Recently, Union Environment Minister Bhupender Yadav addressed the inaugural Sagarmatha Sambaad in Kathmandu, calling for united global action to protect mountain ecosystems.
About the Sagarmatha Sambaad
- The Sagarmatha Sambaad is a high-level global dialogue focusing on urgent environmental challenges facing the world’s mountainous regions.
- 2025 Theme: “Climate Change, Mountains, and the Future of Humanity,”
- Regional Solidarity: India acknowledged shared ecological and cultural ties among Himalayan nations and emphasized the importance of transboundary conservation, particularly through initiatives like the International Big Cats Alliance.
- Call for Action: India outlined a five-point call for global action to address the shared ecological challenges of mountainous regions.
Global Action to Address the Shared Ecological Challenges of Mountainous Regions
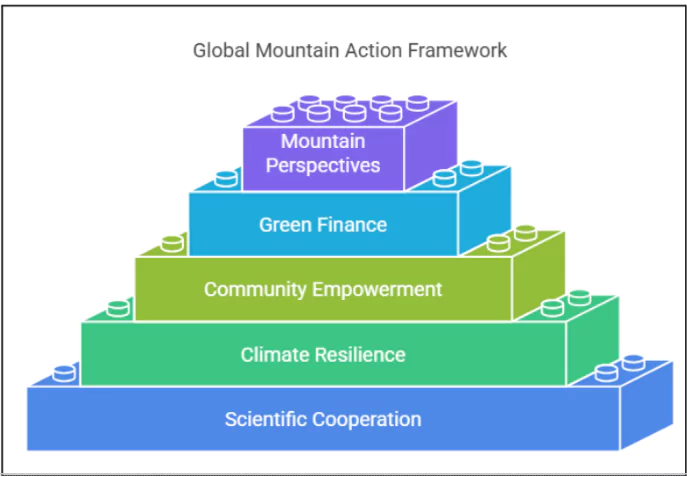
- Enhanced Scientific Cooperation: Strengthening research collaboration, and monitoring cryospheric changes, hydrological cycles, and biodiversity.
- Building Climate Resilience: Investing in climate adaptation measures, early warning systems for disasters like Glacial Lake Outburst Floods (GLOFs), and climate-resilient infrastructure in mountain areas.
- Empowering Mountain Communities: Ensuring that the welfare, needs and aspirations of local communities are at the heart of policy-making and their benefit from green livelihoods and sustainable tourism. Their traditional knowledge is an invaluable resource.
- Providing Green Finance: Making available adequate and predictable climate finance as per the UNFCCC and its Paris Agreement for mountain Nations to implement adaptation and mitigation strategies effectively.
- Recognizing Mountain Perspectives: Ensuring that the unique vulnerabilities and contributions of mountain ecosystems are suitably featured in global climate negotiations and sustainable development agendas.
Significance of Mountains
- Ecological Value: Mountain ecosystems, particularly in regions like the Himalayas, host unique biodiversity including iconic species such as the snow leopard, tiger, and red panda.
- They are crucial to global water cycles and climate regulation.
- Economic Importance: Mountains are vital for sustainable tourism, hydropower, agriculture, and green livelihoods for millions of people.
- They contribute significantly to local and national economies, especially in developing countries.
- Water Source: Often called the “water towers of the world,” mountain glaciers feed major rivers that support over a billion people downstream across Asia.
- Cultural and Traditional Value: Mountain communities maintain rich indigenous knowledge systems, spiritual traditions, and sustainable lifestyles, which are integral to ecological conservation.
- Climate Vulnerability: Mountain regions are among the most climate-sensitive on Earth. Rising temperatures, melting glaciers, and frequent natural disasters pose serious threats to ecosystems and human settlements.
Conclusion
India reaffirmed its commitment to mountain conservation through science, collaboration, and community empowerment. Echoing the spirit of Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam (the world is one family) India urged global unity to ensure mountains continue to be symbols of sustainability and hope.
![]() 17 May 2025
17 May 2025

