Recently, the WEF article, “India Can Be a Global Pathfinder in Digital Health”, was released, which explores how India’s digital healthcare initiatives position the country as a leader in health technology.
- The report emphasizes the role of public-private partnerships, the importance of interoperability, and the need for robust data governance frameworks.
- It underscores how India’s initiatives, such as the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) and the Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS), can set a global benchmark for digital healthcare transformation.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
About Digital Health
- Digital health is the use of digital technologies to improve health.
- It includes a wide range of technologies and applications, such as:
- Electronic health
- Mobile health (mHealth)
- Telehealth
- Health information technology (IT)
- Wearable medical devices
- Software as a medical device (SaMD)
- Personalized medicine
Digital Healthcare Infrastructure in India
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)
- The ABDM, launched in 2021, aims to create a nationwide digital health ecosystem by integrating healthcare service providers and patients through unique health IDs.
- Objective: To fill critical gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance and health research – spanning both the urban and rural areas so that the communities are Atma Nirbhar in managing such pandemic/ health crises.
- Key features of ABDM include:
- Health ID: A unique identifier for individuals to store and share medical records.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): A comprehensive database of registered healthcare professionals.
- Health Facility Registry (HFR): A digital repository of healthcare facilities across India.
- Unified Health Interface (UHI): An open network facilitating digital health services.
- Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA): The Mission provides for assisted and offline mode for creation of Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) for areas with limited internet connectivity or hardware or both.
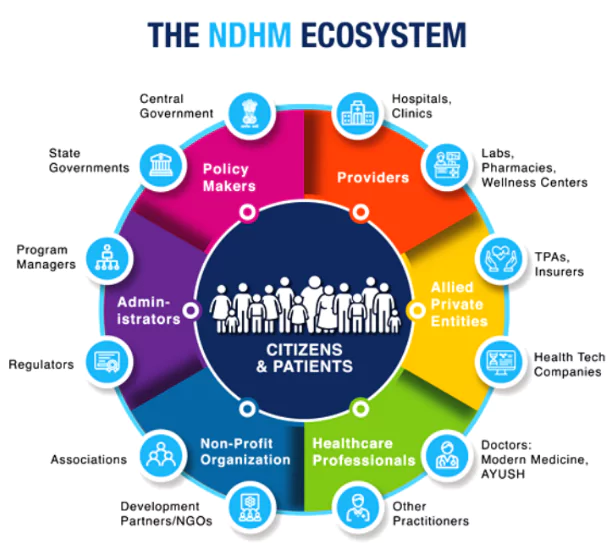 Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system.
Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system.
- Research and development: Recently, in September 2024, the National Health Authority (NHA) and IIT Kanpur signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU)
- A federated learning platform across a variety of machine learning model pipelines, a quality-preserving database, an open benchmarking platform for comparing & validating AI models, and a consent management system for research under ABDM would be developed by IIT Kanpur.
- Achievements:
- As on January 20, 2025, more than 73 crore Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA) have been created successfully
- There are more than 5 lakh health professionals registered.
- Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat are the top 5 states with Ayushman Bharat account holders.
- 49.15% of the total number of beneficiaries are women.
- eSanjeevani Telemedicine Service
- The e-Sanjeevani platform, launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW) in 2019, enables remote consultations, reducing the burden on physical healthcare facilities.
- The platform consists of two modules:
- e-Sanjeevani OPD: Facilitating doctor-to-patient consultations remotely.
- e-Sanjeevani AB-HWC: Connecting Health and Wellness Centers (HWCs) with specialist doctors for better healthcare accessibility in remote areas.
- U-Win Portal
- The U-WIN Portal, launched in October 2024, is developed for the complete digitization of vaccination services, and maintaining vaccination records for pregnant women and children from birth to 17 years under the Universal Immunization Programme.
- The citizen-centric services of the digital platform include ‘
- Anytime Access’ and ‘Anywhere’ vaccination services,
- self-registration by citizens using the U-WIN web-portal or the U-WIN citizen mobile application,
- Universal QR-based e-Vaccination Certificate and
- Create their Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) ID for themselves and Child ABHA ID for their children.
- The portal is available in 11 regional languages, including Hindi.
- By November 2024, 7.43 crore beneficiaries have been registered, 1.26 crore vaccination sessions have been held and 27.77 crore administered vaccine doses have been recorded on U-WIN.
- Aarogya Setu App
- It has been transformed into a National Health App, bringing a whole plethora of digital health services powered by the ABDM
- Services:
- Registration for Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA).
- Seamless access to digital lab reports, prescriptions, and diagnoses.
- Online doctor appointments via e-Sanjeevani OPD.
- Facility to download or update Covid-19 vaccination certificates.
- e-Hospital Initiative
- Hospital Management Information System (HMIS): Simplifies internal workflows for government hospitals using a SaaS model.
- Associated Platforms:
- e-BloodBank: Comprehensive blood bank management.
- Online Registration System (ORS): Enables online access to hospital services linked with ABHA.
- National Tele Mental Health Programme (Tele-MANAS)
- It was launched by the government on 10th October, 2022, to further improve access to quality mental health counselling and care services in the country.
- Progress:
- 53 Tele-MANAS Cells established in 36 States/UTs.
- Handled 17.6 lakh calls as of January 2025.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
Key Policies Shaping Digital Healthcare
- National Health Policy (NHP) 2017:
- NHP 2017 emphasizes the use of digital technology to enhance healthcare delivery.
- It advocates for electronic health records, health information systems, and telemedicine to improve accessibility and efficiency.
- Aim: To integrate digital health solutions within the national healthcare framework to address gaps in service delivery, particularly in rural and underserved regions.
- National Health Mission (NHM):
- NHM is a program that works to achieve the goals of the NHP.
- NHM provides support for
- Improvement in health infrastructure,
- Availability of adequate human resources in health facilities,
- To improve availability and accessibility to quality health care especially for the underserved and marginalized groups in rural areas.
- Two Sub-Missions,
- The National Rural Health Mission (NRHM)
- The National Urban Health Mission (NUHM).
- The Union Cabinet in January 2025 approved continuation of the National Health Mission for another five years.
- Health Data Management Policy (HDM Policy):
- It was released in Dec 2020 by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, outlines data privacy, security, and governance standards for digital health records.
- It ensures patient consent, data anonymization, and secure data exchange.
- The Policy specifies that no data shall be shared with any other entity including insurance and pharmaceutical companies without consent of the individual
- National Digital Health Mission (NDHM)
- The mission was launched by the central government in 2020 to improve healthcare in India by creating a digital health ecosystem.
- Vision: It aims to make India self-reliant (Atma Nirbhar) in providing universal health coverage.
- Alignment: It aligns with the National Health Policy 2017 and the National Digital Health Blueprint (NDHB) to create a robust digital infrastructure for healthcare services.
- Key Components
- Health ID (ABHA): A unique identifier for individuals to access and store their health records digitally.
 Digi Doctor: A repository containing detailed information about certified doctors, including qualifications and experience.
Digi Doctor: A repository containing detailed information about certified doctors, including qualifications and experience.- Health Facility Register (HFR): A centralized database of healthcare facilities across India.
- Personal Health Records (PHR): Electronic records that store health-related information for individuals.
- Electronic Medical Records (EMR): A web-based system to store patients’ comprehensive medical and treatment histories.
- Data Security and Interoperability: The mission uses a federated architecture to ensure data privacy and secure interoperability across the healthcare ecosystem.
- Pradhan Mantri Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (PM-ABHIM):
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme (CSS) that aims to improve health infrastructure and systems across the country which focuses on the primary, secondary and tertiary care services.
- Launched to address gaps in health infrastructure, surveillance, and research.
- It also aims to prepare health systems to respond to future pandemics and disasters.
- Scheme period: 2021-22 to 2025-26.
India: Global Leadership and Collaboration in Digital Healthcare
- India as a Global Pathfinder: India is at the forefront of digital health transformation due to its diverse population, robust digital public infrastructure, and innovative private sector.
- As a key proponent of the WHO Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH), India promotes global collaboration, interoperability, and equitable access to digital health solutions.
- India’s Presidency of the G20 Summit 2023 highlighted its role in advancing digital health frameworks for global adoption.
- Replicable Digital Health Models: India’s digital health initiatives, such as Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), serve as templates for developing nations.
- CoWIN Platform: Managed over 2 billion vaccinations and has been adopted by multiple countries for their vaccination drives.
- e-Sanjeevani Telemedicine Platform: Enabled millions of remote consultations, showcasing telemedicine’s potential in bridging healthcare disparities.
- Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Collaboration between the government and private players is essential for innovation and scalability in healthcare.
- Initiatives like the Digital Healthcare Transformation (DHT) Initiative by the World Economic Forum aim to showcase scalable public-private models for global use.
- Cross-Border Collaboration: India supports cross-border digital health partnerships to:
- Eliminate redundancies in healthcare technology.
- Accelerate innovation in AI-driven diagnostics, blockchain-based health records, and telemedicine.
- Address universal healthcare challenges such as rising costs, unequal access, and chronic disease burdens.
- Scalable and Cost-Effective Solutions: India’s healthcare ecosystem has proven scalable, cost-effective solutions adaptable to other nations:
- The Ayushman Bharat Health Account (ABHA) empowers individuals with control over health records.
- The U-WIN Portal ensures comprehensive vaccination record digitization.
- Recognition of India’s Digital Healthcare Success
- Global organizations, including the World Economic Forum, acknowledge India’s digital public health initiatives as benchmarks for innovation, equity, and scalability.
- The DHT Initiative, launched in 2024, emphasizes knowledge exchange and multi-stakeholder engagement to scale impactful digital health solutions globally.
- Future Outlook: India is poised to lead the global digital health movement by focusing on:
- AI-driven healthcare innovations for early detection and efficient diagnostics.
- Blockchain technologies for secure and interoperable health data management.
- Enhanced cybersecurity frameworks to safeguard sensitive health information.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Opportunities for Digital Healthcare Transformation in India
- Enhanced Accessibility: Platforms like e-Sanjeevani have conducted over 30 crore consultations, bringing healthcare services to remote and underserved areas.
- Telemedicine services have reduced the need for physical visits, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, addressing geographical barriers.
- Scalable Solutions for Vaccination: The CoWIN platform facilitated the administration of over 2 billion vaccine doses and was adopted by several countries.
- It highlights how digital platforms can manage large-scale health initiatives effectively.
- Improved Health Data Management: The Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) integrates health records through a Unified Health Interface (UHI), enabling secure data sharing.
- Patients now have access to comprehensive health records through platforms like ABHA.
- Artificial Intelligence in Diagnostics: Collaboration with IIT Kanpur under ABDM leverages AI for diagnostics, improving early detection in remote areas.
- AI-driven initiatives in cancer care in Northeast India showcase the potential for specialized care.
- Economic Benefits through Digital Infrastructure: Digital platforms like Jan Aushadhi Kendras have saved citizens ₹30,000 crores on medicines.
- Lower treatment costs enhance affordability for low- and middle-income populations.
- Global Leadership and Replicability: India’s CoWIN and ABDM platforms are now global templates, adopted by other nations for vaccination and health record management.
- India’s proactive role in the WHO Global Initiative on Digital Health (GIDH) emphasizes its leadership.
Challenges in Digital Healthcare Transformation in India
- Digital Divide: Despite advances, rural areas often lack reliable internet and digital literacy, limiting access to digital health services.
- BharatNet aims to bridge this gap, but high-speed connectivity is still unavailable in many remote regions.
- Fragmented Healthcare Ecosystem: Health data exists in silos, making interoperability a challenge.
- Limited integration between private and public healthcare providers slows the transition to a unified digital health ecosystem.
- Privacy and Data Security Concerns: Only 20% of healthcare providers are fully compliant with Health Data Management Policy standards.
- The need for strong encryption and consent mechanisms is crucial as digital health adoption grows.
- Low Insurance Penetration: Non-life insurance penetration in India is just 1%, compared to the global average of 7%.
- Many citizens cannot afford digital healthcare services due to limited financial coverage.
- Lack of Standardization: Absence of uniform health record formats complicates interoperability and exchange.
- Private hospital chains like Apollo and Max use advanced systems, but data is not portable across providers.
- Resistance to Change: Many healthcare providers still rely on manual processes, finding digital systems burdensome.
- Training programs and financial incentives are needed to encourage adoption among healthcare workers.
Way Forward for Digital Healthcare Transformation in India
- Bridge the Digital Divide: Focus on expanding high-speed internet connectivity through initiatives like BharatNet, especially in remote and rural areas.
- Launch awareness and literacy campaigns to improve digital adoption among underserved populations.
- Strengthen Data Privacy and Security: Implement robust frameworks under the Health Data Management Policy, ensuring patient consent and secure data sharing.
- Invest in advanced cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive health information against breaches.
- Promote Interoperability and Standardization: Develop uniform standards for health data exchange, ensuring seamless integration across public and private healthcare providers.
- Enforce the adoption of standards like SNOMED and LOINC to enhance data consistency and usability.
- Encourage Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Foster collaboration between government bodies, private hospitals, and health-tech companies to scale innovative solutions.
- Use successful models like e-Sanjeevani and ABDM as templates for new initiatives.
| SNOMED CT (Systematized Nomenclature of Medicine- Clinical Terms) and LOINC (Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes) are two coding standards used in healthcare to reduce errors in patient data.
How they work
- LOINC: Codes the testing method, such as a blood culture or serum glucose test. LOINC codes are used for clinical and laboratory observations.
- SNOMED CT: Codes non-numeric answers, such as the result of a complex test.
- SNOMED CT is used for clinical medicine, including diseases, anatomy, and procedures.
|
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
- Enhance Capacity Building and Training: Provide healthcare workers with training on digital platforms and tools, reducing resistance to technology adoption.
- Offer financial incentives to hospitals and professionals for transitioning to digital systems under schemes like DHIS.
- Implementing AI in healthcare: Integrate AI and machine learning for predictive diagnostics, personalized treatments, and efficient resource allocation.
- Utilize blockchain technology for secure, tamper-proof health records and data interoperability.
- NITI Aayog is closely working with technology giant Microsoft and the medical start-up Forus Health to develop automated solutions for early detection of diabetic retinopathy.
Conclusion
India’s digital healthcare transformation holds immense potential to enhance healthcare accessibility and efficiency. With continued policy support, infrastructure development, and public-private collaborations, the country is poised to emerge as a global leader in digital health. With growing investments in digital health and technological advancements, India’s healthcare system is expected to evolve into a globally recognized model for digital transformation, setting benchmarks for other developing nations.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 23 Jan 2025
23 Jan 2025

 Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system.
Digital Health Incentive Scheme (DHIS): Incentivizes hospitals, clinics, and healthcare startups to embrace digital technologies, accelerating the transition to a paperless healthcare system. Digi Doctor: A repository containing detailed information about certified doctors, including qualifications and experience.
Digi Doctor: A repository containing detailed information about certified doctors, including qualifications and experience.