Context: Shri Ram Janmabhoomi Mandir or Ayodhya Ram Mandir will be inaugurated on January 22.
Ayodhya Ram Mandir: Ram Lalla Idol Consecration Ceremony Or Pran Pratishtha on January 16, 2024
- The Pran Pratishtha or consecration ceremony of the Ram Lalla idol will begin on 16 January with Vishnu Puja and gau daan at the Saryu embankment.
About Pran Pratishtha (Consecration Ceremony)
- It is a ritual or ceremony by which a murti (idol of a deity) is consecrated in a Hindu temple, wherein hymns and mantras are recited to invite the deity to be a resident guest in the idol and the idol is infused with the energies of the Deity.
- The murti’s eye is opened for the first time and thereafter is available for Darshana.
|
About Ayodhya Ram Mandir
-
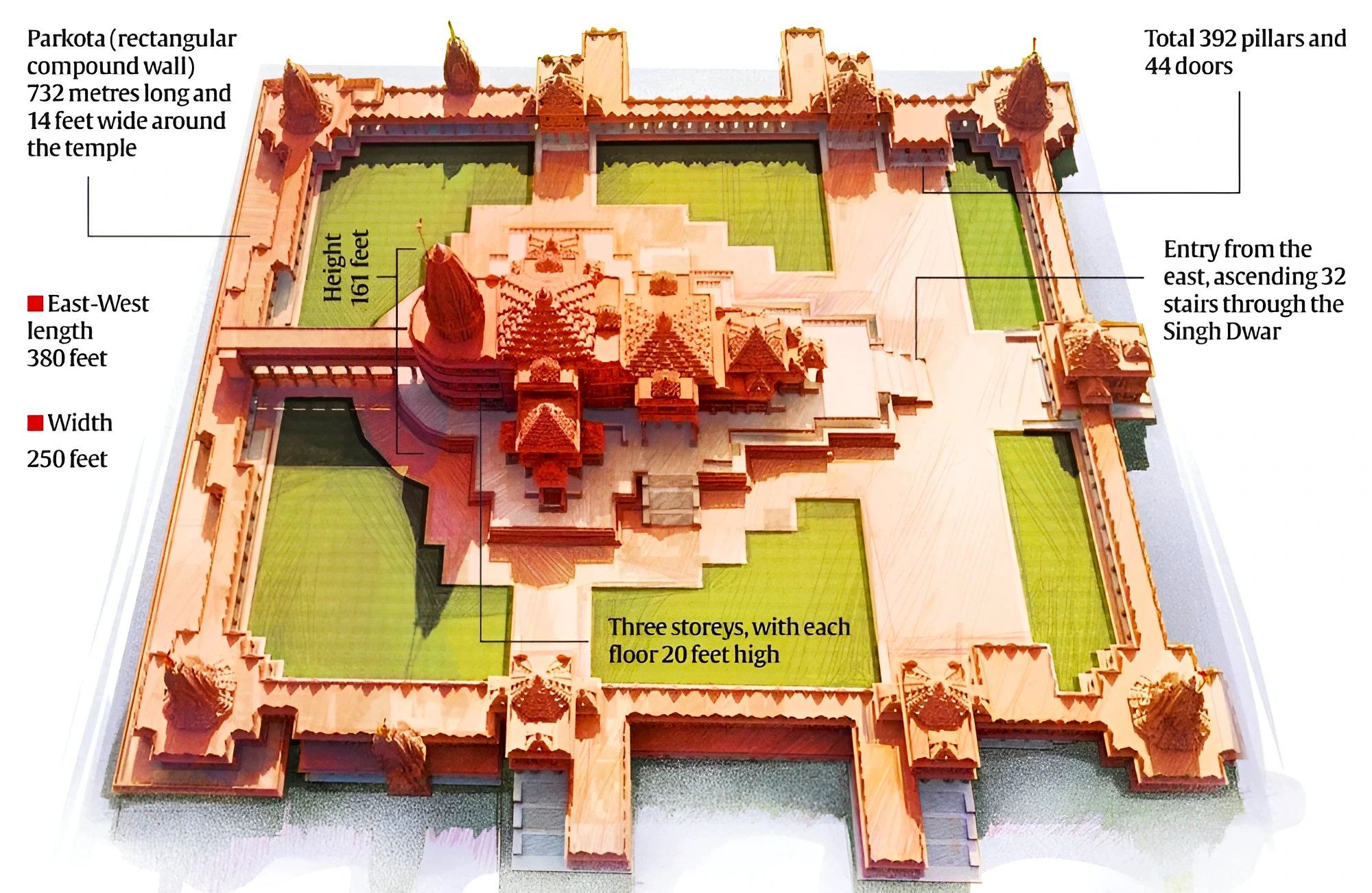
Layout of Ayodhya Ram Mandir
-
- The Temple is built over three 20-foot high floors each with a total of 392 pillars and 44 doors in the complex.
 Foundation of the temple: It is built of a 14-metre-thick layer of roller-compacted concrete. And a 21-foot-high granite plinth has been placed to protect against ground moisture.
Foundation of the temple: It is built of a 14-metre-thick layer of roller-compacted concrete. And a 21-foot-high granite plinth has been placed to protect against ground moisture.- Iron has not been used anywhere in the construction
- Stone used: Makrana Marble and Pink sandstone, granite stone, and colored Marble.
- Ram Katha Darshan: The walkways and columns during Parikrama have been engraved with 100 events from Valmiki’s Ramayana.
-
Architecture style of Ayodhya Ram Mandir: Nagara style
- Sanctum Sanctorum (garbhagriha): Placed with the idol of Ram Lalla
- Mandaps (halls): Nritya Mandap, Rang Mandap, Sabha Mandap, Prarthana Mandap and Kirtan Mandap.
- Mandirs: At each corner of the compound will be dedicated to Surya, Bhagwati, Ganesh, Shiv. On the northern and southern arms, temples to Annapurna and Hanuman will be built respectively.
- Temples of Maharshi Valmiki, Vashishtha, Vishwamitra, Agastya, Nishad Raj, Shabri etc have also been proposed.
-
Other features of Ayodhya Ram Mandir
-
- Installed 200KA light arresters over the temple structure for protection against lightning strikes.
About Nagara Style of Temple Architecture
- First developed in North India during the Gupta period in the 5th century AD, this style is popular in Northern, Western and Eastern India (except the Bengal region), especially in the regions around Malwa, Rajputana and Kalinga.
- Foundation: It is built on a simple stone platform with steps leading up to the temple.
- Features:
- Sikharas: The garbhagriha is always located directly below the highest Sikhara. There is also a Kalash (Amalaka) installed on Shikhara.
- Types of Shikaras: Rekha-Prasad or Latina (The Sri Jagannath Temple of Odisha), Shekari (The Khajuraho Kandariya Mahadev Temple), Valabhi (Teli ka Mandir), Phamsana (The Jagmohan of Konark Temple).
- Absence of boundary walls or gateways.
- Sub schools: They are Orissa school, Chandel school and Solanki school.
|
Also Read: Jagannath Temple Beautification Project
News source: Indian Express
![]() 8 Jan 2024
8 Jan 2024
 Foundation of the temple: It is built of a 14-metre-thick layer of roller-compacted concrete. And a 21-foot-high granite plinth has been placed to protect against ground moisture.
Foundation of the temple: It is built of a 14-metre-thick layer of roller-compacted concrete. And a 21-foot-high granite plinth has been placed to protect against ground moisture.