Context:
This article is based on the news “Two years on, global support for Ukraine won’t falter” which was published in the Indian Express. Two years into the Russia Ukraine War, there appears little signs of de-escalations and ceasefire.
Current Status of Russia Ukraine War
-
Russia Ukraine War: Multidimensional Sanctions on Russia
-
-
On Russia’s Financial Sector and Payment Systems
- Mir Payment System: Sanctions are targeted to disrupt Russia’s efforts to evade earlier sanctions and maintain international financial transactions.
- Russian Banks and Financial Institutions: Sanctions are imposed on over a dozen entities including banks, investment firms, venture capital funds, and fintech companies, notably SPB Bank.
-
-
Energy Sector and Military Industrial Base
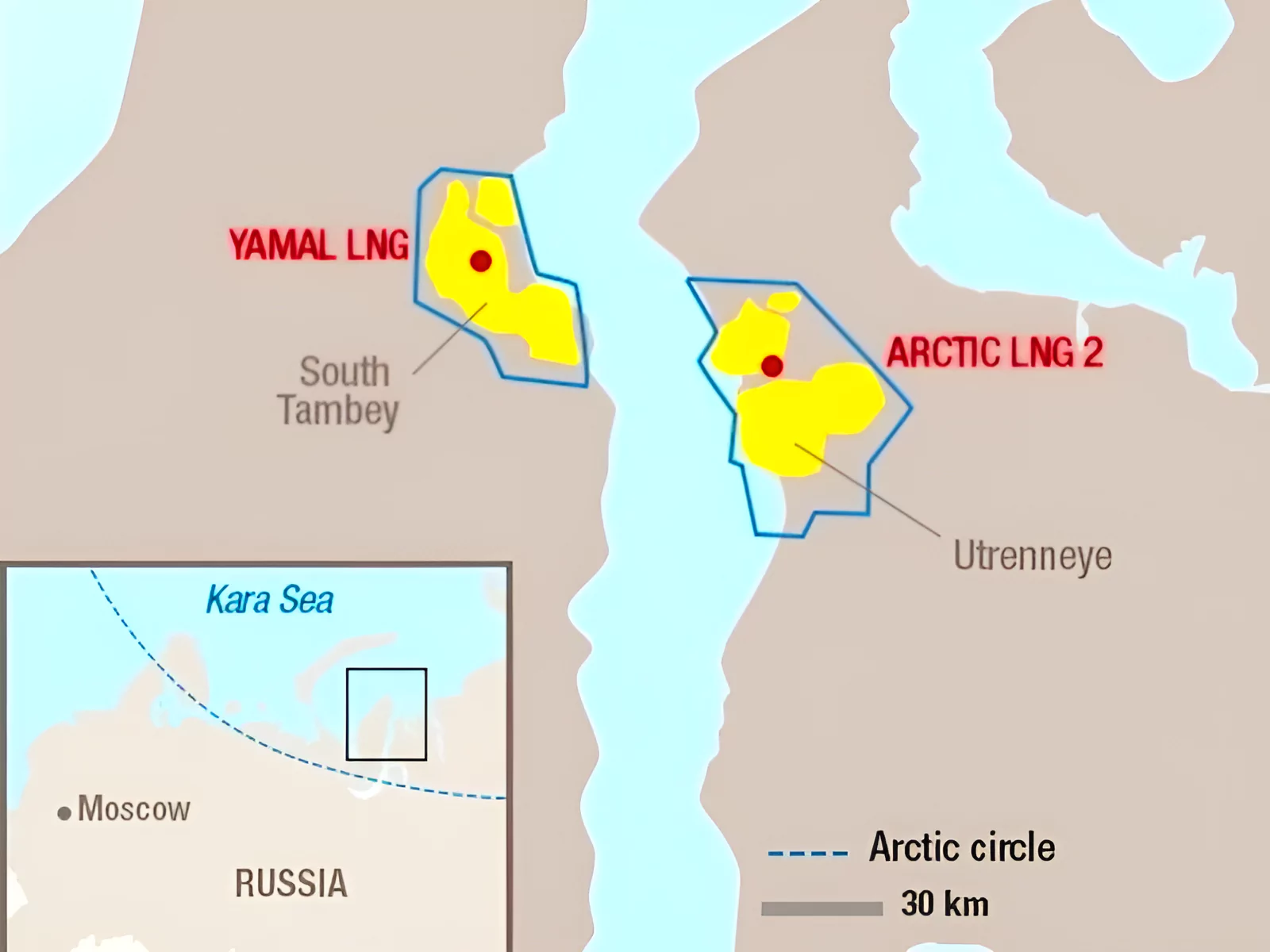
- Arctic-2 LNG Project: Sanctions have been targeted on specific entities involved in the development and operation of Arctic-2 LNG Project. It aims to cut off resources for future energy production.
- Sanctions Evasion Networks: Sanctions are imposed on entities based in China, Turkey, UAE, Kazakhstan, and Liechtenstein for facilitating Russia’s evasion of sanctions and supporting its military infrastructure.
-
Human Rights Violations During Russia Ukraine War
- Officials Linked to Navalny’s Death: Sanctioning of Russian Federal Penitentiary Service officials connected to the opposition leader’s death.
- Alexei Navalny is a prominent Russian opposition leader, anti-corruption activist, and politician.
- Forcible Transfer of Ukrainian Children: Targeting individuals involved in the deportation and indoctrination of Ukrainian children to camps in Russia, Belarus, and Crimea.
-
Russia Ukraine War: Military and Financial Support to Ukraine
-
- US Support: The US has already sent Ukraine $111 billion in weapons, equipment, and humanitarian assistance.
- EU Support: European Union has recently approved a new €50 billion package for Ukraine. In past two years EU has provided more than €144 billion as aid to Ukraine
- Security Agreements: Germany and France signed security agreements with Ukraine for the next 10 years, with very significant announcements of additional military aid in 2024.
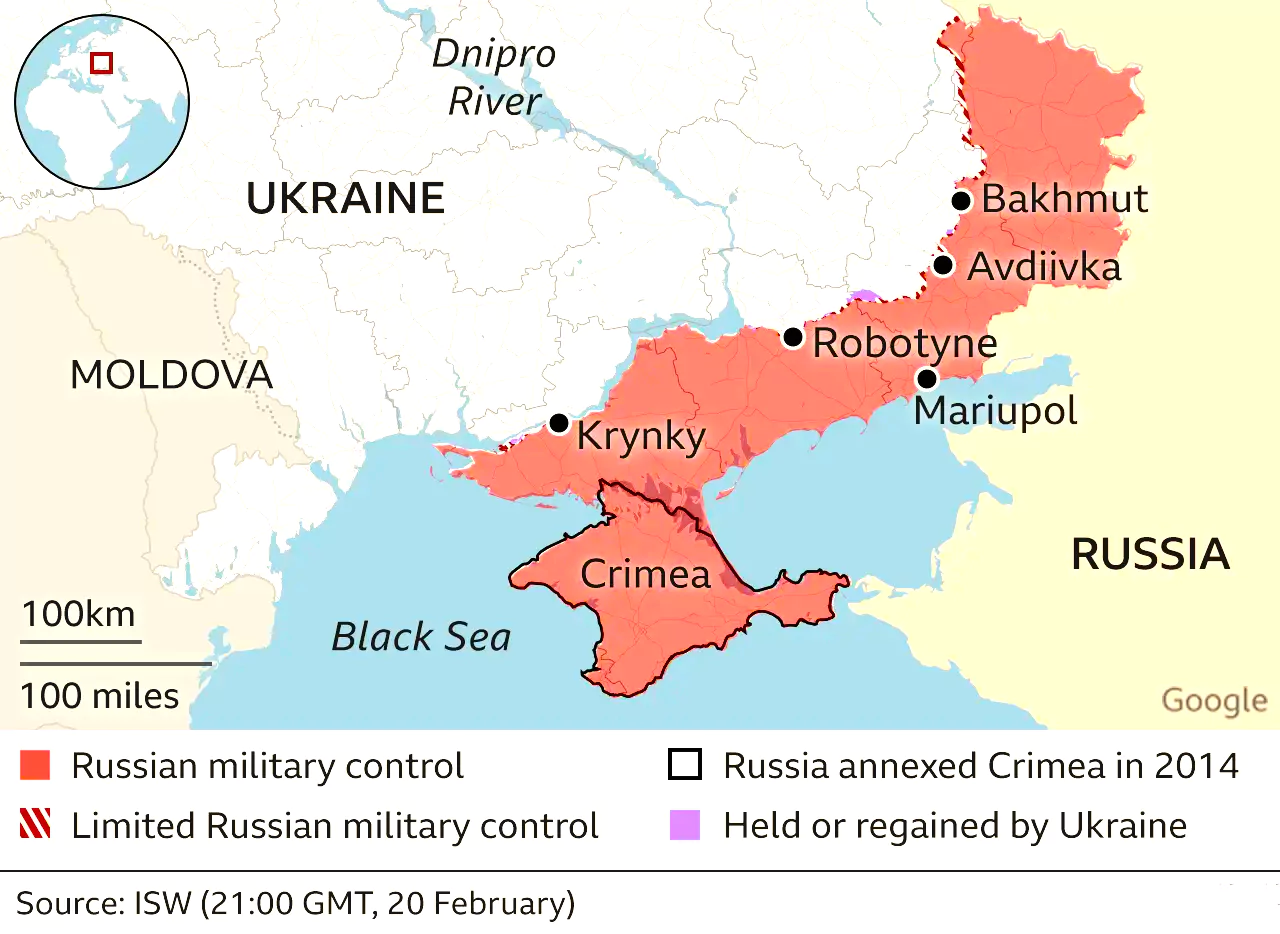
- Russia’s hidden mobilization: Russian forces have slowly inched forward, capturing the town of Avdiivka recently after a fierce, months-long battle.
- Ukraine has inflicted heavy losses on Russia in recent fighting around the eastern city of Avdiivka — including 13,000 casualties and over 220 combat vehicles lost.
- Military Stalemate: The Russia Ukraine War has morphed into a grinding war of attrition, with neither side making significant territorial gains in recent months.
- Russia controls about 20% of Ukrainian territory, mainly in the east and south.
- Humanitarian Crisis: The Russia Ukraine War has caused a devastating humanitarian crisis, with millions displaced internally and soldiers killed.
- 315,000 soldiers wounded or killed on the Russian side, while 70,000 Ukrainian soldiers had been killed and between 100,000 and 120,000 wounded, as per estimates.
Global Impact of the Russia Ukraine War in Two Years:
-
Humanitarian Crises During Russia Ukraine War
- Loss of Lives: As per UN, more than 10,000 civilians have been killed and nearly 20,000 others wounded. Nearly 45,000 Russians have been killed in action since February 2022.
- Displacement: The UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) estimates over 8 million Ukrainian refugees have fled the country, with over 13 million internally displaced.
-
Economic Impact During Russia Ukraine War
- Global Inflation in Food and Energy Markets: The war has disrupted global supply chains, particularly for wheat, oil, and gas, contributing to global inflation and supply chain challenges.
- Sanctions and Economic Disruptions: Sanctions against Russia and the damage to Ukraine’s infrastructure have further strained global economic stability.
- Loss to Ukraine: Ukraine’s economic output is now at a fraction of its pre-war levels. In the first year of the conflict, the country lost 30-35% of GDP leading to largest recession in Ukraine.
- Its GDP is projected to grow in 2023, if only by 0.5%.
- Poverty in Ukraine has soared from 5.5% of the population to 24.2% in 2022, according to the World Bank, pushing 7.1 million more people into poverty.
- Food Security: Ukraine and Russia were the biggest producers in agriculture and food globally. War between these nations has caused issues of food security globally.
- Loss to Russia: Russia’s economy contracted by 1.2% last year and €300 billion of Russian Central Bank reserves are blocked in the EU, other G7 countries.
- Around €20 billion of assets of more than 1,500 sanctioned persons and entities have been frozen.
-
Geopolitical Impact During Russia Ukraine War
-
- Strengthening of NATO: North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) has been strengthened by Russia’s actions. New countries like Finland and Sweden have joined NATO, and the length of Russian borders with NATO has actually gone up.
- Global Trust Deficit: The trust deficit between Russia and the West is at an-all time high. Smaller countries have started looking for military arrangements with militarily powerful nations.
- Failure of UN: The collapse of global rule-based order and the failure of the UN Security Council to achieve ceasefire due to veto by permanent members has raised questions over UN’s role.
- Russia-China Axis: The economic sanction of Russia and China by a common enemy, the USA has brought the two nations politically and economically closer.
- Focus on National Interest: The Israel-Gaza war coupled with Russia Ukraine war has brought forth the practical aspect of diplomatic relations where national interests overshadow the diplomatic positions over issues.
Russia Ukraine War: Impacts on India
- India’s Balanced Relations: Indian policymakers walked on a diplomatic tightrope in balancing the relationship with the West and Russia. They did not join the chorus of condemnation of Russia which paid dividends while evacuating students from Ukraine.
- Access to Russian Crude Oil: India’s practical positions highlighting national interest ensured availability of Russian crude oil and helped contain price shocks.
- Growing interest in the Indo-Pacific and the Quad: There has been a growing pivot towards focus on Indi-Pacific security. This has put India in a strategic position to be a “Net Security Provider”.
- Strengthening China-Russia Relations: Closer Russia-China relations becomes a new challenge for Indian diplomacy.
Future of the Russia Ukraine War
- No visible end to the Russia Ukraine War: The stalemate between Ukraine and Russia, both on the war ground and negotiation tables is resulting in no visible end to the war.
- Contradictory Peace Plans: Ukraine’s peace plans are fundamentally premised on a return to the 1991 borders, which is not acceptable to Russia.
- Russia, in addition to Ukraine’s military neutrality, is unlikely to cede territories it has already constitutionally incorporated – Crimea (in 2014), and more recently, Donetsk, Kherson, Luhansk, and Zaporizhzhya.
Conclusion:
It is imperative for all stakeholders to prioritize dialogue and return to the negotiation table. The escalation of hostilities and violence serves no one’s interests and only exacerbates suffering and instability.
- Furthermore, upholding international principles and jurisprudence is paramount, particularly concerning the safety of civilians and civilian infrastructure during conflicts. Parties involved must adhere to these standards to minimize civilian casualties and protect vital infrastructure.
Also Read: India’s Diplomacy With West Asia Countries
| Prelims PYQ (2019):
Consider the following pairs: Sea Bordering country
1. Adriatic Sea : Albania
2. Black Sea : Croatia
3. Caspian Sea : Kazakhstan
4. Mediterranean Sea : Morocco
5. Red Sea : Syria
Which of the pairs given above are correctly matched?
(a) 1, 2 and 4 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b) |
![]() 24 Feb 2024
24 Feb 2024


