Malicious APKs (Android Package format) files are being used by cybercriminals by using social engineering methods as new means to scam users.
- Example: In a Recent case of cyber fraud, a woman claimed having lost upto Rs.1 lakh after she downloaded an app on her iPhone via an APK file on WhatsApp at the Bengaluru airport lounge.
- Social Engineering Technique was used to download the malicious apps by which the device was accessed and likely enabled call forwarding.
About Social engineering in Cyber Crime
- Social Engineering is a cyber crime technique that uses psychological manipulation and deceiving human emotion to trick users into revealing sensitive information or making security mistakes.
-
Common Techniques:
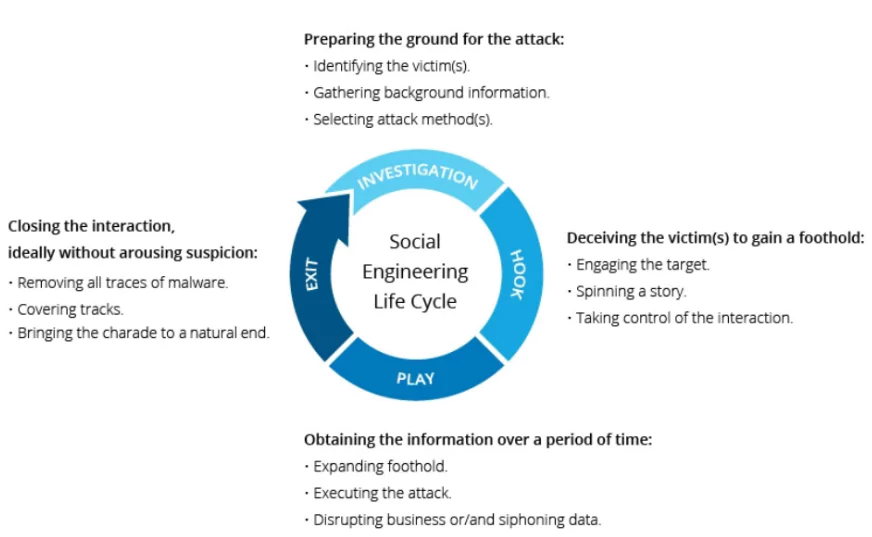
-
- Phishing: These are email and text message campaigns which are aimed at creating a sense of urgency, or fear in victims prodding them into revealing sensitive information, clicking on links to malicious websites, or opening attachments that contain malware.
- Example: An email sent to users of an online service that alerts them of a policy violation requiring immediate action on their part, such as a required password change.
- Baiting: A technique that uses a false promise to lure victims into a trap that steals their personal information or infects their systems with malware.
- Example: Baiting usually uses physical media to disperse malware (typically malware-infected flash drives) in areas where potential victims are certain to see them (e.g., bathrooms, elevators etc). Also Online forms of baiting consist of enticing ads that lead to malicious sites
- Scareware: A technique that involves bombarding victims with false alarms and threats to trick them into installing software that is either malware or has no real benefit.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Cybercrime in India
- India ranked fifth globally in the number of breached accounts in 2023, with 5.3 million leaked accounts and citizens losing close to ₹1.3 – ₹1.5 lakh to cyber criminals every minute.
- According to the National Cybercrime Reporting Portal (NCRP), at least ₹10,319 crore was reported lost by victims of digital financial fraud in 2023 with 5,252 suspect URLs reported so far.
- A report by the Indian Cybercrime Coordination Centre (I4C) says that digital financial frauds amounted to a staggering ₹1.25 lakh crore over the last three years.
- The Parliamentary Standing Committee on Finance’s report on ‘Cybersecurity and Rising Incidents of Cyber/White Collar Crimes‘ noted that domestic fraud reported by Supervising Entities (SE) in FY23 totalled ₹2,537.35 crore.
Measures to Prevent Attacks
- Standardisation: All the banks have been asked to have ‘160’ in the beginning of their customer care numbers to identify as genuine.
- The three-digit number will be a part of the 10-digit mobile number and any call without the number should not be picked up by the citizens.
- URL phishing frauds: All banks in India will have .bnk.in in their URL and financial institutions will have .fin.in
- White Listing: All telecom operators will ‘white-list’ links sent via messages (including SMS) to citizens. The Links which are not white-listed will be disposed of at the operator level and will not reach customers.
- Strengthen Know Your Customer (KYC) procedures, improve oversight and audit and ensure compliance to regulation
|
- Example: A common example being the popup banners appearing in browser while surfing the web, displaying such text such as, “Your computer may be infected with harmful spyware programs.”
- Pretexting: A technique that involves gaining a victim’s trust through a series of lies, often by pretending to need sensitive information to perform a critical task.
- Quid pro quo: A technique that exploits people’s tendency to reciprocate good gestures.
- For example, an attacker may offer free technical support in exchange for the victim turning off their antivirus software.
- Deep Fakes: A technique that uses artificial intelligence (AI) to create realistic but fake audio, video, or images that impersonate real people.
- Watering hole attacks: A targeted technique that involves compromising a website that is likely to be visited by a particular group of people.
-
Reasons for its Prevalence:
-
-
- Lack of Security Knowledge: Many employees lack the knowledge to identify and defend themselves against these types of attacks as social engineering attacks are designed to exploit human weaknesses.
- Social Media Presence: Social engineers use deception and manipulation to pose as friends or family members or pretend to be from a trusted organisation like a bank or government agency often targeting people with an active social media presence.
- Appealing to Greed: The infamous Email Nigerian Prince scam of 2018 is an example of catering to the human nature of greed. In the scam,a Nigerian royal claims to offer a giant financial reward in exchange for the recipient’s bank account information or a small advance fee.
- Appealing to Generosity: It can also appeal to victims’ better nature like to offer technical help to a friend or ask for participation in a survey, claiming that the recipients’ post has gone viral and providing a spoofed link to a fake website or malware download.
-
Social Engineering Prevention:
-
- Double Check on the Information: Do not open emails and attachments from suspicious or unknown sources. Also always cross-check and confirm the news in an email from other sources, such as via telephone or directly from a service provider’s site if suspicion arises.
- Use Multifactor Authentication: Using multi factor authentication helps ensure your account’s protection in the event of system compromise as user credentials are one of the most valuable pieces of information seeked by attackers
- Up to date Antivirus/Antimalware Software: Periodically check to make sure that the updates have been applied, and scan your system for possible infections.
- Cyber Security Awareness: General Education on the multiple types of social engineering scams and use of free tools such as phishing simulators, training videos, and cyber security assessments to strengthen organisation and reduce human risk
- Training Modules: Social engineering awareness training model uses animated videos, interactive online training, managed security services, microlearning modules, and phishing simulations to provide continual support.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
About APKs (Android Package Format or Android Package Kit) Files
-
- APKs are in the format of files that Android uses to distribute and install apps. An APK file contains all the data an app needs, including all of the software program’s code, assets and resources.
- All Android apps either downloaded from the Google Play Store or manually use the APK files
- Nature: An APK is an archive file (it contains multiple files, plus some metadata about them, eg: ZIP Files) and is a variant of the JAR (Java Archive) file format
- All APKs are ZIP files at their core, but they must contain additional information to properly function as an APK. So all APKs are ZIPs, but not all ZIPs are APKs.
- Components:
-
-
- DEX files: Compiled code that’s essential for running the app
- Resources: External elements like images, strings, and XML files
- Manifest file: Declares the app’s permissions, features, and requirements
- Way to open an Android Package Kit file:
-
- Android: Apps can be downloaded either through the Google Play Store on Android phones or manually
- Manually: User will have to first enable downloads from unknown sources in the Android OS settings and then download it like they would any other file and open it upon request
- Windows 11 and macOS : Users can manually install APK files using Windows Subsystem for Android enabling users to download Android applications available on the Amazon Appstore.
- An Android emulator, like BlueStacks, can also be used to open APK files on a Windows OS.
- iOS Devices: APK files usually cannot be installed on iOS devices but iPhone users by enabling a hidden setting within iOS allows users to test beta or unreleased versions of apps from developers.
- Apple’s Swift SDK also allows screen sharing (both in-app and in the background)
|
![]() 4 Nov 2024
4 Nov 2024

