Context:
Recently, India’s first National Highway (NH) steel slag road section on NH-66 (Mumbai-Goa NH) was inaugurated.
NH 66 Mumbai-Goa National Highway: India’s First Steel Slag Road
- CSIR-CRRI Technological Guidance: JSW Steel, under the expertise of CSIR-CRRI, has constructed the 1-km-long, four-lane steel slag road section on NH 66 Mumbai-Goa.
- CONARC Steel Slag Utilization: Approximately 80,000 tons of CONARC Steel slag were converted as processed steel slag aggregates.
CONARC Steelmaking Process
- The CONARC steelmaking process combines electrode arc melting with oxygen steelmaking.
- The processed steel slag aggregates are superior to natural aggregates in terms of various mechanical properties. They are utilized for steel slag road construction in all layers of the road in place of natural aggregates.
About Steel Slag Road Technology (SSRT)
- Steel Slag Road Technology (SSRT): It is a method that uses steel slag to build roads. SSRT was developed by CSIR-Central Road Research Institute (CSIR-CRRI) to transform the waste of steel industries into wealth.
- Steel Slag: It is a by-product of steel making, produced during the separation of the molten steel from impurities in steel-making furnaces.
- The slag occurs as a molten liquid melt and is a complex solution of silicates and oxides that solidifies upon cooling.
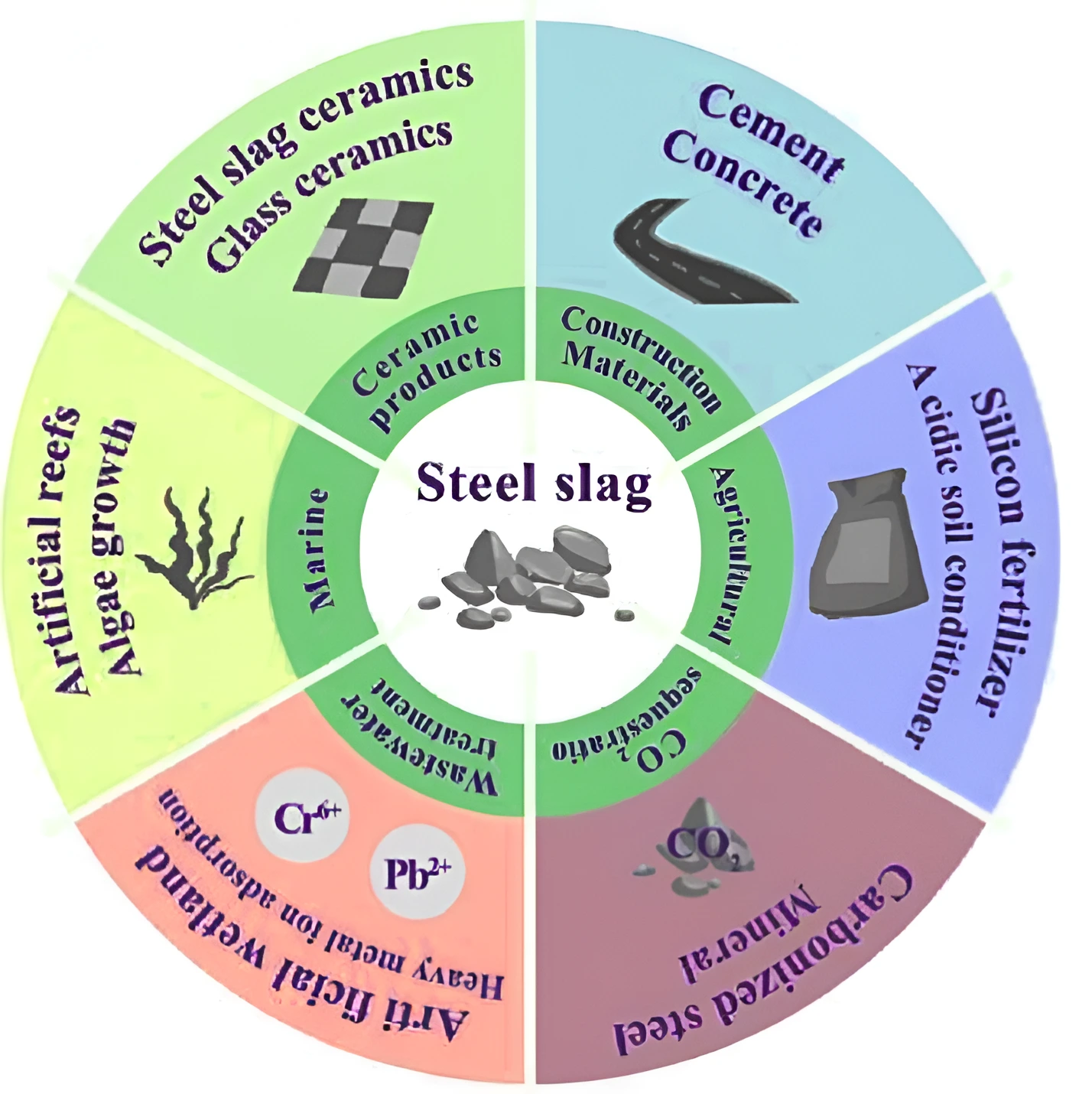
- Uses of Steel Slag: It is used as an aggregate and is considered a standard practice with applications that include its use in granular base, embankments, engineered fill, highway shoulders, and hot mix asphalt pavement.
Significance of SSRT
- Stronger Roads: The roads made out of steel slag are 30% less thick because of better material characteristics. It is helping the National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) to build stronger national highways in the country.
- Cost-Efficient Process: In comparison to normal highways, the construction costs will also be around 30% cheaper.
- Eco-Friendly Road Construction:
- SSRT paves the way for sustainable use of waste and reduces the reliance on perishable natural aggregates.
- This process is also expected to reduce Greenhouse Gas emissions and carbon footprint in road construction activity.
- It aligns with India’s commitment to the UN SDG (Goal 9) for building resilient infrastructure through inclusive and sustainable industrialization and green technologies.
Also Refer: Road Accidents In India-2022′ Report Released By MoRTH
News Source: PIB
![]() 16 Jan 2024
16 Jan 2024

