India is entering a decisive phase where Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping economic growth, governance capacity, and social inclusion.
- With large datasets, a strong digital public infrastructure, and a young workforce, India seeks to leverage AI not merely for efficiency, but for inclusive and sustainable development.
What is Artificial Intelligence?
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the ability of machines to perform tasks that normally require human intelligence
- It involves learning from data, adapting to new inputs, recognising patterns, and generating predictions or decisions.
- Modern AI systems rely on large datasets, algorithms, and Large Language Models (LLMs), and their performance improves with continuous data feedback.
| AI is no longer a niche technology; it has become a general-purpose technology, similar to electricity or the internet, with economy-wide spillover effects. |
Recent Breakthroughs in Artificial Intelligence
- Generative AI: Advanced models such as GPT-5 and Google Gemini enable AI-driven content creation across education, healthcare, and creative industries.
- Multimodal AI: Technologies like DALL·E 3 and LLaMA integrate text, image, and video processing, broadening real-world AI applications.
- AI in Drug Discovery: AlphaFold has transformed biomedical research by predicting protein structures at unprecedented scale.
- AI–Robotics: AI enables robots to learn, adapt, and make autonomous decisions, moving beyond pre-programmed tasks.
- AI for Software Development: Tools like GitHub Copilot X and Codex assist developers through automated code generation.
- Speech and Voice AI: Platforms such as ElevenLabs and VALL-E enable realistic voice synthesis for multiple industries.
- Autonomous AI Agents: Systems like AutoGPT can independently execute complex, multi-step tasks.
- AI in Climate Science: Models such as GraphCast improve the accuracy of weather and climate predictions.
| While breakthroughs are impressive, most frontier models are compute-intensive and concentrated in a few countries and corporations, raising concerns of technological dependency. |
AI Ecosystem in India at Present
- Tech sector growth: India’s technology revenues are projected to cross USD 280 billion this year.
- Employment: Over 6 million people are employed in the tech and AI ecosystem.
- Global Capability Centres: India hosts 1,800+ Global Capability Centres, including 500+ focused specifically on AI.
- Startup strength: India has about 1.8 lakh startups, and around 89% of newly launched startups last year used AI in products or services.
- Enterprise adoption: India scores 2.45/4 in the NASSCOM AI Adoption Index, indicating that 87% of enterprises are actively deploying AI solutions.
- High-value sectors: AI value is concentrated in industrial and automotive, retail and consumer goods, BFSI, and healthcare, contributing nearly 60% of overall AI value.
- Maturity scale: About 26% of Indian companies have achieved AI maturity at scale, as per a BCG survey
Global AI Competitiveness
- Rank: India placed 3rd globally in AI competitiveness (Stanford 2025 Global AI Vibrancy Tool).
- Coverage: Measures AI growth and innovation 2017–2024.
- Drivers cited: Talent, research, startups, investment, infrastructure, policy & governance.
- India is also the second-largest contributor to AI projects on GitHub, reflecting the strength of its developer ecosystem
Government Initiatives
Recognising both the transformative potential and strategic risks of AI, India has adopted a mission-mode approach.
IndiaAI Mission
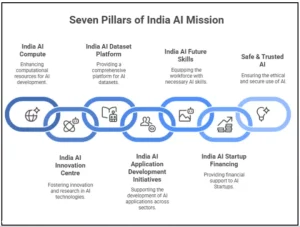
- The IndiaAI Mission is a national-level programme approved by the Union Cabinet in March 2024 to strengthen India’s AI innovation ecosystem.
- It seeks to position India as a global leader in Artificial Intelligence (AI) by promoting research, innovation, computing infrastructure, and skilling.
- Implemented by: Digital India Corporation (DIC) under Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY).
- Objectives:
-
- Develop AI Infrastructure – Establish world-class computing capabilities and data platforms.
- Promote AI Research and Startups – Foster indigenous AI technologies and innovation.
Key Components
- IndiaAI Compute Infrastructure:
-
- Establishes a high-end AI supercomputing ecosystem with over 10,000 GPUs.
- Provides AI computing resources to startups, researchers, and public institutions.
Graphics Processing Unit
- A GPU is a high-performance computer chip that can process large amounts of data quickly.
- It is critical for running AI models, handling complex computations, and enabling faster machine learning and image processing than regular processors.
|
- IndiaAI Innovation Centres (IICs):
-
- Set up centres of excellence for AI research and product development.
- Focus on strategic areas such as agriculture, healthcare, governance, and language AI.
- IndiaAI Datasets Platform: A unified data repository for AI model training with secure access and privacy safeguards.
- AIKosh curates datasets and models for training AI systems using government and non-government sources.
- It hosts 5,500+ datasets and 251 AI models across 20 sectors, enabling developers to build applications faster.
- IndiaAI Application Development Initiative:
- This pillar supports AI solutions for India-specific needs in healthcare, agriculture, climate action, governance, and assistive learning.
- By July 2025, 30 applications were approved. It also runs sector-linked hackathons such as the CyberGuard AI Hackathon.
- IndiaAI FutureSkills Program: This pillar aims to train AI professionals at all levels, from foundational to advanced.
- AI labs are being set up across Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities, with 31 labs launched via National Institute of Electronics and Information Technology (NIELIT) and industry partners.
- IndiaAI Startup Financing: Provides funding support to AI startups via grants, seed funding, and venture partnerships.
- The IndiaAI Startups Global Programme launched in March 2025 to help Indian startups expand in Europe through partnerships like Station F and HEC Paris.
- IndiaAI Responsible AI Framework: Develops ethical and governance frameworks ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency in AI systems.
- It also supports the development of an IndiaAI Safety Institute through partner institutions.
India AI Impact Summit 2026
- India will host the India AI Impact Summit in February 2026, aimed at showcasing the country’s artificial intelligence capabilities and promoting innovation across multiple sectors.
- India unveiled the event logo and key flagship initiatives.
- AI Pitch Fest (UDAAN): A global platform for AI startups, with special emphasis on women-led ventures and differently-abled innovators, to showcase scalable AI solutions.
- AI Expo: A large-scale exhibition focused on Responsible Intelligence, featuring 300+ exhibitors from India and over 30 countries, showcasing AI applications, products, and policy innovations.
- Global Innovation Challenges: Open challenges for youth, women, and diverse participants to develop AI-driven solutions addressing real-world public and developmental problems across sectors.
- Research Symposium: An international forum bringing together leading researchers from India, the Global South, and the wider global community to present cutting-edge AI research, exchange methodologies, and foster collaboration.
AI for Inclusive Societal Development – NITI Aayog Report
- The Report highlights how AI can support India’s 490 million informal workers.
- The report envisions India as a global leader in inclusive AI by 2035, where technology amplifies workers’ capabilities rather than replacing them.
- The report also stresses that AI can reduce structural inequalities by bridging deep social and economic divides, ensuring that the benefits of technology reach every citizen.
- The report proposes the Digital ShramSetu Mission, aimed at deploying frontier technologies for India’s informal sector.
- The roadmap focuses on removing barriers through voice-first AI, smart contracts for transparent payments, micro-credentials for skilling, and scalable partnerships.
Phased roadmap:
- Phase 1 (2025–2026): Mission Orientation
- Drafting of the mission charter with clear goals, timelines and measurable outcomes.
- Stakeholders from government, industry, academia and civil society will be engaged to set priorities and define objectives.
- Phase 2 (2026–2027): Institutional Setup and Governance Design
-
- Establishment of cross-sectoral governance structures, leadership roles and an implementation blueprint.
- This phase will also focus on legal, regulatory and digital infrastructure readiness, while promoting domestic innovation and public–private partnerships.
- Phase 3 (2027–2029): Pilots and Select Programme Launch
-
- Pilot projects will be rolled out in high-readiness sectors to test solutions in real-world conditions.
- Accessibility and last-mile adoption will be prioritised, supported by strong monitoring and evaluation frameworks.
- Phase 4 (2029 onwards): Nationwide Rollout and Integration
-
- Proven solutions will be scaled across states and cities.
- Local adaptation will ensure regional relevance and worker mobility across sectors. The phase will aim to institutionalise the mission and sustain its benefits at scale.
|
Other Government Initiatives and Policy Support
- Centres of Excellence for AI:
- The government established three CoEs in healthcare, agriculture, and sustainable cities, and announced a fourth CoE for education in Budget 2025.
- These CoEs act as collaborative innovation hubs connecting government, academia, and industry.
- Five National CoEs for skilling have also been created to develop a future-ready workforce
- AI Competency Framework: This framework provides structured AI training to government officials to strengthen policy design and governance readiness in the AI era.
- Sarvam AI for Aadhaar Services: Sarvam AI is working with UIDAI to enhance Aadhaar services using generative AI.
- In April 2025, it received approval to build India’s sovereign open-source Large Language Model (LLM) ecosystem to improve public service delivery and digital trust.
- Bhashini for Digital Inclusion
- Bhashini enables translation and speech tools across Indian languages to make digital services easier for citizens.
- In June 2025, Bhashini and CRIS signed an MoU to deploy multilingual AI solutions in railway platforms.
- Bhashini supports 20 languages, and integrates 350+ AI models.
- BharatGen AI
- Launched on 2 June 2025, BharatGen AI is India’s first government-funded multimodal LLM.
- It supports 22 Indian languages and enables text, speech, and image understanding using India-specific datasets.
AI in Everyday Life (In India)
- Healthcare:
- Clinical support: AI improves early diagnosis, scan analysis, and personalised treatment. AI-enabled telemedicine connects rural patients to specialists.
- India’s participation in HealthAI and collaborations involving ICMR and IndiaAI promote safe and ethical healthcare innovation.
- Agriculture:
- Decision support: Weather prediction, pest alerts, irrigation/sowing timing.
- Government tool: Tools like Kisan e-Mitra virtual assistant for scheme access (e.g., PM-Kisan).
- Surveillance: National Pest Surveillance System & Crop Health Monitoring using satellite, weather inputs and soil analysis.
- Education & Skilling
- CBSE integration: CBSE offers AI learning through a module from Class VI and an optional AI subject from Class IX to XII.
- DIKSHA integrates AI features like keyword search and read-aloud tools.
- YUVAi trains students from Classes 8 to 12 across eight themes such as Krishi, Aarogya, Shiksha, and Smart Cities.
- Governance & Justice Delivery:
- e-Courts Phase III: AI tools are being integrated under e-Courts Phase III for translation, scheduling, administrative efficiency, and chatbots.
- Vernacular access: High Courts are translating judgments into regional languages, making justice delivery more inclusive.
- Weather & Climate Services
-
- Forecasting: IMD uses AI for forecasting rainfall, lightning, fog, fires, and cyclone intensity.
- Cyclone estimation: Tools like Advanced Dvorak Technique support cyclone assessment.
- MausamGPT is being developed as a weather advisory chatbot.
Key Opportunities AI Offers for India’s Economic Growth
- Productivity-Led Economic Growth:
- AI can significantly raise productivity across manufacturing, services, and MSMEs by automating repetitive tasks, improving decision-making, and optimising supply chains.
- For a labour-abundant economy like India, AI offers a pathway to “more output per worker” without necessarily reducing employment.
- AI-driven automation improves efficiency in agriculture; Precision farming, AI-enabled supply chains, and smart production systems reduce costs and boost output.
- AI could add $1.7 trillion to India’s economy by 2035.
- Expanding IT and Knowledge Services
- Indian IT firms are leveraging AI in cloud services, cybersecurity, and enterprise solutions.
- The global AI services market is projected to reach $297 billion by 2027, with companies like TCS, Infosys, and Wipro leading large-scale AI projects.
- AI as a Governance Multiplier:
- AI enables faster, data-driven governance by improving targeting, monitoring, and service delivery.
- Predictive analytics can reduce leakages in welfare schemes, while AI-powered grievance redressal can enhance administrative responsiveness.
- Inclusion Through Language and Voice AI
- India’s linguistic diversity makes text-based digital governance exclusionary.
- Voice-first and multilingual AI systems, such as Bhashini and BharatGen, allow citizens to access services in their native languages.
- This positions AI as an instrument of digital inclusion, especially for women, the elderly, and informal workers.
- Climate Resilience and Disaster Management
- AI improves weather forecasting, disaster prediction, and early-warning systems for floods, cyclones, heatwaves, and forest fires.
- In a climate-vulnerable country like India, such predictive capacity can reduce loss of life and economic damage.
- Healthcare Access at Scale
- AI supports early diagnosis, personalised treatment, and remote healthcare delivery.
- Telemedicine and AI-assisted diagnostics can bridge the rural–urban healthcare divide and reduce pressure on tertiary hospitals.
- Global AI Services and Innovation Hub
-
- India’s strength in software services, cost-efficient talent, and application-layer innovation positions it as a global AI services hub.
- Export of AI solutions tailored for developing countries can become a new source of strategic and economic influence.
Challenges Posed by AI to India’s Economy
- Data Privacy and Trust Deficit
- AI systems rely on large volumes of personal and behavioural data.
- Weak consent mechanisms, low digital literacy, and enforcement gaps under the Digital Personal Data Protection Act, 2023, risk eroding public trust.
- Without trust, AI adoption in governance and public services will face resistance.
- Digital Divide and Uneven Access
- AI adoption remains concentrated in urban, high-income, and formal sectors.
- Limited internet access, device availability, and digital skills in rural and informal settings restrict inclusive AI diffusion. This risks deepening existing social and regional inequalities.
- Concentration of Compute and Capital
- Advanced AI development requires expensive GPUs, cloud infrastructure, and capital.
- Dependence on Foreign AI Technologies: India’s reliance on AI technologies from global firms such as Google, Microsoft, and OpenAI raises concerns over technological sovereignty, foreign exchange outflows, and strategic dependence.
- This creates entry barriers for startups, researchers, and public institutions, limiting innovation diversity.
- Skill Polarisation and Labour Displacement Risks
- India’s skilling ecosystem remains fragmented and biased towards formal sectors.
- Skill Deficit: India’s workforce lacks adequate AI-focused training. According to Economic Survey 2023-24, Only 51% graduates employable
- Without timely reskilling, AI may widen income inequality and job insecurity.
- Disruption of Traditional Business Models
- AI-powered digital platforms are reshaping retail, agriculture, and small-scale manufacturing.
- Local traders, artisans, and small producers are losing competitiveness to AI-enabled e-commerce platforms and automated supply chains, threatening the sustainability of small businesses that form the backbone of the economy.
- Algorithmic Bias and Lack of Explainability
- AI models trained on biased or incomplete datasets can reproduce social discrimination.
- Opaque “black-box” systems reduce accountability in critical sectors like justice, policing, and welfare delivery.
- This challenges constitutional values of equality and due process.
- Cybersecurity Risks
- As traditional sectors integrate AI, their exposure to cyber threats increases. Many small businesses lack the technical capacity to secure AI systems and data.
- As per the information reported to and tracked by CERT-In, there were 20,41,360 cyber security incidents in India in 2024, raising concerns over trust, data protection, and resilience of AI adoption in conventional industries
- Regulatory and Institutional Lag
-
- AI evolves faster than laws, standards, and oversight mechanisms.
- India currently lacks a unified AI regulatory framework and independent audit institutions.
- Delayed regulation risks both over-regulation and under-protection.
Will AI Lead to Unemployment?
- AI is often viewed as a job threat, but it is also generating new opportunities.
- NASSCOM’s report “Advancing India’s AI Skills” (August 2024) estimates that India’s AI talent pool will grow from about 6–6.5 lakh professionals to 12.5 lakh by 2027.
- Demand is expanding in areas such as data science, AI engineering, analytics, and data curation
- To prepare the workforce, MeitY launched FutureSkills PRIME for reskilling in 10 emerging technologies.
- By August 2025, over 18.56 lakh candidates had signed up, with more than 3.37 lakh completing courses
|
Steps India Can Take to Harness Artificial Intelligence
Addressing these challenges requires a coordinated strategy spanning infrastructure, skills, governance, and inclusion.
- Build Sovereign and Scalable AI Infrastructure:
- India must invest in public AI compute capacity, including GPUs, cloud infrastructure, and high-performance computing accessible to startups, academia, and states.
- This reduces dependence on foreign Big Tech and prevents concentration of AI capabilities in a few private actors.
- Strengthen Data Governance and Data Quality
- AI performance depends on the quality, diversity, and representativeness of data.
- India should standardise data collection, anonymisation, interoperability, and consent mechanisms across sectors.
- Platforms like AIKosh must prioritise trustworthy, bias-checked, and India-specific datasets.
- Develop a Skilled and Adaptive Workforce
- India should move beyond narrow technical skilling to AI literacy across society.
- This includes integrating AI concepts in school education, vocational training, and reskilling programmes for informal and gig workers.
- The focus must be on human–AI collaboration, not just coding skills.
- Promote Application-Driven and Problem-First AI
- India’s comparative advantage lies in applying AI to real developmental challenges.
- Policy should incentivise AI solutions for agriculture, healthcare, climate resilience, education, and governance.
- This ensures that AI adoption remains context-sensitive and socially relevant, rather than technology-driven alone.
- Ensure Responsible and Ethical AI Deployment
- India must embed principles of fairness, transparency, accountability, and human oversight into AI systems from the design stage.
- Independent audits, explainability requirements, and grievance redressal mechanisms should be institutionalised.
- Support Startups, MSMEs, and Innovation Ecosystems
- Targeted funding, regulatory ease, and access to public computers can enable startups and MSMEs to innovate using AI.
- Public procurement policies can be leveraged to create early markets for Indian AI solutions. This strengthens domestic innovation and employment generation.
- Develop AI-Based Climate Resilience
- AI can support climate adaptation through real-time monitoring of air quality, water resources, and renewable energy.
- Integrating AI into the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC) can improve disaster forecasting and energy efficiency via smart grids.
- Use AI in Tourism Development
-
- AI-powered tourism platforms can personalise travel experiences, manage tourist flows, and promote heritage.
- Integrating AI with initiatives like Dekho Apna Desh can strengthen domestic tourism through smart services and immersive technologies.
Conclusion
If governed wisely, Artificial Intelligence can become India’s most powerful development multiplier, enhancing state capacity, empowering citizens, and sustaining long-term growth without compromising equity, trust, or democratic values.
![]() 31 Dec 2025
31 Dec 2025


