Recently, the Centre has approved interest-free loans worth ₹3,295 crore to States for 40 new projects, identified across 23 States for the development of tourism sites and infrastructure under ‘Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment (SASCI)
About Development of Iconic Tourist Centres to Global Scale under SASCI
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
SASCI Scheme (Special Assistance to States for Capital Investment)
- It was launched in 2020-21 in response to the economic challenges posed by the COVID-19 pandemic.
- Objective: To provide 50-year interest-free loans to States, enabling them to undertake critical capital investments.
- It continued in subsequent years under its current name.
Key Features of the scheme
- Principle: The scheme is based on the principle of Multiplier Effect, where it is believed that every ₹1 spent as capital expenditure will result in an impact worth ₹3.
- Capital investment Sectors: Projects in Health, education, irrigation, water supply, power, roads, bridges and railways are approved.
- Focus Areas: Key sectors targeted under the scheme include:
- Vehicle Scrappage Policy: Incentivizing the removal of old, polluting vehicles.
- Urban Planning Reforms: Enhancing governance and infrastructure in cities.
- Housing for Police Personnel: Ensuring better living conditions for security forces.
- Unity Mall Projects: Promoting national integration through the development of these cultural hubs.
- Libraries: Establishing digital libraries at the Panchayat and Ward levels to improve educational accessibility.
- Support for National Projects:
- The scheme helps accelerate the implementation of important infrastructure initiatives such as:
- Jal Jeevan Mission (water supply).
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (rural road connectivity).
|
-
- The loans will be provided to the States for a period of 50 years and will be interest-free.
- The State governments are responsible for providing land for the projects, implementing them, and managing their operations after completion.
- All projects must be completed within a timeline of two years.The State Government is solely responsible for the project’s operations and maintenance, potentially through Public-Private Partnership (PPP) mode.
- Fund Distribution
- The Department of Expenditure will release 66% of the funds as the first instalment directly to the States.
- Nodal Ministry: The Ministry of Tourism
- States can submit multiple projects, with a maximum funding of Rs. 100 crores per project.
- Project Identification
- These projects include lesser-known tourist destinations such as Bateshwar in Uttar Pradesh, Ponda in Goa, Gandikota in Andhra Pradesh, and Porbandar in Gujarat. .
Tourism in India
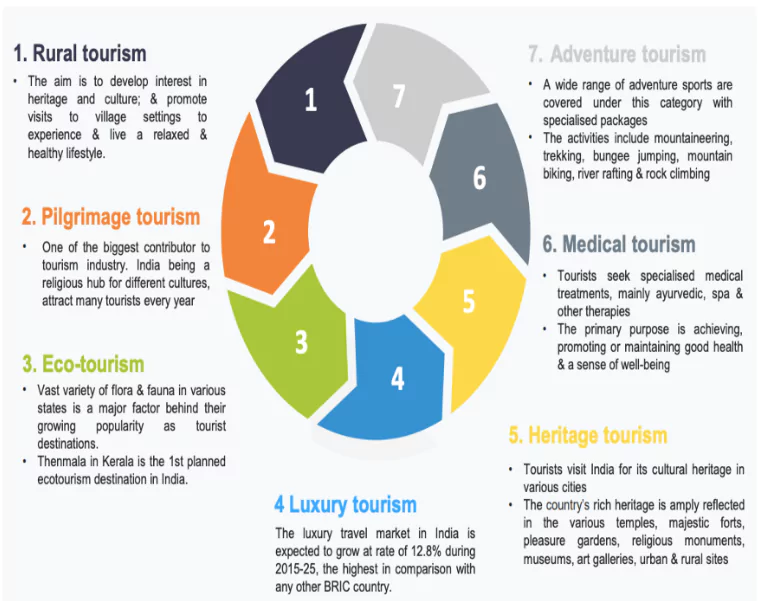
- India’s tourism sector is a major industry that contributes to the country’s GDP and creates jobs.
- The tourism sector contributes around 9% of the country’s GDP.
- Growth and status:
- India’s tourism sector has grown significantly over the past two decades.
- In 2023, India recorded 9.24 million foreign tourist arrivals, a 43.5% increase from 2022.
- The World Travel and Tourism Council (WTTC) projects that India’s travel and tourism sector will contribute almost INR 21.15 trillion to the economy in 2024.
- India ranked 39th among 119 countries according to the Travel and Tourism Development Index (TTDI) 2024 report published by World Economic Forum (WEF).
- Growth in Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs): India recorded 9.24 million FTAs in 2023, reflecting a 43.5% growth compared to 6.44 million in 2022.
-
- This growth contributed to significant foreign exchange earnings (FEEs).
- Growth in Domestic Tourist Visits (DTVs): Domestic tourism has shown remarkable growth, with 2509.63 million Domestic Tourist Visits (DTVs) recorded in 2023 (provisional), up from 1731.01 million DTVs in 2022.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Impact of Tourism in India
- Economic
- Economic Contributions:
- Employment: Tourism accounted for approximately 7% of India’s GDP in 2022 and created 76.17 million jobs directly and indirectly in the same period.
- Foreign exchange earnings: The foreign exchange earnings (FEEs) from tourism rose significantly, reaching ₹2.3 lakh crore in 2023, showing its economic importance.
- Employment Generation: The tourism sector created 76.17 million direct and indirect jobs in 2022-23, an increase from 70.04 million jobs in 2021-22.
- Infrastructure Development: Over the last few years, India has invested $1 billion (₹7,000 crore) to improve tourism infrastructure, enhancing the overall experience for visitors.
- Promotion Efforts: The Government is holistically promoting India’s tourism products in domestic and international markets to establish India as a leading global travel destination.
- Cultural Impact
- Tourism promotes cultural exchange and heritage preservation.
- For instance, the Taj Mahal in Agra attracts millions of visitors annually, generating funds for conservation.
- Social Impact
- Tourism empowers local communities through employment and skill development.
- Rural tourism initiatives like those in Raghurajpur, Odisha, support artisans and craftspeople, enabling the preservation of traditional skills such as Pattachitra painting while enhancing livelihoods for over 2,000 families.
- Environmental Impact
- While tourism boosts economic growth, it also leads to environmental concerns such as waste and pollution.
- For example, in 2023, the influx of over 1.2 million tourists to Leh-Ladakh resulted in a significant increase in plastic waste, with over 200 tons of waste collected monthly in peak tourist seasons.
- Tourism has driven the adoption of eco-friendly practices and conservation efforts in India.
- For example, Kaziranga National Park in Assam has seen increased funding for wildlife conservation due to eco-tourism.
Government Initiative to promote tourism in India
- Swadesh Darshan Scheme (2014): This scheme aims to develop theme-based tourist circuits across India, leveraging cultural, historical, and natural heritage. It focuses on creating world-class tourism infrastructure and experiences.
- PRASAD Scheme (2014): The Pilgrimage Rejuvenation and Spiritual, Heritage Augmentation Drive (PRASAD) scheme focuses on the development and beautification of pilgrimage sites in India. It aims to enhance the overall pilgrimage experience for domestic and international tourists.
- Paryatan Parv (2015): This nationwide campaign encourages domestic tourism by organizing cultural events, festivals, and activities across the country. It aims to promote India’s diverse cultural heritage and attract domestic tourists to explore different regions.
- Dekho Apna Desh Initiative (2015): This initiative encourages domestic tourism by promoting the exploration of India’s diverse landscapes and cultural heritage. It aims to create awareness about lesser-known destinations and promote domestic travel.
- Ek Bharat Shreshtha Bharat (2015): This initiative promotes cultural exchange and integration between different states of India. It encourages state pairings to organize cultural exchange programs, festivals, and activities, fostering a sense of unity and promoting domestic tourism.
- E-Visa (2014): The Indian government has implemented an e-Visa system, making it easier for foreign tourists to obtain visas and travel to India. This has significantly streamlined the visa process and made it more convenient for international tourists.
- Dharamshala Declaration (2022): It outlines India’s plan to revitalize tourism post-pandemic, aiming for a $150 billion GDP contribution, $30 billion in foreign exchange earnings, and 15 million foreign tourist arrivals by 2024.
- By 2030, it targets a $250 billion GDP contribution, 137 million jobs, 56 million foreign tourists, and $56 billion in earnings, establishing India as a global tourism hub.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Potential of India’s Tourism Sector
- Diverse Attractions:
- India’s varied geography and culture offer destinations ranging from natural wonders like the Himalayas and backwaters of Kerala to historical landmarks such as the Taj Mahal and Hampi.
- With 40 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, India has a global edge in cultural and natural heritage.
- For example, the tourism circuit in Varanasi, integrated with Buddhist sites like Sarnath, appeals to both domestic and international tourists.
- Growing Domestic Tourism:
- Government initiatives such as Dekho Apna Desh and Swadesh Darshan 2.0 have fueled domestic travel.
- In 2023, domestic tourist visits increased to 2509.63 million, reflecting the effectiveness of these campaigns.
- Foreign Tourist Arrivals (FTAs):
- The rise in FTAs, with 9.24 million visitors in 2023 (up from 6.44 million in 2022), highlights India’s increasing appeal as a global tourist destination.
- This was bolstered by e-visa availability and a multilingual tourist helpline.
- Niche Tourism:
- Growth in adventure tourism, eco-tourism, medical, and wellness tourism is evident, with Kerala’s Ayurveda and yoga retreats being standout offerings.
- India has also become a popular destination for Himalayan trekking.
Challenges with India’s Tourism Sector
- Infrastructure and Connectivity:
- Many tourist destinations, especially in remote regions like the Northeast, lack basic infrastructure.
- For example, Arunachal Pradesh’s scenic locales remain underexplored due to inadequate road and air connectivity.
- Safety and Hygiene:
- Safety concerns, particularly for women, and sanitation issues negatively impact tourism.
- Varanasi, despite being a spiritual hub, faces challenges with waste management, deterring many visitors.
- Underutilized Heritage:
- While sites like Jaipur and Agra are over-visited, others, such as Khajuraho and Hampi, suffer from neglect and poor promotion, missing opportunities for global attention.
- Seasonal Tourism:
- Popular destinations like Shimla and Manali experience overcrowding during peak seasons but lack strategies to attract tourists in off-seasons, leading to uneven economic benefits.
- Skilled Workforce:
- The shortage of trained personnel in hospitality and tourism affects service quality. This includes a lack of skilled guides and managers in many tourist hubs.
Way Forward
- Infrastructure Development: Developing better connectivity in remote areas, such as new airports in the Northeast and enhancing rail networks, can unlock tourism potential.
- For instance, improved roads and transport to Ladakh have boosted visitor numbers.
- Sustainable Tourism: Kerala’s Responsible Tourism initiative integrates community development with eco-tourism, providing a successful model for other states.
- Focused Marketing Campaigns: Revamping the Incredible India campaign with themes like spiritual tourism and Ayurveda can attract specific traveler groups.
- Similar efforts in Rajasthan, focusing on its desert culture, have shown success.
- Safety and Security Measures: Deploying tourist police in key hotspots, improving signage, and enhancing digital safety for travelers, especially women, can improve India’s global image.
- Promotion of Off-Season Tourism: Events like the Ladakh Winter Festival or discounted travel packages during lean periods can help spread tourism activity year-round
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
India’s tourism sector has immense potential to drive economic growth, create jobs, and enhance global cultural engagement. By addressing challenges like infrastructure gaps, seasonal dependency, and safety concerns, alongside leveraging its diverse heritage and natural attractions, India can establish itself as a global tourism powerhouse, contributing significantly to its development goals.
![]() 30 Nov 2024
30 Nov 2024

