Recently, the Union Cabinet approved the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS), which will be effective from April 1, 2025.scheme
- Maharashtra has become the first state to offer its employees the UPS.
About the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)
The UPS pension scheme will provide government employees with assured pensions after retirement.
- Need: Over the last few years, the political opposition showed dissatisfaction with the New Pension Scheme (NPS).
- The governments in Himachal Pradesh (2023), Rajasthan and Chhattisgarh (2022) and Punjab (2022) have reverted to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS).
- Concern with the NPS:
- Market-based: The pension payout depends on the market returns on the corpus, which is mostly invested in federal debt.
- It also leaves the employees with less disposable income as they too have to contribute under this scheme.
- Fund Management: The public is of the view that their fund would not be secure in the hands of fund managers, and their pensions may be reduced.
- Lack of Flexibility: Government employees are obligated to contribute 10% of their monthly pay.
- Mandatory Annuity Plans: The NPS requires a mandatory 40% allocation of maturity proceeds to purchase an approved annuity plan, which entails locking in hefty premiums for life and yielding meager returns of 5-5.5%, subject to taxation.
- Background: Due to persistent demands for a return to the Old Pension Scheme (OPS), a committee under the chairmanship of then Finance Secretary T V Somanathan in 2023 was constituted.
- This committee held more than 100 meetings with different organisations and states. The recommendations of this committee have now resulted in the announcement of the UPS.
- Availability: Currently, the new scheme is for central government employees, but states can adopt it as well.
- Eligibility: Applicable to all those who have retired under the NPS from 2004 onwards.
-
- NPS retirees will get arrears adjusted with whatever they have already drawn under the NPS.
- Term in Service: Employees who have completed a minimum of 10 years of service.
- However, the full benefits of the scheme, including the assured pension, apply to those with at least 25 years of service.
- Existing Pension Holders: The scheme is optional for existing employees under the NPS and those opting for Voluntary Retirement Scheme (VRS) under NPS.
- Future Employees: They will also have the option to join the UPS. However, once an employee opts into the UPS, the decision is final and cannot be reversed.
- Contribution: The government will increase its contribution to the pension fund from 14% to 18.5%. This increase does not affect the employee’s contribution, which remains unchanged.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Key Features of the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)
According to the government’s notification, the UPS has five key features:
- Assured Pension: 50% of the average basic pay drawn over the last 12 months prior to superannuation for a minimum qualifying service of 25 years. This pay is to be proportionate for lesser service periods upto a minimum of 10 years of service.
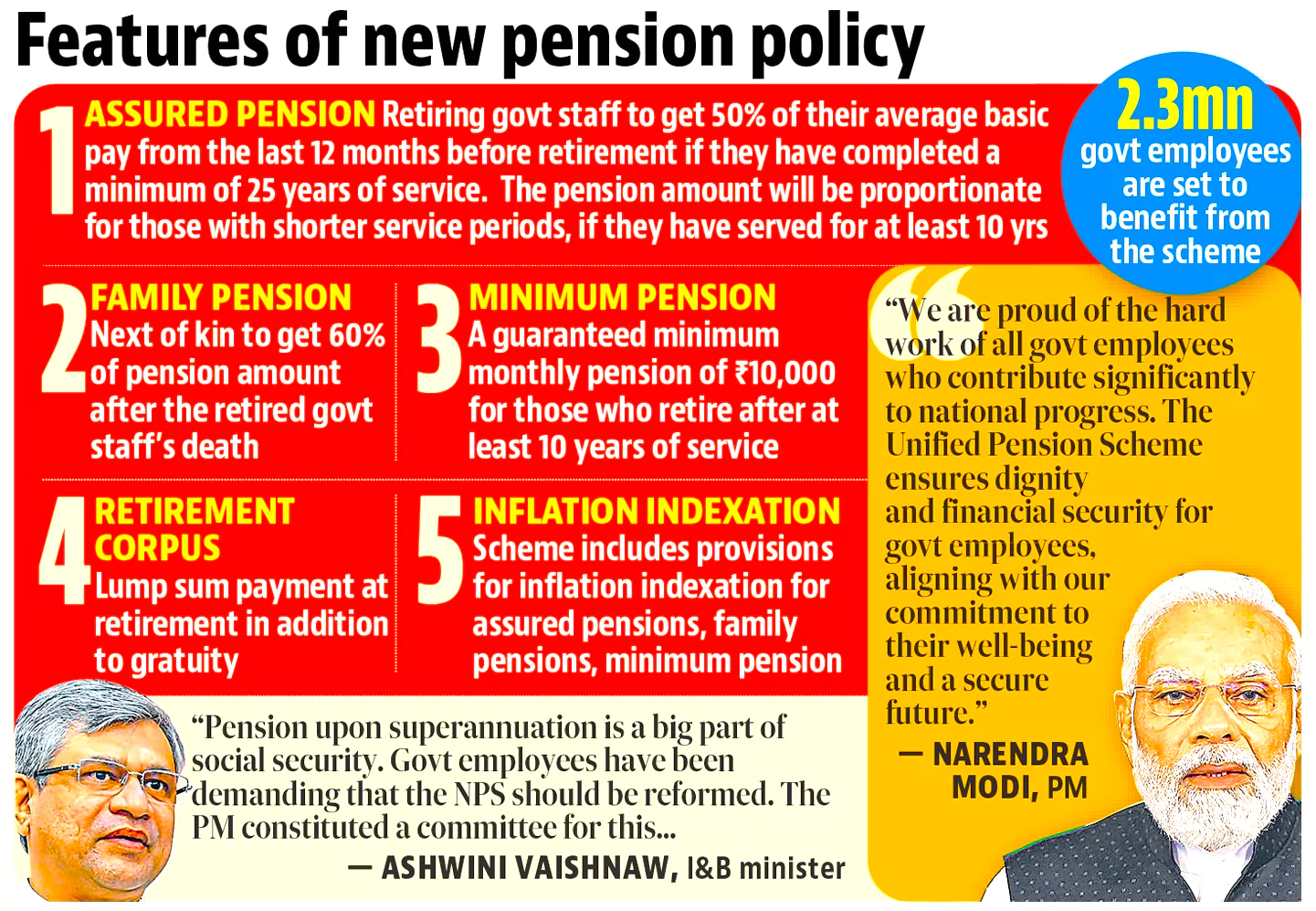 Assured Family Pension: 60% of pension of the employee immediately before her/his demise.
Assured Family Pension: 60% of pension of the employee immediately before her/his demise.- Assured Minimum Pension: Rs 10,000 per month on superannuation after minimum 10 years of service.
- Inflation Indexation: On assured pension, on assured family pension and assured minimum pension.
- Dearness Relief based on All India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW) as in case of service employees.
- Inflation indexation: A technique that adjusts income payments using a price index to maintain the purchasing power of the public in the face of inflation.
- It can also be used to adjust the purchase price of an investment to account for inflation.
- Lump-Sum Payment at Superannuation: This will be in addition to gratuity, and will be calculated as 1/10th of the monthly emolument (pay plus dearness allowance) on the date of superannuation for every six months of service completed.
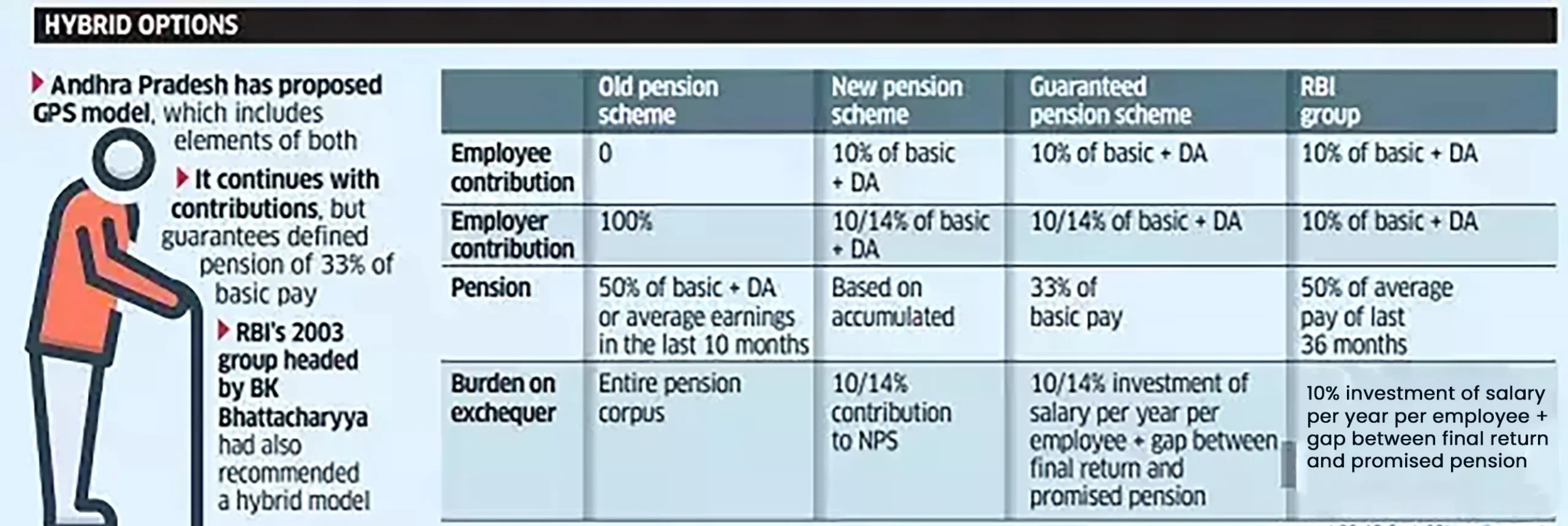
Key Comparisons between Unified Pension Scheme (UPS), New Pension Scheme (NPS) and Old Pension Scheme (OPS)
| Features |
UPS |
NPS |
OPS |
| Pension Amount |
- 50% of average basic pay over the last 12 months before retirement
- For service between 10-25 years, proportional
|
- Market-linked, depends on contributions and market performance
|
- 50% of the last drawn salary
- Increases with DA hikes
|
| Family Pension |
- 60% of the employee’s pension upon their death
|
- Depends on accumulated corpus and annuity plans at retirement
|
- Continued pension benefits to family after retiree’s death
|
| Employee Contribution |
|
|
- None. Government bears the entire cost
|
| Government Contribution |
|
|
- Entire cost borne by the government
|
| Inflation Indexation |
- Yes, based on All India Consumer Price Index for Industrial Workers (AICPI-IW)
|
- Not applicable; pension is market-linked
|
- Yes, pension amount increases with DA hikes
|
Key Benefits of the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)
The Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) provides following benefits:
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
- Striking a Balance: The UPS represents a policy shift, aiming to balance fiscal responsibility with the need for a secure and predictable pension system for government employees.
- It offers a defined benefit pension similar to the OPS, while retaining the contributory nature of the NPS.
- Employees will receive a “defined benefit” — a pension equivalent to 50% of their average basic pay drawn in the year prior to retirement.
- To finance this, there will also be a “defined contribution” — the government will now contribute 18.5% of the basic salary of employees.
- Guaranteed Benefits: In the UPS, the government’s contribution may be adjusted periodically based on actuarial assessments to ensure the scheme remains fiscally sustainable.
- While the NPS will continue to be an option, the UPS is expected to be more attractive due to its guaranteed benefits and reduced exposure to market risks.
- Fiscally Prudent: The UPS is more fiscally prudent. It remains in the same architecture of a contributory funded scheme.
- The OPS is an unfunded non-contributory scheme, while the UPS is a funded contributory scheme.
- It is to give an assurance and not leave things to vagaries of market forces. The structure of UPS has the best elements of both OPS and NPS.
- Inclusivity: The UPS will be implemented by the Central Government, directly benefiting approximately 23 lakh Central Government employees.
- The scheme’s architecture is designed for adoption by State Governments as well. If fully adopted, the UPS could benefit over 90 lakh government employees currently under the NPS across India.
- Portability: The UPS would be the portability of benefits, which means that workers can carry their pension benefits with them across different jobs and geographical locations.
- It is making the system more adaptable to the modern and mobile workforce.
- Others:
- Uniformity: As the scheme would be administered by a centralised authority, it would help in ensuring uniformity in the implementation and management of benefits.
- Enhanced Benefits: By pooling resources and managing funds more efficiently, it provides enhanced pension benefits to retirees, ensuring a more secure and stable retirement.
- Flexibility: Allows choice between UPS and NPS based on personal financial needs.
- Financial Literacy: As part of the initiative, there would be efforts to improve financial literacy among workers, particularly those in the informal sector, to make informed decisions about their retirement planning.
Challenges with the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS)
Following are the few challenges with the Unified Pension Scheme (UPS) that need to be considered:
- Transition Process: Merging different schemes could be complex and requires careful planning to ensure that existing beneficiaries are not disadvantaged.
 Funding and Sustainability: Ensuring the financial sustainability of the UPS is critical. This includes determining contribution rates, government support, and investment strategies to ensure long-term viability.
Funding and Sustainability: Ensuring the financial sustainability of the UPS is critical. This includes determining contribution rates, government support, and investment strategies to ensure long-term viability.- Legal and Regulatory Framework: The implementation of the UPS would require significant changes to the existing legal and regulatory framework governing pension schemes in India.
- Higher burden on the Exchequer: The UPS set to provide an assured pension to 23 lakh eligible central government employees, will bring an additional financial burden of Rs 6,250 crore per year to the exchequer.
- A return to defined benefits, which essentially involves providing generous benefits, runs the risk of not just increasing the burden on the exchequer, but also further constraining the space for spending on other avenues.
- In 2023-24, the central and state governments had allocated Rs 2.3 lakh crore and Rs 5.2 lakh crore respectively for pensions.
- Put together, for all states and Union Territories, allocations to pension were estimated at 12% of their revenue expenditure in 2023-24.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Conclusion
Social security for older people must cover the widest segment of the population. Government employees are an organised pressure group, and have managed to restore their guaranteed pension. The UPS is a significant step, however the government should consider that all significant reforms must come with broad political consensus.
![]() 26 Aug 2024
26 Aug 2024

 Assured Family Pension: 60% of pension of the employee immediately before her/his demise.
Assured Family Pension: 60% of pension of the employee immediately before her/his demise. Funding and Sustainability: Ensuring the financial sustainability of the UPS is critical. This includes determining contribution rates, government support, and investment strategies to ensure long-term viability.
Funding and Sustainability: Ensuring the financial sustainability of the UPS is critical. This includes determining contribution rates, government support, and investment strategies to ensure long-term viability.