![]() 9 Feb 2024
9 Feb 2024
English
हिन्दी

This article is based on the news “Need to launch next phase of Smart Cities Mission: Parliamentary Committee” which was published in the Hindu. The Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs recently presented a report in the Lok Sabha on “Smart Cities Mission: An Evaluation”.
| Relevancy for Prelims: Interim Budget 2024-2025, Smart Cities Mission, Smart Cities Award, Jamshedpur Model, Urbanization, and Urban Governance Model
Relevancy for Mains: Smart Cities Mission (SCM): Current Progress, Achievements, Challenges, and Way Forward. |
|---|
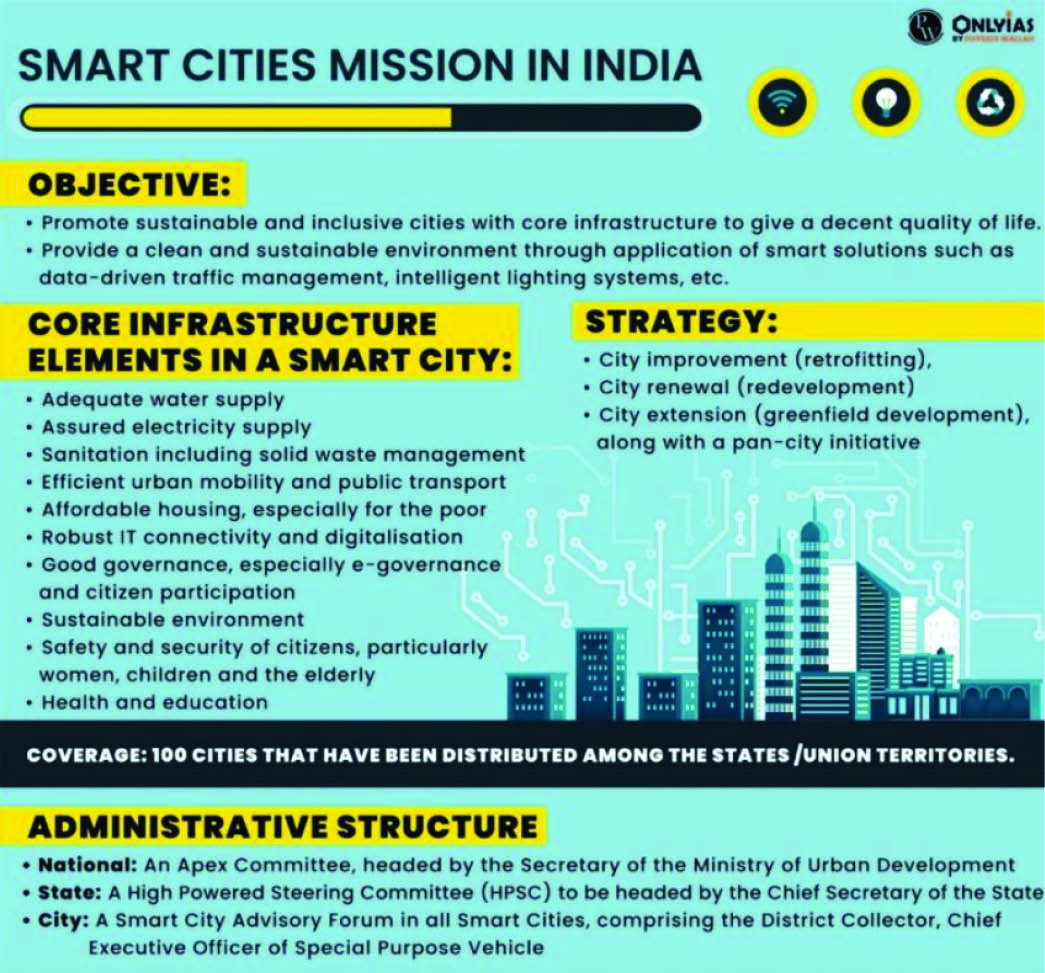
Smart Cities Mission Success Stories
|
|---|
| Government Programs for Sustainable Urban Development: |
|---|
News Source: The Hindu
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>