![]() 29 Dec 2025
29 Dec 2025

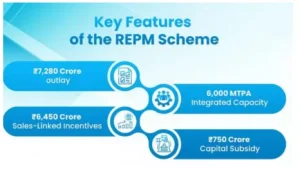
The Government of India has approved the ‘Scheme to Promote Manufacturing of Sintered Rare Earth Permanent Magnets’ (REPM).
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
Rare Earth Minerals
Why Are They “Rare Earth”?
|
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
