A new method to manage ecological risks from DDT by binding it with biochar has been developed by the researchers of Sweden’s Chalmers University of Technology.
About the Research
- It is a three-year study conducted on a 23-hectare DDT-contaminated former tree nursery in southern Sweden by mixing Biochar into the contaminated soil.
- Finding:
- Uptake of DDT by earthworms in the soil was found to have been halved.
- Biochar is found to bind DDT efficiently, so that it is not taken up by soil organisms.
- Significance:
- Enable the cultivation of certain crops on degraded and unusable land due to the environmental risks.
- Improved Soil Health: Biochar is an environmentally friendly product and binds contaminants and can improve soil health when added to soil improving the soil health.
- Cost Effective Solution: Biochar is economical to produce, therefore is a cost effective solution for rehabilitating degraded soil.
- Climate Change Mitigation: Mixing biochar is also useful for climate change mitigation since it can contribute to long-term storage of carbon in the soil.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane (DDT)
- DDT is a toxic, man-made, hazardous chemical which is also a persistent organic pollutant (POPs), first synthesized in 1874.
- Insecticidal Properties: DDT’s insecticidal properties were discovered in 1939 to control vector borne diseases and used to control insects in crops and livestock production, institutions, homes and gardens.
- Impacts:
- Bioaccumulation: DDT bioaccumulates in fatty tissues of humans and animals with high intake associated with developmental and reproductive abnormalities.
- Carcinogenic: DDT is classified as ‘probably carcinogenic’ to humans and can suppress the immune system and disrupt sex hormones
- Omnipresent: DDT being a POP and its widespread use is stable and persistent in the environment with its residues found everywhere such as the Artic, the Antarctic, open oceans, and high mountain areas.
- Animal health: DDT causes eggshell thinning in birds and is also acutely toxic to fish and marine invertebrates.
- Endocrine Disruptor: DDT is highly stable and can accumulate in adipose tissue, so it can be found in the tissues of all living organisms.
- Soil Health: DDT was widely used as a pesticide in agriculture and resulted in devastating effects on soil health making it infertile.
- In 1962, Rachel Carson published “The Silent Spring” documenting the devastating effect of pesticides on the natural world, focusing on DDT.
- DDT in India:
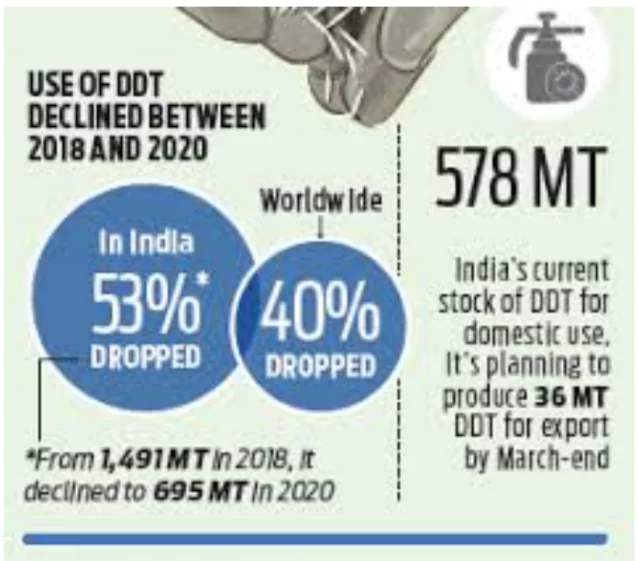 India banned the agricultural use of DDT by 1972.
India banned the agricultural use of DDT by 1972.- Usage: The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the only consumer of DDT
- It is used to control vector borne diseases by spraying DDT over walls in malaria-infected houses and buildings in rural and urban areas.
- Nodal Ministry: Department of Chemicals, Petrochemical and Fertilizers (DCP) being the nodal committee overseeing the production and supply of DDT.
- India is the sole producer of DDT globally since 2008.
- Phase Out: In 2014, India got the first extension for 10 years to phase out DDT by 2024 under the Stockholm Convention. However, it missed the deadline
- The Convention had outlawed the production and use of DDT and other toxic chemicals and limited it to mosquito control.
- Exports: India exports the chemical to Botswana, South Africa, Zambia, Mozambique, Namibia and Zimbabwe.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Biochar
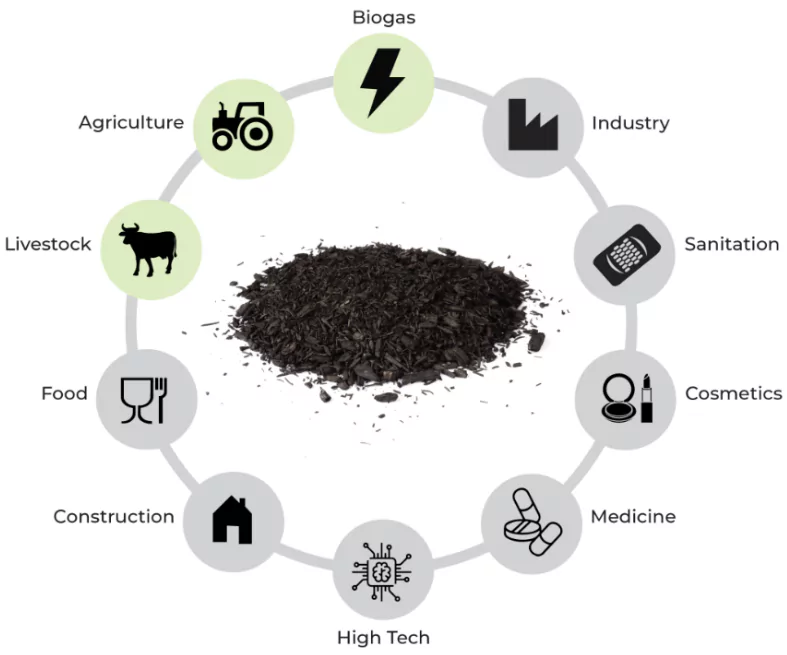

- Biochar is a charcoal-like substance that’s made by burning organic material from agricultural and forestry wastes (also called biomass) in a controlled process.
- Biochar converts carbon into a stable form and is cleaner than other forms of charcoal.
- Raw Material: It is made from biomass sources like, wood chips, plant residues, manure or other agricultural waste products
- Process: Biochar is produced during pyrolysis, a thermal decomposition of biomass in an oxygen-limited environment called pyrolysis.
- Physical Attributes: Biochar is black, highly porous, lightweight, fine-grained and 70 percent composed of carbon
- Benefits:
- Biochar has proven to improve the quality of construction materials such as concrete or asphalt
- It is widely used as a fodder additive for animal health
- It helps in regulating humidity, absorbs toxins, fosters beneficial microbial life
|
![]() 18 Jan 2025
18 Jan 2025

 India banned the agricultural use of DDT by 1972.
India banned the agricultural use of DDT by 1972.