses on researching, advocating, and communicating the need for sustainable and equitable development.
- In 2018 the CSE was awarded the Indira Gandhi Prize for Peace, Disarmament and Development.
|
- Formation Process: The formation involves Nitrogen Oxides (NOx), Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs), and carbon monoxide from sources like vehicles, power plants, and factories.
- Reaction Mechanism: Ground-level or tropospheric ozone is created by chemical reactions between NOx gases (oxides of nitrogen produced by combustion) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- The combination of these chemicals in the presence of sunlight form ozone.
Key Findings of the Report
- High Ozone Exceedances: All areas studied witnessed exceedances of the national ozone standard, with Delhi being the most affected.
- Smaller cities like Ahmedabad and Pune are experiencing a particularly rapid increase in ozone pollution.
- Night-Time Exceedances: Elevated ozone levels were observed even at night, with Mumbai recording the most instances.
- The average duration of ozone exposure lasting 12-15 hours across most cities is concerning
- Ozone Exposure in Different Neighbourhoods
- High-End and Green Neighbourhoods: Despite having lower levels of other pollutants, these areas are ironically more susceptible to ozone build-up.
- Seasonal and Year-Round Issues: While summer is the peak season for ozone, the problem continues throughout the year in many areas, especially in sunnier southern cities.
- Health Impacts
- Vulnerable Groups: High ozone levels pose serious risks to individuals with respiratory conditions, children, and older adults.
- Health Issues: Can cause airway inflammation, exacerbate asthma, chronic bronchitis, and increase hospitalizations.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
National Air Quality Standards for Ozone
- Short-Term Exposure Standards: Given its highly toxic nature, the national ambient air quality standard for ozone is established only for short-term exposures, measured as one-hour and eight-hour averages.
- Compliance Measurement: Compliance is assessed by counting the number of days that exceed these short-term standards.
- Need for Early Action: Researchers emphasise the importance of taking early action to address ozone exposure.
Other Recommendations
- Need for Stringent Regulations: Urgent action is needed to curb NOx emissions from vehicles, industries, and other sources.
- Multi-Pollutant Approach: National Clean Air Programme’s reform agenda has to address the multi-pollutant crisis and the combined threat from PM2.5, ozone, nitrogen oxides and other gases.
- The programme currently focuses more on controlling PM10 or coarse dust.
- Local and Regional Actions: Ozone’s ability to travel long distances necessitates both local and regional efforts to combat this pollutant.
- Challenges and Data Gaps need to be addressed: At present, Current monitoring and data analysis methods are inadequate for tracking and mitigating ozone pollution.
Efforts to Check the Depletion of Stratospheric Ozone
- Montreal Protocol: The Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer is a landmark multilateral environmental agreement designed to regulate the production and consumption of nearly 100 man-made chemicals known as ozone-depleting substances (ODS) mainly chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs).
- Adoption Date: The Protocol was adopted on 16 September 1987.
- Universal Ratification: It is the sole UN treaty universally ratified by all 197 member states, aiming to safeguard the Earth’s ozone layer by phasing out the use of ozone-depleting substances.
- Substances controlled by the treaty: The substances controlled by the treaty are listed in Annexes A (CFCs, halons), B (other fully halogenated CFCs, carbon tetrachloride, methyl chloroform), C (HCFCs), E (methyl bromide), and F (HFCs).
- India as a party since 1992 has successfully implemented the Montreal Protocol for phasing out Ozone-Depleting Substances (ODS).
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Kigali Amendment to the Protocol: Adopted in 2016, the Kigali Amendment aims to phase down the production and consumption of hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), which are potent greenhouse gases
- In 2016, countries agreed to include HFCs in the list of controlled substances under the Montreal Protocol and decided on a schedule for its phase-down.
- Before the middle of this century, current HFC use has to be curtailed by at least 85 percent. India has to achieve this target by 2047 while the developed countries have to do it by 2036.
- Air Quality Index (AQI) in India:
- Definition: The Air Quality Index (AQI) is a numerical scale used to communicate the quality of the air and its potential impact on health.
- Components: It covers eight pollutants under its ambit: PM10, PM2.5, Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2), Sulphur Dioxide (SO2), Carbon Monoxide (CO), Ozone (O3), Ammonia (NH3), and Lead (Pb), for which short term (up to 24 hours) National Ambient Air Quality Standards are established.
- Scale: The AQI typically ranges from 0 to 500, with higher values indicating worse air quality and increased health risks.
- Categories: There are six AQI categories, namely Good, Satisfactory, Moderately polluted, Poor, Very Poor, and Severe.
- Purpose: It helps individuals understand the air quality in their area and take appropriate actions to protect their health, especially those in sensitive groups
![]() 8 Aug 2024
8 Aug 2024

