Recently, the Union finance minister presented the Union Budget for FY 2025-26 in the Lok Sabha.
- The Union Budget outlines key economic policies, reforms, and allocations that will shape India’s growth trajectory.
- Theme of Union Budget 2025-26: “Sabka Vikas” stimulating balanced growth of all regions.
- India’s Union Budget for 2025-26 has set the total government expenditure at Rs 50.65 lakh crore, reflecting an increase from Rs 47.16 lakh crore in the revised estimates for 2024-25.

Budgetary Allocations & Estimates
Revised Estimates (2024-25)
- Total Receipts (Excluding Borrowings): ₹31.47 lakh crore
- Net Tax Receipts: ₹25.57 lakh crore
- Total Expenditure: ₹47.16 lakh crore
- Capital Expenditure: ₹10.18 lakh crore
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Budget Estimates (2025-26)
- Total Receipts (Excluding Borrowings): ₹34.96 lakh crore
- Net Tax Receipts: ₹28.37 lakh crore
- Total Expenditure: ₹50.65 lakh crore
| Where Rupee comes from |
Where Rupee goes to |
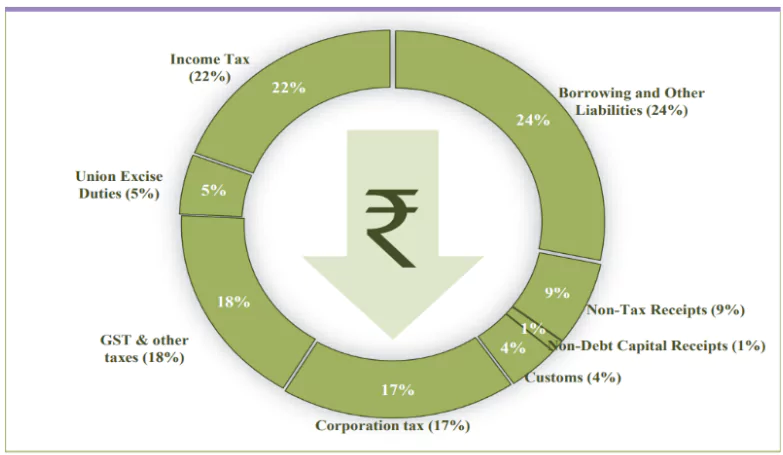 |
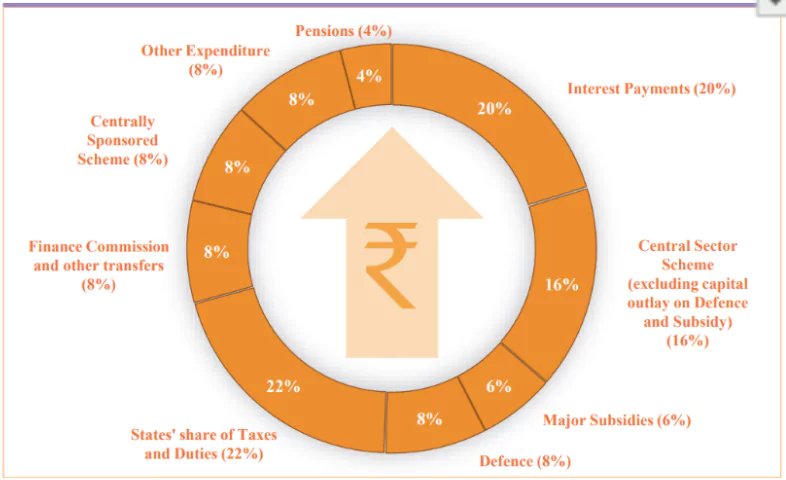 |
Fiscal Consolidation: Strengthening Economic Stability

- Committed to Fiscal Discipline: The Government aims to maintain a sustainable fiscal deficit, ensuring Central Government debt remains on a declining trajectory.
- Fiscal Deficit Targets:
-
- Revised Estimate (2024-25): 4.8% of GDP
- Budget Estimate (2025-26): 4.4% of GDP
Key Highlights of Union Budget 2025-26
The Finance Minister started presenting the budget by quoting Telugu poet and playwright Shri Gurajada Appa Rao’s famous saying, “A country is not just its soil; a country is its people” emphasizing people centric budgets.
Aspiration of Viksit Bharat:
- Zero-poverty;
- Hundred percent good quality school education;
- Access to high-quality, affordable, and comprehensive healthcare;
- Hundred per cent skilled labour with meaningful employment;
- Seventy per cent women in economic activities; and
- Farmers making our country the ‘food basket of the world’.

The Union Budget 2025-2026 promises to continue Government’s efforts to accelerate growth, secure inclusive development, invigorate private sector investments, uplift household sentiments, and enhance spending power of India’s rising middle class.
Focus Areas of Budget
The Budget proposes development measures focusing on the Poor (Garib), Youth, Farmer (Annadata) and Women (Nari).
The Budget aims to initiate transformative reforms in Taxation, Power Sector, Urban Development, Mining, Financial Sector, and Regulatory Reforms to augment India’s growth potential and global competitiveness
Engines for journey towards Viksit Bharat
The Union Budget highlights that Agriculture, MSME, Investment, and Exports are engines in the journey to Viksit Bharat using reforms as fuel, guided by the spirit of inclusivity.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
1st Engine: Agriculture
- Prime Minister Dhan-Dhaanya Krishi Yojana: Covers 100 districts for productivity growth, crop diversification, post-harvest storage, irrigation, and credit access.
- Rural Prosperity and Resilience Programme: Aims to tackle underemployment through skilling, investment, technology, and economic revitalization. Focuses on rural women, young farmers, and small/marginal farmers.
- Mission for Aatmanirbharta in Pulses: A 6-year initiative targeting Tur, Urad, and Masoor, with NAFED and NCCF ensuring procurement for the next 4 years.

- Agricultural Productivity Measures: Includes a Comprehensive Programme for Vegetables & Fruits, National Mission on High Yielding Seeds, and a five-year Mission for Cotton Productivity.
- Kisan Credit Card Loan Limit Increase: Raised from ₹3 lakh to ₹5 lakh under a Modified interest subvention scheme (MISS)
- Makhana Board for Bihar: To enhance production, processing, and value addition of makhana.
- India Post as Rural Growth Facilitator:
- Rural community hub colocation
- Institutional account services;
- DBT, cash out and EMI pickup
- Credit services to micro enterprises
- Insurance; and
- Assisted digital services.
2nd Engine: MSMEs
- MSMEs as Growth Drivers: Contribute 45% of exports; investment and turnover limits raised to 2.5x and 2x, respectively.
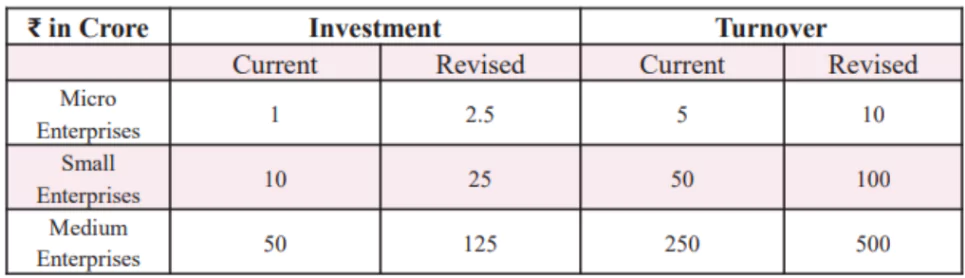
- Significant enhancement of credit availability with guarantee cover
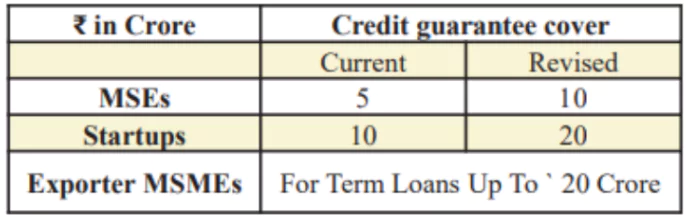
- Credit Cards for Micro Enterprises: Customised Credit Cards with a ₹ 5 lakh limit for micro enterprises registered on Udyam portal.
- In the first year, 10 lakh such cards will be issued.
- New Entrepreneur Scheme: Offers term loans up to ₹2 crore for 5 lakh women, Scheduled Caste, and Scheduled Tribe first-time entrepreneurs over five years.
- Toys Manufacturing Promotion: A new scheme to establish India as a global hub for ‘Made in India’ toys.
- National Manufacturing Mission: Supports MSMEs alongside medium and large industries to promote “Make in India”
3rd Engine: Investment
Investment in People
- Atal Tinkering Labs : 50000 new ATL in government schools.
- Broadband connectivity for rural government schools and primary health centers under Bharatnet.
- Bharatiya Bhasha Pustak Scheme for digital Indian-language books.
- 5 National Centres of Excellence for skilling with global partnerships.
- ₹500 crore for AI Centre of Excellence for education.
- Gig worker’s identity cards, e-Shram registration, and healthcare under PM Jan Arogya Yojana.
- PM SVANidhi : To be revamped with enhanced loans from banks , UPI linked Credit Card and Capacity Building Support.
- Saksham Anganwadi and Poshan 2.0
- Day Care Centres in all Districts.
- Expansion of Capacity in IITS
- Expansion of Medical Education: 10,000 additional seats with goal of Adding 75000 seats in next 5 years
Investing in People , Economy and Innovation
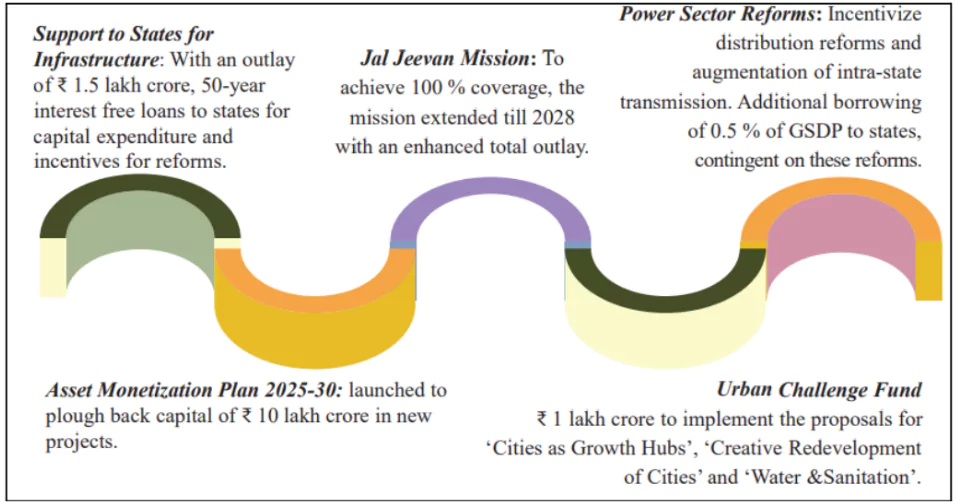
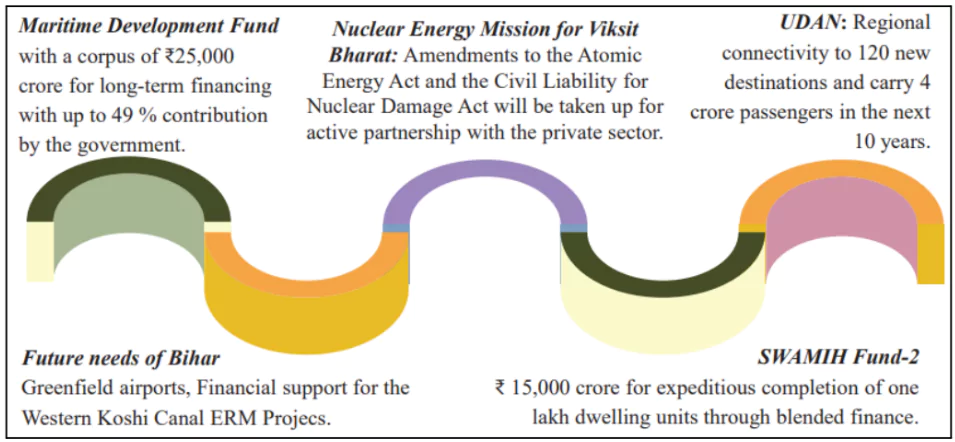
Investment in Innovation
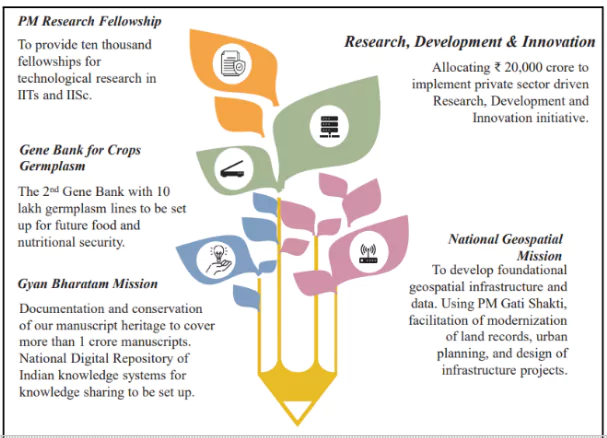
- ₹20,000 crore allocated for private-sector-driven R&D and innovation.
- National Geospatial Mission for urban planning infrastructure.
- Gyan Bharatam Mission for documenting 1 crore manuscripts and a National Digital Repository of Indian Knowledge Systems.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Employment Generation through Tourism
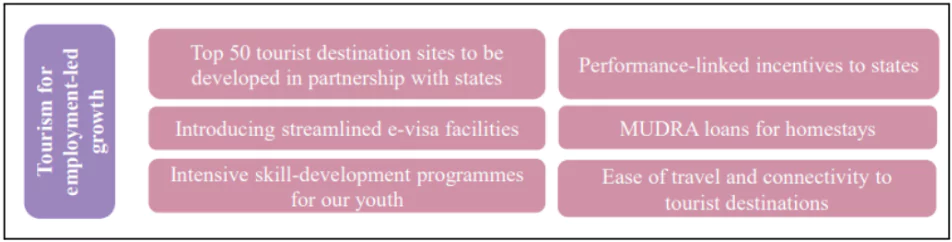
4th Engine: Exports
- Export Promotion Mission: Collaborative effort by the Ministries of Commerce, MSME, and Finance to help MSMEs enter global markets.
- BharatTradeNet (BTN): A digital public infrastructure for trade documentation and financing solutions.
- Domestic Manufacturing Support: Strengthens integration into global supply chains and promotes Industry 4.0 readiness.
- Global Capability Centres: Proposed National Framework to establish emerging tier-2 cities as global service hubs.
- Infrastructure & Warehousing: Government-backed improvements in air cargo facilities, especially for high-value perishable horticulture products.
Reforms as the Fuel to the Engines of Viksit Bharat
Recognizing reforms as the driving force behind economic growth, the Union Finance Minister emphasized the Government’s continuous efforts over the past decade to enhance ease of doing business, simplify taxation, and strengthen the financial sector.
- These reforms serve as the essential fuel propelling the four engines Agriculture, MSMEs, Investment, and Exports towards the vision of Viksit Bharat.
Taxation & Compliance Reforms
- Faceless Assessment & Taxpayer-Centric Reforms: Implementation of faceless assessment, taxpayer charter, faster refunds, and self-assessment-based returns (99% acceptance).
- “Trust First, Scrutinize Later” Approach: Strengthened taxpayer trust with Vivad se Vishwas scheme and minimal scrutiny for compliance.
Financial Sector Reforms & Development
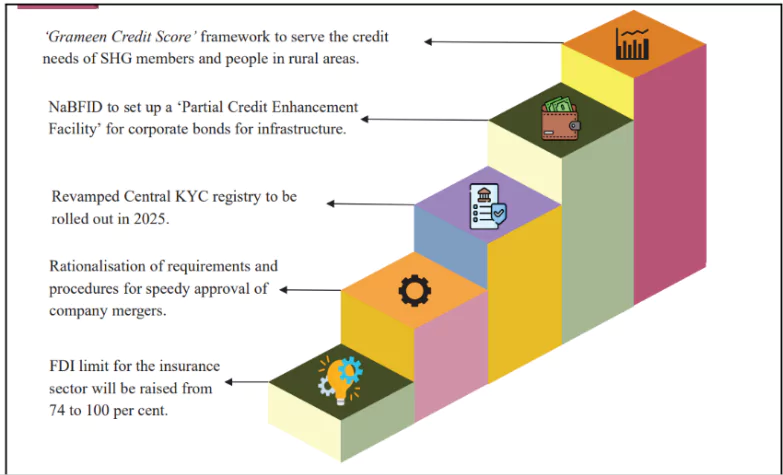
- Ease of Doing Business: Comprehensive changes across financial regulations to streamline compliance, encourage investment, and promote a robust regulatory environment.
- FDI Limit in Insurance: Increased from 74% to 100%, applicable to companies reinvesting all premiums in India.
- Light-Touch Regulatory Framework: A principle-based, trust-driven regulatory environment to boost productivity and job creation.
Key Reform Measures
- High-Level Committee for Regulatory Reforms
- Reviews non-financial sector regulations, certifications, licenses, and permissions.
- Strengthens trust-based economic governance, simplifying inspections and compliance.
- States encouraged to onboard, recommendations expected within a year.
- Investment Friendliness Index of States (2025): Aims to promote competitive cooperative federalism by ranking states based on investment climate.
- Financial Stability & Development Council (FSDC) Mechanism: Evaluates current financial regulations to improve responsiveness and financial sector growth.
- Jan Vishwas Bill 2.0: Decriminalizes over 100 provisions across various laws, ensuring a pro-business legal environment.
- Tax Reform: Changes in direct taxes and proposal to introduce the New Income Tax Bill.
Taxation Proposals
Direct Taxes Proposals
1. New Direct Tax Slabs
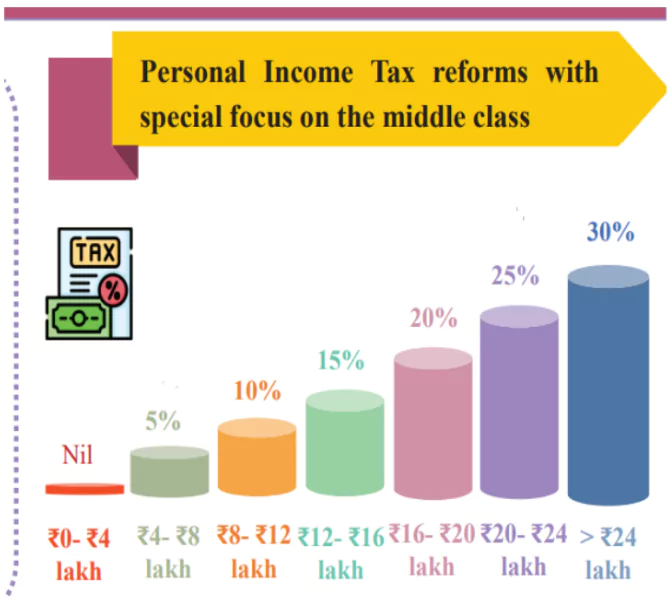
- Tax-Free Income Limit Raised: No income tax on annual income up to ₹12 Lakh.
- Salaried Taxpayers Benefit: Those earning up to ₹12.75 Lakh pay NIL tax due to a ₹75,000 standard deduction.
- Revenue Impact: ₹1 Lakh Crore loss due to tax reductions.
2. Ease of Doing Business
- Introduction of a scheme for determining arm’s length price of international transaction for a block period of three years.
- Expansion of scope of safe harbour rules to reduce litigation and provide certainty in international taxation
3. TDS/TCS Rationalization & Compliance Ease
- Senior Citizens’ Interest Income: TDS deduction limit doubled from ₹50,000 to ₹1 Lakh.
- Rent TDS Threshold Increased: From ₹2.4 Lakh to ₹6 Lakh per annum.
- Higher TDS Deductions Only for Non-PAN Cases.
- Delay in TCS Payments Decriminalized.
Check Out UPSC Modules From PW Store
4. Encouraging Voluntary Compliance
- Encouraging voluntary compliance: Extended Time for Filing Updated Tax Returns from 2 years to 4 years.
- Charitable Trusts & Institutions: Registration period extended from 5 years to 10 years.
- Self-Occupied Property: Tax payers to be allowed to claim the annual value of 02 self occupied properties (previously 01) without any conditions (previously conditions attached).
- Vivad Se Vishwas Scheme Success: 33,000 taxpayers availed the scheme.
- Senior Citizens’ Benefits:
- Exemption on withdrawals from National Savings Scheme (NSS) after August 29, 2024.
- Similar exemptions extended to NPS Vatsalya accounts.
5. Ease of Doing Business & International Taxation
- New Scheme for Determining Arm’s Length Pricing: Introduced for a block period of three years.
- Expansion of Safe Harbor Rules: To ensure certainty in international taxation.
- Extension for incorporation by 5 years of Start-Ups.
- Specific benefits to ship-leasing units, insurance offices and treasury centres of global companies which are set up in IFSC
- Certainty of taxation to Category I and category II AIFs, undertaking investments in infrastructure and other such sectors, on the gains from securities.
6. Incentivizing Employment & Investment
- Presumptive Taxation for Non-Residents: For those providing services to Indian electronics manufacturing firms.
- Tonnage Tax Scheme Extended to Inland Vessels.
- Start-ups Encouraged: Incorporation period extended by five years.
- Infrastructure Investment: Sovereign and Pension Fund investment deadline extended to March 31, 2030.
Indirect Tax Proposals
1. Rationalisation of Customs Tariff Structure for Industrial Goods
- Removal of 07 tariff rates
- Apply not more than one cess or surcharge
- Apply equivalent cess to maintain effective duty incidence on most items and lower cess on certain items.
2. Sector specific proposals
- Make in India- Exemption to open cell for LED/LCD TV, looms for textiles, capital goods for lithium ion battery of mobile phones and EVs
- Promotion of MRO – exemption for 10 years on goods for ship building and ships for breaking, extension of time limit for export of railway goods imported for repairs.
- Export promotion – duty free inputs for handicraft and leather sectors.
- Trade Facilitation: Time limit fixed for finalisation of provisional assessment; new provision for voluntary declaration of material facts post clearance and duty payment with interest but without penalty; IGCR Rules amended to extend time limit to 1 year and file quarterly statement instead of monthly.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
3. Improved access to life saving medicines
- Addition of:
- 36 lifesaving drugs/medicines are exempted from Basic Customs Duty (BCD).
- 6 medicines in 5% duty list;
- 37 medicines and 13 new patient assistance programmes in exempt list
4. Rationalization of Customs Tariffs on Industrial Goods
- Seven Tariffs Removed.
- Cess Adjustments to Maintain Effective Duty.
- No More than One Cess or Surcharge to be Levied.
5. Supporting Domestic Manufacturing & Value Addition
- Customs Duty Exemptions:
- 25 critical minerals, including cobalt, lithium-ion battery waste, lead, and zinc.
- Two additional shuttle-less looms added to the exempted textile machinery list.
- Knitted Fabric BCD Revision: From “10% to 20%” changed to “20% or ₹115/kg, whichever is higher”.
6. Boost to ‘Make in India’
- Inverted Duty Structure Fixes:
- BCD on Interactive Flat Panel Displays (IFPD) increased to 20%.
- BCD on Open Cells reduced to 5%.
- BCD exemption on Open Cell Parts to boost domestic manufacturing.
7. Electric Vehicle & Mobile Battery Manufacturing Support
- Exemptions on Capital Goods Imports:
- 35 items for EV battery manufacturing.
- 28 items for mobile battery production.
8. Shipbuilding & Telecommunications Support
- BCD Exemption Extended for Another 10 Years on shipbuilding materials.
- Carrier-Grade Ethernet Switches BCD Reduced from 20% to 10% to match non-carrier grade switches.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books From PW Store
9. Export Promotion & Industry-Specific Relief
- Handicrafts Export Incentives.
- Duty Exemptions & Reductions:
- Wet Blue Leather: Fully exempted for export value addition.
- Frozen Fish Paste: BCD reduced from 30% to 5%.
- Fish Hydrolysate: BCD cut from 15% to 5% for fish & shrimp feed production.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
![]() 1 Feb 2025
1 Feb 2025














