Amid concerns over lithium import dependence and supply-chain risks, India is rethinking its battery strategy, with sodium-ion batteries emerging as a safer, strategic alternative.
Why India needs Sodium-ion Batteries
- Reduces dependence on imported critical minerals like lithium, cobalt and nickel.
- Enhances energy security through use of abundant, geographically diversified sodium.
- Supports cost-effective grid-scale storage and domestic manufacturing.
About Sodium-ion Batteries
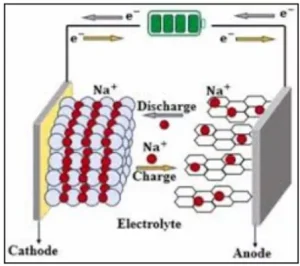
- Sodium-ion batteries (SiBs) are rechargeable batteries that use sodium ions (Na⁺) as charge carriers instead of lithium ions.
- They belong to the same “rocking-chair” battery family as lithium-ion cells but rely on more abundant raw materials.
- A “rocking-chair” battery is a rechargeable system where ions (Li / Na ion ) “rock” or shuttle back and forth between the cathode and anode through an electrolyte during charging and discharging cycles.
- Working of Sodium-ion Batteries
- Charging: Sodium ions move from cathode to anode through the electrolyte; electrons flow via the external circuit.
- Discharging: Sodium ions migrate back to the cathode, releasing electrical energy.
- Key design feature: Aluminium is used as the current collector on both electrodes, unlike lithium-ion batteries which require copper on the anode side.
- Applications
- Grid-scale energy storage for renewable energy integration.
- Two and three wheeler EVs where ultra-high energy density is not critical.
- Stationary storage for households, telecom towers, and industrial backup.
- Energy storage systems (ESS) for load balancing and peak shaving.
- Limitations
- Lower energy density compared to lithium-ion batteries, limiting long-range EV use.
- Volumetric energy density still trails advanced lithium chemistries.
- Ecosystem and commercial deployment are at an early stage.
Lithium ion vs Sodium ion Batteries
| Aspect |
Lithium-ion Battery |
Sodium-ion Battery |
| Charge carrier |
Lithium ions (Li⁺) |
Sodium ions (Na⁺) |
| Raw material availability |
Scarce, geographically concentrated |
Abundant, widely available |
| Current collector |
Copper (anode), aluminium (cathode) |
Aluminium on both electrodes |
| Energy density |
Higher (suitable for long-range EVs) |
Lower (better for stationary use) |
| Safety & transport |
Higher thermal runaway risk
State of charge (SOC) limits |
Safer; can be stored at 0% SOC |
Conclusion
By combining safety, material abundance, manufacturing compatibility and strategic resilience, sodium-ion batteries can complement lithium-ion systems and strengthen India’s long-term energy and industrial security.
![]() 7 Feb 2026
7 Feb 2026



