Context
According to geologists, the African continent is currently experiencing a rare geological phenomenon that could lead to the formation of a sixth ocean in 5 to 10 million years.
Earth’s Sixth Ocean is Currently Forming in Africa: Geologist
- About the Experiment: Scientists analysed a diamond from Botswana that formed at 660 kilometers below the surface of the planet at the interface between the transition zone and the lower mantle.
- It confirmed that the transition zone is not a dry sponge, but holds considerable quantities of water.
- Potential Ocean Formation in the Afar Triangle: Geologists predict that in 5 to 10 million years, the tectonic movement will eventually split the African continent into two, creating a new ocean basin.
- This process is taking place in the Afar Triangle, also known as the Afar Depression, located in the Horn of Africa.
- Gradual Tectonic Plate Separation in East Africa: This rare geological phenomenon involves the gradual separation of tectonic plates, resulting in the creation of a distinct continent in East Africa.
- The presence of volcanic eruptions in the area, notably at the Erta Ale volcano, provides insights into the tectonic shift, exhibiting traits reminiscent of a mid-ocean ridge.
- Flooding of Afar region: This new body of water would be the result of the Red Sea and the Gulf of Aden flooding over the Afar region and into the East African Rift Valley.
- Consequently, this part of East Africa would evolve into its own distinct continent.
About Afar Triangle
- Afar Triangle Geology: The Afar Triangle is a geological depression where three tectonic plates-the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates- converge.
- Part of the East African Rift system: This area is part of the East African Rift system, which extends from the Afar region down through eastern Africa.
- Rifting Process in the Afar Triangle: The rifting process occurring here is a result of the tectonic plates slowly moving apart, a phenomenon that has been taking place for millions of years.
- Paleontological Significance: The region has disclosed fossil specimens of the very earliest hominins; that is, the earliest of the human clade, and it is thought by some paleontologists to be the cradle of the evolution of humans.
|
What is the Sixth Ocean?
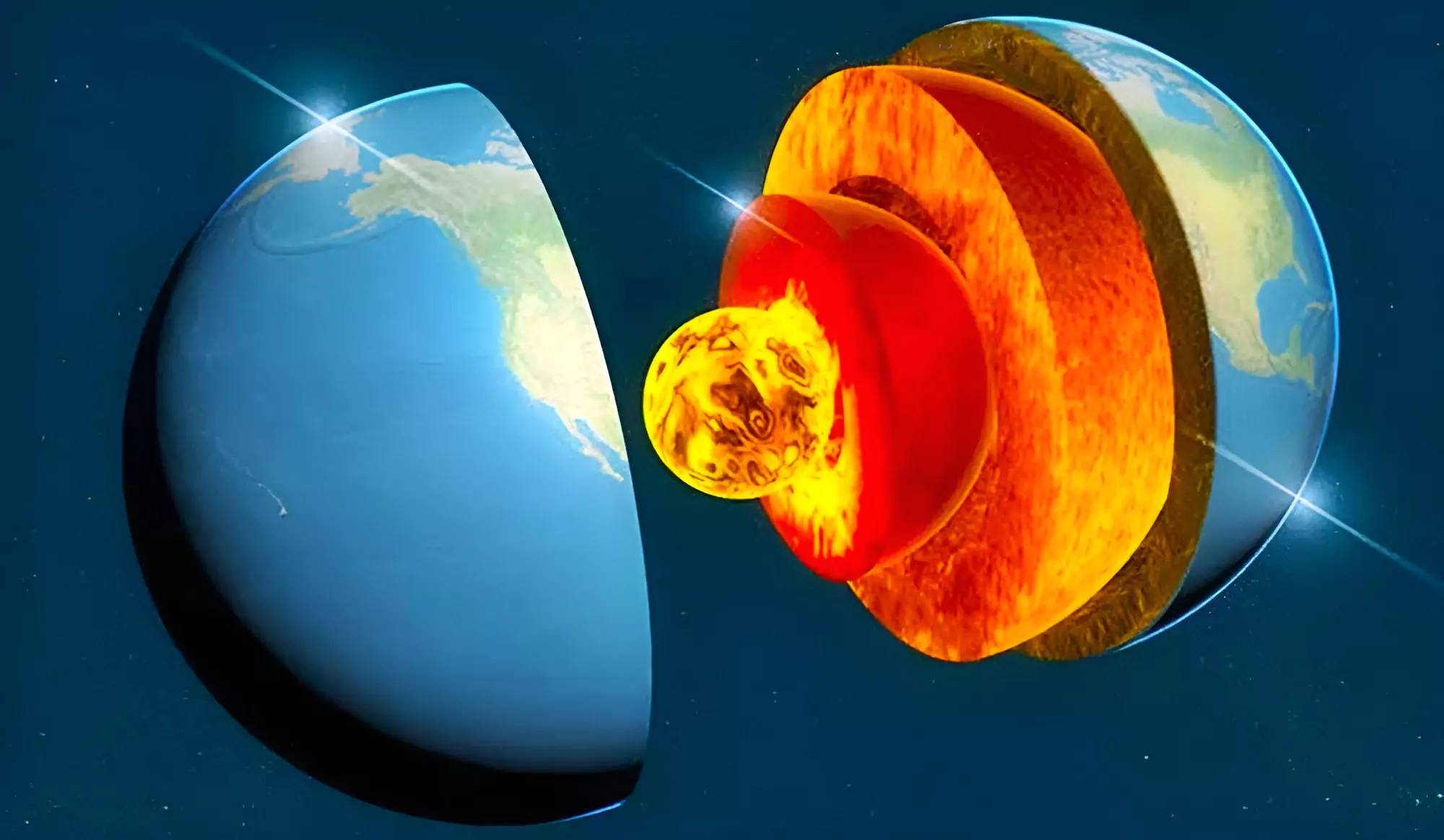
- Location: According to researchers, the transition zone between the Earth’s upper (brown) and lower mantle (orange) contains considerable amounts of water, bound in the rock.
- Evidence points to water in the transition zone (TZ), the boundary layer that separates the Earth’s upper mantle and the lower mantle.
- The boundary is located at a depth of 410 to 660 kilometers, where immense pressure of up to 23,000 bar causes the olive-green mineral olivine to alter its crystalline structure.
Factor Driving the Rifting Process
- Rise of Mantle Plume beneath East Africa: A massive plume of superheated rocks rising from the mantle beneath East Africa.
| Oceans on earth: The Atlantic, Pacific, Indian, Arctic, and Southern Ocean.
Rifting: It is defined as the splitting apart of a single tectonic plate into two or more tectonic plates separated by divergent plate boundaries.
The rifting of a continental tectonic plate creates normal fault valleys, small tilted block mountains, and volcanism. |
- This plume could be exerting pressure on the overlying crust, causing it to stretch and fracture.
Significance of Findings
-
Dynamic Nature of Earth:
- The potential formation of a sixth ocean in Africa is a reminder of the Earth’s ever-changing nature.
- The birth of a new ocean is a process that spans millions of years, and the evidence of its onset provides insight into the dynamic evolution of the Earth and the possible transformation of its landscapes over thousands of years.
-
Background of Earth Dynamism Concept:
- In 2005, a significant event brought global attention to this gradual process.
- A 35-mile-long fissure appeared in the Ethiopian desert, signifying the ongoing division of the African continent. This fissure serves as the visible surface manifestation of the process.
- The emergence of this rift signifies the surface expression of deep-seated tectonic forces at play, as the Somali plate gradually moves apart from the Nubian plate, resulting in the stretching and thinning of the Earth’s crust.
-
Opportunity to Study Ocean Formation Stages:
- The formation of a new ocean is a complex and lengthy process that involves various stages of rifting, from continental breakup to the development of a mid-ocean ridge.
- The East African Rift provides a unique opportunity for scientists to study these stages.
-
Implications for Future Continent and Ocean Configuration:
-
- It highlights the importance of understanding our planet’s geological processes, as they have profound implications for the future configuration of continents and oceans.
About Tectonic Plates
A tectonic or lithospheric plate is a vast slab of solid rock. Comprising both continental and oceanic lithosphere, these Indian Plates glide over the asthenosphere as cohesive units.
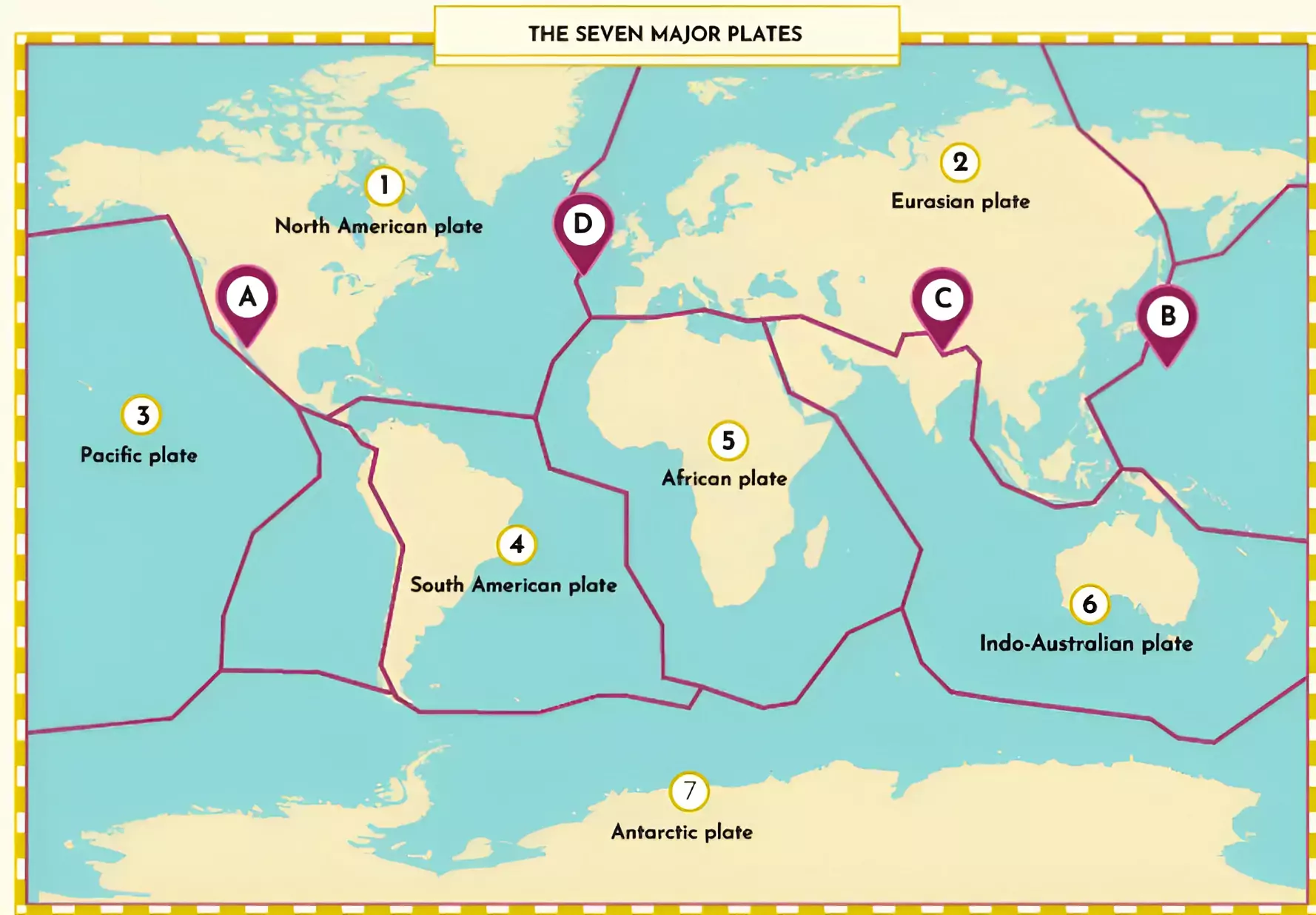
Major Plates:
- Antarctica and its adjacent oceanic plate
- North American plate (with a part of the western Atlantic floor, distinct from the South American plate along the Caribbean islands)
- South American plate (separate from the North American plate along the Caribbean islands)
- Pacific plate
- India-Australia-New Zealand plate
- African plate (including the eastern Atlantic floor)
- Eurasia plate, along with its neighbouring oceanic portion.
Some Minor Plates:
- Cocos Plate: Situated between Central America and the Pacific Plate.
- Nazca Plate: Lying between South America and the Pacific Plate.
- Arabian Plate: Primarily the Saudi Arabian landmass.
- Philippine Plate: Positioned between the Asiatic and Pacific Plate. Caroline Plate: Nestled between the Philippine and Indian plate (north of New Guinea).
- Fuji Plate: Located to the northeast of Australia.
Also Read: Global Ocean Heat Content in 2023
![]() 1 Apr 2024
1 Apr 2024



