![]() 19 Dec 2023
19 Dec 2023
English
हिन्दी
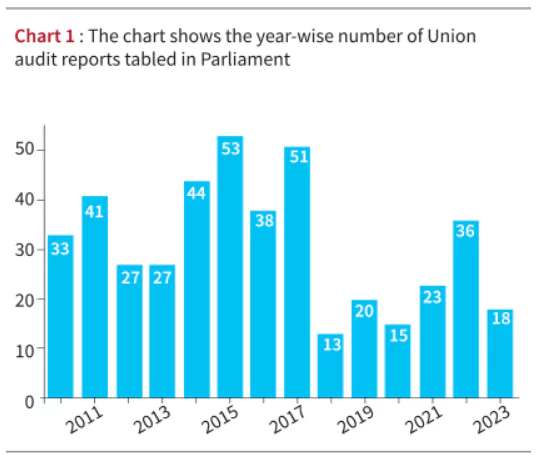
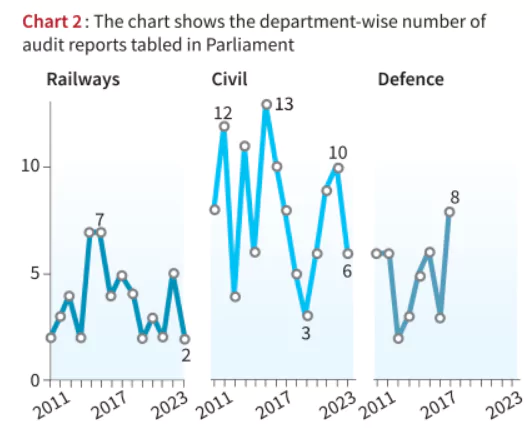
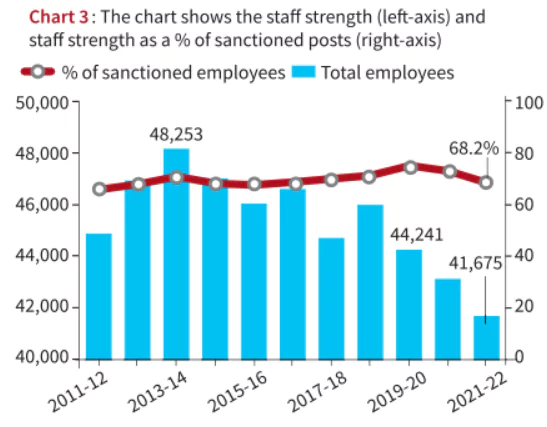
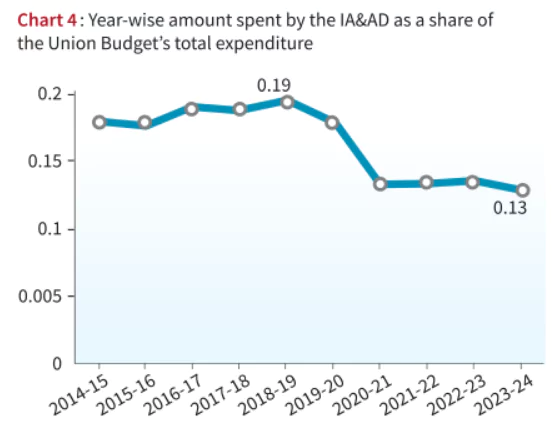
Context: Only 18 CAG audit reports on the Union government’s accounts are tabled in parliament.
| About Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG)
Constitutional Body: Comptroller and Auditor General of India (CAG) is a constitutional authority entrusted with the responsibility of auditing the accounts of the Union and state governments. Constitution provisions: Article 148 of the constitution provides for an independent office of CAG. Indian Audit and Accounts Department: CAG is head of the Indian Audit and Accounts Department Supreme Audit Institution Of India: The CAG and Indian Audit and Accounts Department (IA&AD) are known as the Supreme Audit Institution of India (SAI). Public Purse: CAG is considered the “Guardian of Public Purse.” Appointment: He is appointed by the President of India. Tenure: CAG holds office for a period of 6 years or 65 years, whichever is earlier. Process of CAG report: The reports of the CAG are submitted to the President in case of the Union and to the Governor in case of the State who thereafter tables it in the respective houses. Functions of CAG: Regular Audit: Every year, it is called a transactional audit through which we cover all states and schemes. Performance Audit: It is an independent, objective, and reliable examination of whether the public sector undertakings, programs, activities, or organizations operating in accordance with the principles of economy, efficiency, and effectiveness. |
|---|
News source: The Hindu
<div class="new-fform">
</div>