Commission for air quality management in NCR and adjoining areas ordered the imposition of the graded response action plan (GRAP) stage IV restrictions as the air quality index (AQI) in Delhi goes above 400.
About Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP)
- The Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) is an emergency response plan that aims to reduce air pollution in the Delhi-NCR region.
- The Supreme Court of India approved GRAP in 2016 in the case M. C. Mehta v. Union of India. The MoEFCC notified GRAP in 2017.
- Implementation: The Commission for Air Quality Management in NCR & Adjoining Areas (CAQM) is responsible for implementing GRAP.
- The CAQM uses forecasts from the India Meteorological Department (IMD) and the Indian Institute of Tropical Meteorology (IITM) to inform its decisions.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Key Features of GRAP
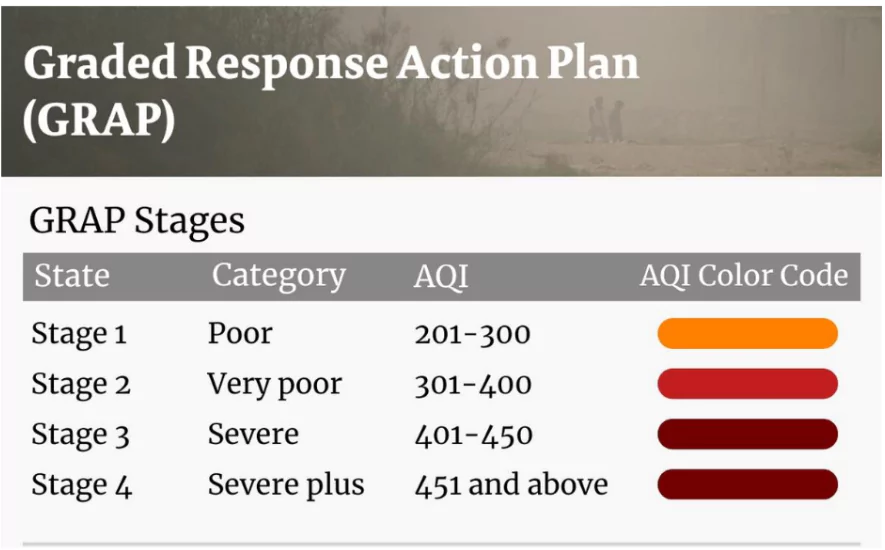
- GRAP is a set of measures that are implemented when the Air Quality Index (AQI) in the Delhi-NCR region reaches a certain level.
- Incremental Nature: GRAP is designed to be incremental, meaning as air quality worsens, measures from successive stages are triggered.
- Stage 1 (Poor AQI – 201 to 300)
- Stage 2 (Very Poor AQI – 301 to 400)
- Stage 3 (Severe AQI – 401 to 450)
- Stage 4 (Severe + AQI – More than 450)
About Air Quality Index (AQI)
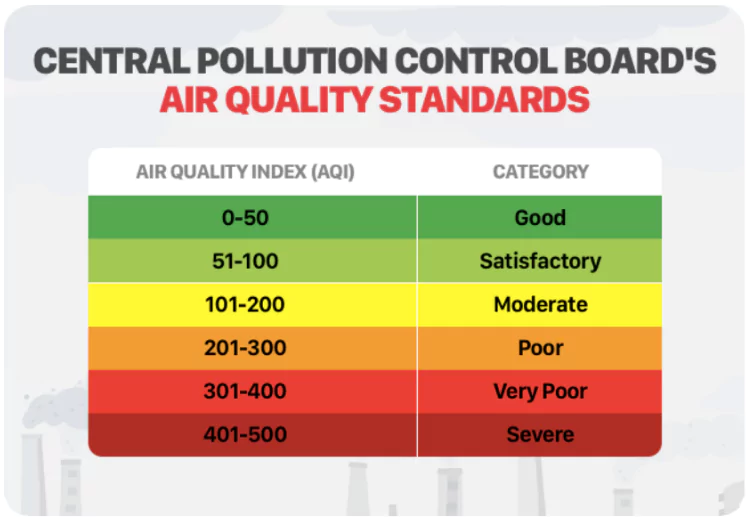
- The Air Quality Index (AQI) was introduced in 2014 to systematically monitor and report the air quality in India.
- Categories: The AQI is based on six categories:
- Good, Satisfactory, Moderately Polluted, Poor, Very Poor, and Severe.
- Pollutants Considered:
- The AQI is calculated using the average concentrations of eight key pollutants:
- PM10 (Particulate Matter ≤ 10 micrometers)
- PM2.5 (Particulate Matter ≤ 2.5 micrometers)
- Nitrogen dioxide (NO₂)
- Sulphur dioxide (SO₂)
- Carbon monoxide (CO)
- Ground-level ozone (O₃)
- Ammonia (NH₃)
- Lead (Pb)
- Time Interval for Measurement:
- The AQI uses 24-hourly average values for PM10, PM2.5, NO₂, SO₂, NH₃, and Pb.
- For CO and O₃, 8-hourly average values are used.
- Calculation Criteria:
- A minimum of data from three pollutants is required to calculate the AQI.
- At least one of these pollutants must be either PM10 or PM2.5.
- AQI Range and Scale: The AQI is categorized on a scale ranging from 0 to 500 to determine the level of air quality in different states and cities.
- Development: The AQI was developed by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) in collaboration with air quality experts.
About the Commission for Air Quality Management (CAQM)
- The CAQM is a statutory body established under the Commission for Air Quality Management in National Capital Region (NCR) and Adjoining Areas Act, 2021.
- Mandate: The primary mandate of CAQM is to ensure better coordination, conduct research, identify issues, and find resolutions related to air quality in the region, along with managing related matters or any connected concerns.
- Composition of CAQM
- Chairperson: A government official at the rank of Secretary or Chief Secretary, serving for three years or until the age of 70.
- Ex officio Members: Five members, who are Chief Secretaries or Secretaries from the environment departments of Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh.
- Full-Time Members: Three technical experts.
- NGO Representation: Three members from non-governmental organisations.
- Technical Experts: Members from CPCB, ISRO, and NITI Aayog.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
- Jurisdiction: The jurisdiction of CAQM extends to the National Capital Region (NCR), which includes Delhi and parts of Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, and Rajasthan.
- The jurisdiction may also cover any other adjoining areas notified by the central government.
- Overriding Powers: The CAQM holds overriding authority over other regulatory bodies like the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and State Pollution Control Boards (SPCBs) within its jurisdiction, ensuring that it has comprehensive control over air quality management.
![]() 18 Nov 2024
18 Nov 2024


