SEBI now allows AIFs in Category I and II to borrow for operational needs.
About Alternative Investment Funds
- Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs) pool funds to invest in alternative asset classes like private equity, venture capital, hedge funds, real estate, commodities, and derivatives.
-
Regulation and Structure
-
- Regulated by SEBI: AIFs are governed by the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI).
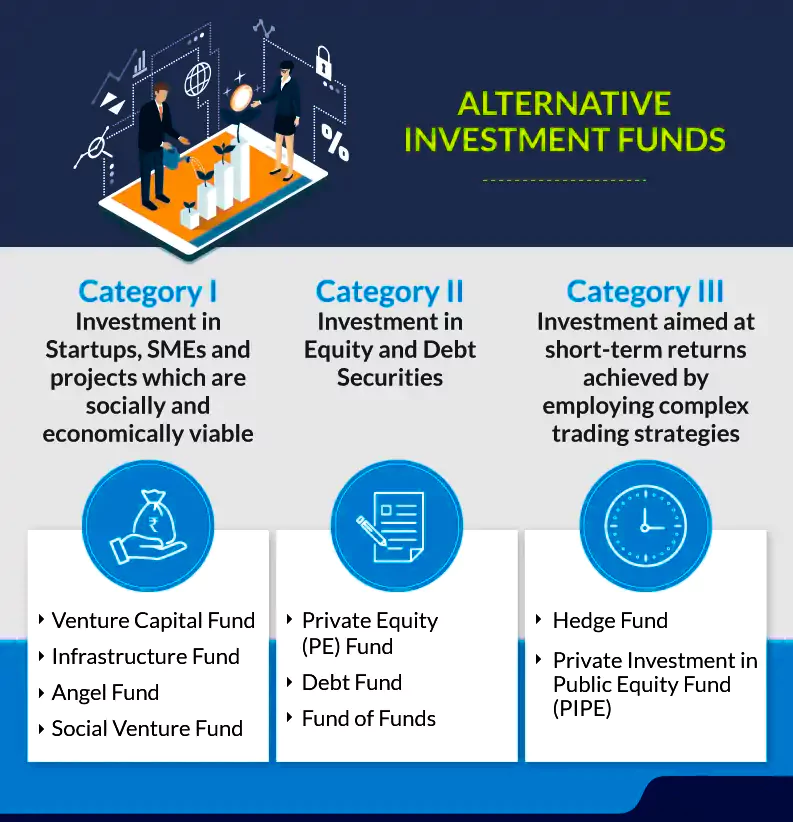
- SEBI Regulations: As per SEBI’s 2012 regulations, AIFs can be structured as a trust, company, limited liability partnership (LLP), or corporate body.
 Common Structure: Most AIFs registered with SEBI are set up as trusts.
Common Structure: Most AIFs registered with SEBI are set up as trusts.
Benefits of Investing in Alternative Investment Funds (AIFs)
- High Return Potential
- Better Returns: AIFs often offer higher returns than regular investments because they pool together a large amount of money.
- Flexible Strategies: Fund managers have more flexibility to create strategies that aim for maximum returns.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
- Private equity: It is an investment in which an investor buys shares in privately owned companies.
- Venture capital: It is an investment in which an investor buys shares in an emerging high potential growth company.
- Hedge funds: It is a type of investment in which investors pool money and then invest in other various assets.
- Commodities: These are another class of assets that can be traded.
- Derivatives: These are financial contracts whose value is based on the performance of the underlying entity.
|
- Low Volatility
- Less Dependent on Stock Markets: AIFs are not tied to the ups and downs of the stock market, making them less volatile.
- Stable Investment: These funds are more stable and are a good option for investors who want to avoid high risks.
- Portfolio Diversification
- Wider Investment Options: AIFs help spread out investments into different areas, providing variety in a portfolio.
- Protection During Market Changes: They act as a safeguard during financial crises or when the market is unstable.
SEBI’s Recent Guidelines and Impact
- Borrowing Limits
- Cap on Borrowing: AIFs (Alternative Investment Funds) can now borrow up to 10% of investible funds or 20% of the drawdown value, which is the amount collected from investors for investment purposes.
- This step promotes operational ease with risk caps.
- Disclosure Requirement
- Transparency: AIFs are required to disclose details about any leveraging to their investors, ensuring greater transparency.
- Borrowing Guidelines and Restrictions
- Cooling-Off Period: AIFs must observe a 30-day cooling-off period between two borrowings to prevent excessive leverage.
- Borrowing as Last Resort: Borrowing should only be used when absolutely necessary, and the costs associated with borrowing must be borne by investors who failed to provide the required funds during the drawdown.
- Transparency: Stricter disclosure norms ensure clearer information for investors.
- Tenure Extension for Large Value Funds (LVFs)
- Extended Duration: The tenure for Large Value Funds has been extended to five years, providing more flexibility for investment.
- Immediate Implementation: These guidelines are effective immediately, it impacts AIF operations and investment strategies right away.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
These steps enhance market stability, transparency, and investor confidence.
Role of SEBI
This board was established in 1988 and given statutory powers in 1992.
SEBI’s Key Functions
- Regulation of Stock Exchanges: SEBI supervises stock exchanges to ensure fair trading and prevent unethical practices.
- Investor Protection: SEBI ensures market transparency and fairness by requiring companies to disclose important information.
- Regulation of Market Intermediaries: SEBI oversees brokers, underwriters, and mutual funds to ensure they follow legal rules.
- Market Development: SEBI works on improving and modernizing the securities market for better efficiency and accessibility.
- Enforcement of Regulations: SEBI investigates and takes action against entities that break securities laws.
|
![]() 20 Aug 2024
20 Aug 2024
 Common Structure: Most AIFs registered with SEBI are set up as trusts.
Common Structure: Most AIFs registered with SEBI are set up as trusts.