Context:
This article is based on the news “NITI Aayog Releases Position Paper– Senior Care Reforms” which was published in the PIB. NITI Aayog recently released a position paper titled “Senior Care Reforms in India: Reimagining the Senior Care Paradigm” discussing the current trends, challenges and reforms for the ageing population.
Population Ageing Trends in India and Global
- Ageing In India: Senior citizens in India, who currently represent over 10% of the population, are projected to grow to 158 million by 2025 and 319 million by 2050, marking a significant demographic shift.
- Global Ageing Trends: According to WHO, the global population aged 60+ is expected to double from 12% in 2015 to 22% by 2050.
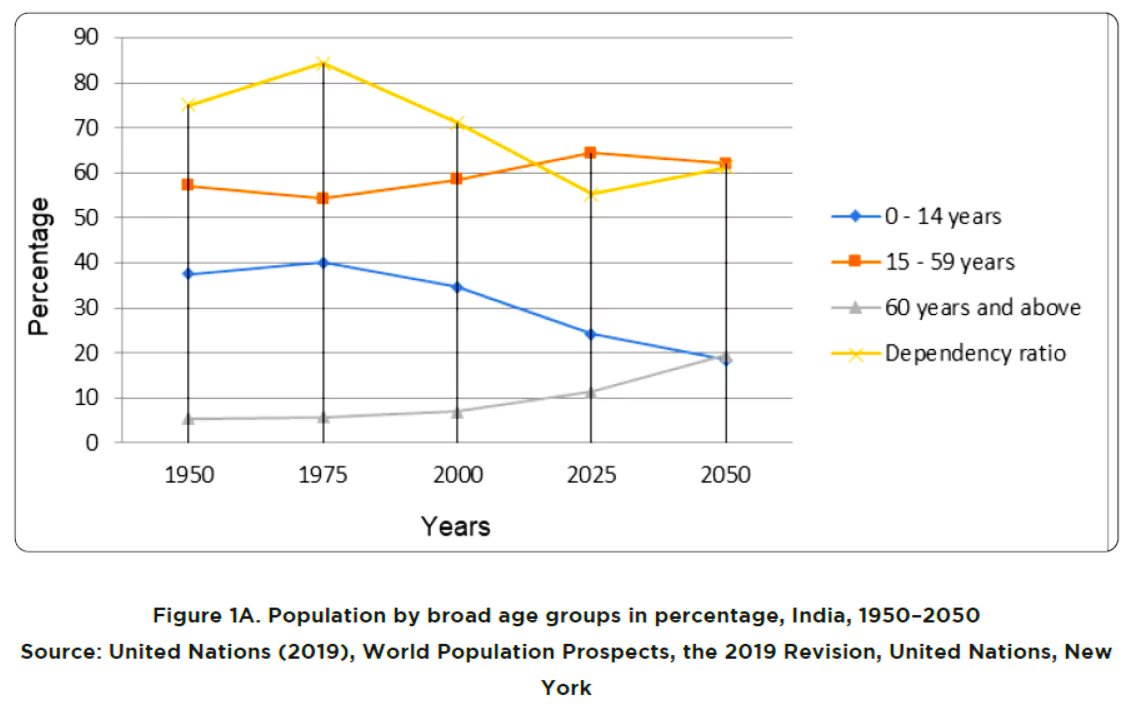
- Dependency Ratio Changes: India’s total dependency ratio is forecasted to decrease until 2025 due to a growing working-age population initially, then increase to 61.22 by 2050.
Concept Of Ageing
- The ageing of the population can be described as an increase in the number and proportion of older adults in a population.
- According to WHO Healthy Ageing is developing and maintaining the functional ability that enables well-being in older age.”
|
Key Findings of Longitudinal Ageing Study of India (LASI) 2021 Report
It was launched in 2016 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. It is a full-scale national survey and a seminal study on the status of the ageing population in India.
-
Health
- Physical health: Around 75% of the elderly have one or more chronic diseases and 40% have one or more disabilities.
- Mental Health: In India, 20% of the elderly face mental health challenges, with undiagnosed depression likely being much higher than reported, suggesting a significant hidden burden.
- Functional Abilities: Among elderly citizens, 11% face impairments, 24% have daily living activity limitations, 58% struggle with mobility tasks, and 43% rely on aids or supportive devices.
-
Social
-
- Demography: The sex ratio of India’s elderly population stands at 1065 with women making up 58% of the population.
- A dependency ratio of 62 per 100 working-age individuals highlights a significant reliance on the younger workforce.
- Knowledge and Awareness: 12% are aware of the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act 2007 and around 28% are aware of any senior concession.
- Additionally, nearly a quarter face challenges in providing necessary documentation for these services.
- Food Security: Food insecurity among India’s elderly is rising, with nearly 6% consuming less or skipping meals, and 5.3% not eating despite hunger.
-
Financial and Economic Status Of Senior Citizens in India
-
- Employment: Approximately 50% of male and 22% of female senior citizens in India are employed, with a higher work participation rate in rural areas.
- Pension Facility: 78% of the elderly population without a pension.
- Access to healthcare finance: Only 18% of India’s seniors have health insurance, facing an average out-of-pocket expense of ₹31,933 for private healthcare, with health costs being a leading cause of debt among 26% in urban areas.
- Digital Wellbeing: Access to mobile phones is limited for senior citizens, with only 13 % of senior citizens having ever used the internet.
Also Read: Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) Annual Report 2022
Impact of Ageing Population
- Lack of Support System for the Elderly: The increase in the average age of the population, shift towards smaller nuclear families and increased migration due to work, education, and marriage have left the elderly behind with scarce or practically no support system.
- Ageing-related Stereotypes and Stigma: Ageing is increasingly viewed negatively with the elderly often being viewed as a burden in society. This contributes to social isolation and mental health issues among the elderly.
- Economic Impact: The growing number of older adults leads to a decline in their contribution to the labour force.
- Also, the social benefits extended by the elderly population through their unpaid work, are neither recognized nor quantified.
- Digital Divide: A considerable gap in digital literacy among senior citizens has led to hindrances in accessing several online services.
Challenges Faced By Senior Citizens Care System
-
Health Domain Fragmented approach to Service Delivery
-
- Fragmented services provided by various small-scale or unorganised providers like nursing agencies and physiotherapists result in suboptimal care.
Impact of Climate Change on Senior Citizen:
- The elderly are disproportionately vulnerable to climate change with a significant increase in ill health and premature deaths, reduced mobility, social isolation (in some cultures), and poor access to health and social services.
- India recorded an estimated 31,000 heat-related deaths among people over 65 years.
|
-
- Healthcare Gaps for the Elderly: Lack of availability of targeted immunisation programs, mental health services, assistive devices, home-based care services etc are significant healthcare gaps for the elderly.
- Eldercare Infrastructure Gap: There is a Mismatch between the demand and supply of care & support institutions and a high dependence on the private sector for Tertiary care services.
- Paucity of trained manpower for the healthcare needs of seniors: There is insufficient focus on geriatric healthcare and a limited senior care workforce.
- Limited financing of elderly health care: Senior people have long-term healthcare needs with high health expenditures. Furthermore, senior health care insurance has a very shallow penetration (18%).
-
Social Domain
- Narrow and inadequate social security system: Senior citizens have a limited scope of social security nets and are vulnerable to gaps in implementing social security schemes & programs.
- Limited awareness of rights and provisions: Low awareness regarding social security schemes. Only 12% of elderly people know the Maintenance and Welfare of Parents and Senior Citizens Act 2007 and the Annapurna scheme.
- Changing family structure and loss of social support: Change in family structure has led to mental, physical, social, and financial insecurity among elderly people.
- Social Inequality: Rural-Urban regional divide, gender-based disparity & inequality and caste-based discriminations also determine the elderly care facilities.
- Inadequate elderly- friendly infrastructure: Lack of accessible physical infrastructure such as accessible transportation, disabled-friendly toilets, accessible buildings, wheelchairs, ramps, wide doors is a major barrier to the social inclusion of elderly people.
-
Economic Domain
- Need for a universal and comprehensive financial support system: Less than 20% of the elderly population is covered with any health insurance and nearly 78% of them remain without any pension cover.
- Insufficient financial literacy and awareness about available financial schemes: Financial illiteracy and digital divide leads to reduced awareness about financial support schemes.
- Deficient support in lifetime financial planning: Many adults reach old age without sufficient savings, insurance, or public or private pensions to live on or to fund long-term care. 70% are dependent on family for everyday maintenance.
-
Digital Domain
-
- Insufficient digital access: Senior citizens comprise almost 8.6% of the country’s population, and less than 3% are Internet users
- Paucity of digital training modules for the elderly: A Help age India analysis highlights that urban elderly people, despite having access to smartphones, do not know how to use them beyond the basics.
Action Plan for Development of Senior Citizens Care Support System
-
Health Empowerment and Inclusion
- Health Literacy Enhancement: Improving health knowledge among seniors and their caregivers.
- Geriatric Healthcare Strengthening: Integrating elderly care within existing healthcare frameworks, including specialised services.
- Infrastructure and Workforce Development: Upgrading healthcare facilities to cater to elderly needs and enhancing the skills of healthcare workers.
- Mental Health and Emergency Services: Focusing on mental well-being and emergency response for seniors.
- Nutritional and Holistic Health: Addressing dietary needs through initiatives and integrating Ayush systems for comprehensive senior care.
-
Social Inclusion and Empowerment
- Community Sensitization: Raising awareness about the elderly’s needs and challenges to foster a supportive community.
- Peer Support Groups: Creating networks for the elderly to share experiences and support each other.
- Legal and Welfare Awareness: Informing the elderly about their rights, legal safeguards, and available welfare schemes.
- Legal Reforms: Strengthening laws for elderly welfare and ensuring swift resolution of cases in maintenance tribunals.
- Housing and Care Homes Reform: Improving elderly-friendly living conditions and senior care facilities.
- Centralised Senior Care Portal: Developing a comprehensive online resource for senior care services and promoting the care economy sector.
-
Economic Empowerment and Inclusion
- Reskilling: Offering programs to update the skills of the elderly for better employment opportunities.
- Public Fund Coverage: Expanding the reach of public funds and infrastructure to support the elderly financially.
- Savings Plans: Implement mandatory savings schemes for those who can afford them to ensure financial security.
- Reverse Mortgage: Utilizing reverse mortgage mechanisms to enhance seniors’ liquidity.
- Tax Reforms: Adjusting tax and GST policies on senior care products for easier adoption and financial relief.
- Geriatric Health Insurance: EncourAgeing the private sector to develop targeted health insurance products for the elderly.
 Capital for Senior Care: Boosting liquidity and investment in the senior care sector.
Capital for Senior Care: Boosting liquidity and investment in the senior care sector.
-
Digital Empowerment and Inclusion
-
- Affordable Access: Implement senior discounts to make digital devices more accessible.
- Digital Literacy: Launch targeted campaigns and workshops to boost digital skills among the elderly.
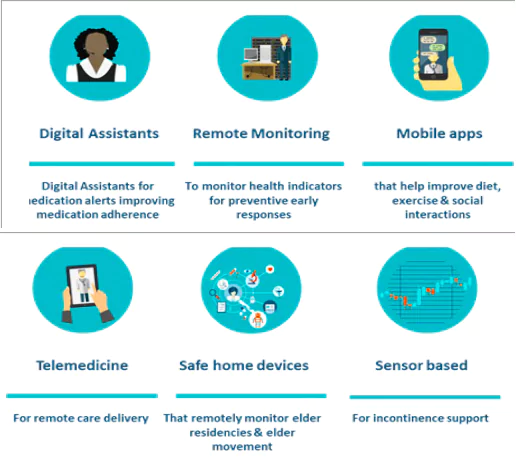
- Technology Utilisation: Leverage AI, IoT, big data, and machine learning for routine senior care procedures.
Important Schemes By Government of India for Welfare of Senior Citizens
- Atal Vayo Abhyudaya Yojana (AVYAY): It provides four basic needs of senior citizens: financial security, food, health care, and life of dignity
- Pradhan Mantri Vaya Vandana Yojana: It aims to protect elderly persons against a future fall in their interest income due to the uncertain market condition.
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana: The scheme is available to people in the age group of 18-70 years, with risk coverage of 2 lakhs in case of accidental death and 1 lakh for partial permanent disability.
- Atal Pension Yojana: It provides a universal social security system in the form of pensions for all Indians, especially the poor, underprivileged, workers in the unorganised sector.
- Varishtha Pension Bima Yojana: Ensures guaranteed pension to subscribers on payment of a lump sum amount.
- National Social Assistance Program: It is a scheme under which the elderly, widows, and disabled persons belonging to BPL category are provided financial assistance ranging from `200/- to `500/- p.m.
|
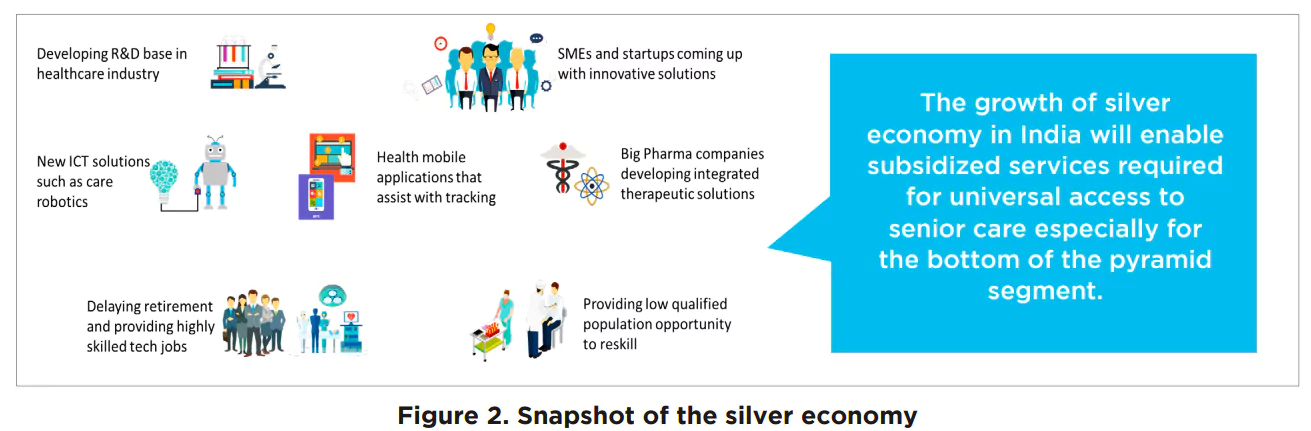
Silver Economy
- The silver economy refers to the economic opportunities arising from the public and consumer expenditure related to elderly citizens.
- It includes the products and services they purchase directly and the indirect economic activities they stimulate.
- India’s silver economy is estimated to be worth approximately 73,082 crore rupees at present and is expected to grow multi-fold in the coming years.
- The Government has launched initiatives to promote the idea of a silver economy:
- Senior Able Citizens for Re-Employment in Dignity (SACRED) portal: It will connect senior citizens with job providers in the private sector.
- Senior Ageing Growth Engine (SAGE) initiative: It will promote and incentivize senior care products and services.
|
![]() 19 Feb 2024
19 Feb 2024



 Capital for Senior Care: Boosting liquidity and investment in the senior care sector.
Capital for Senior Care: Boosting liquidity and investment in the senior care sector.