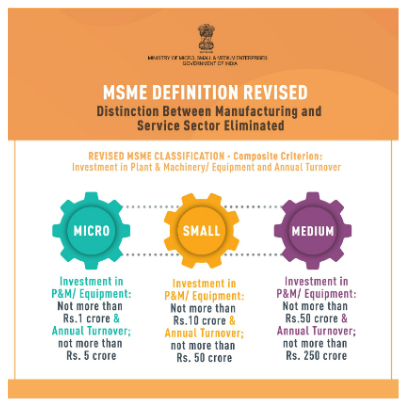
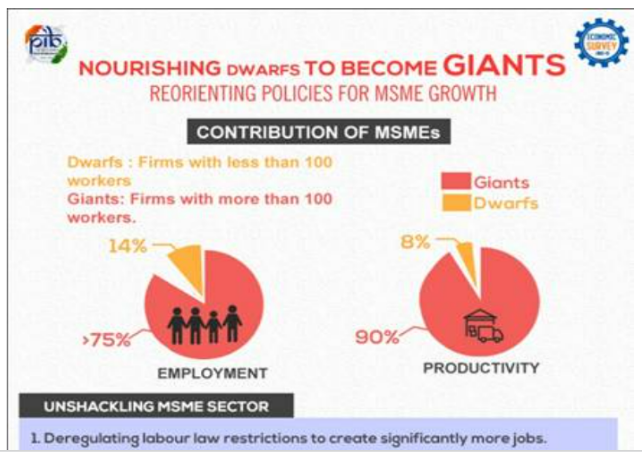
 However, to address the global market, India must aim for at least a 10 percent share of the global trade.
However, to address the global market, India must aim for at least a 10 percent share of the global trade.Schemes/ Government Initiatives for MSME Sector:
|
Source: Business Standard
To get PDF version, Please click on "Print PDF" button.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>