![]() 8 Mar 2024
8 Mar 2024
English
हिन्दी
A committee of 18 scientists have voted down a proposal to declare the start of the Anthropocene or Human Epoch in a geologic time scale.
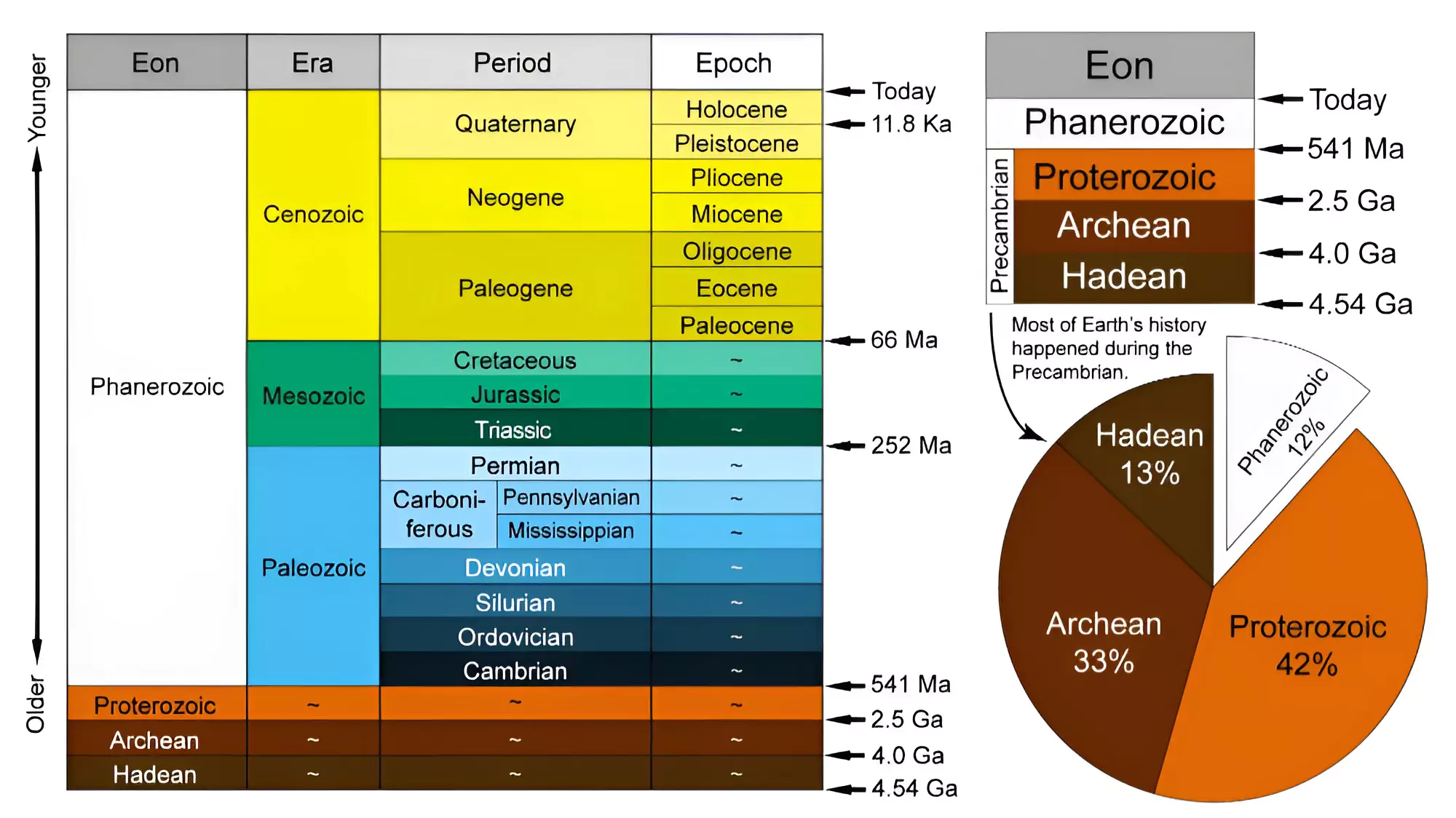
Geologic Time Scale (GTS)
|
|---|
The International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS)
The International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS)
|
|---|
Holocene Epoch:
|
|---|
News Source: the Indian Express
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
<div class="new-fform">
</div>