The US Federal Reserve recently cut interest rates by 25 basis points, marking its second reduction in 2024.
Key Highlights of the Reduction
- Interest Rate Reduction: A 25 basis point cut, signaling efforts to manage inflation.
- Future Outlook: The Fed remains open to further rate cuts based on economic performance, with a decision pending in December.
- Political Influence: US Federal Reserve asserted that the Fed’s decisions are unaffected by political changes or external pressures, including any influence from the White House.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Relation between Interest Rate and Inflation
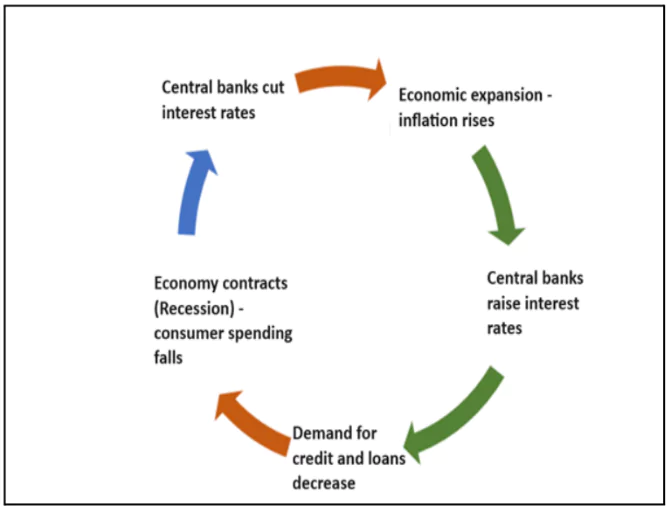
- Inverse Relation: The relationship between inflation and interest rates is fundamentally inverse, meaning when one rises, the other tends to fall.
- This connection is rooted in the Quantity Theory of Money, which indicates that changes in the money supply influence inflation.
- This inverse relationship helps central banks manage economic stability.
- By adjusting interest rates, central banks can influence inflation and purchasing power, aiming to maintain price stability and support a healthy economy
- High Interest Rates: When the central bank raises interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive.
- This reduces the money supply, as people and businesses are less inclined to take out loans. As a result, spending declines, leading to lower demand for goods and services, which helps control and reduce inflation.
- Low Interest Rates: When interest rates are low, borrowing is cheaper, leading to an increase in the money supply.
- People and businesses are more likely to spend and invest, boosting demand for goods and services. With demand outpacing supply, prices rise, driving up inflation.
Market Reactions and Global Implications
- US Debt and Inflation Concerns: Following the rate cut, US debt interest rates spiked, with analysts warning of inflationary pressures from Trump’s proposed tax cuts and tariff plans.
- Impact on Global Currencies: A lower US interest rate could make investments in other currencies more attractive, especially in emerging markets such as India.
- This could drive higher returns for currency carry trades, attracting foreign investments in countries with higher rates.
Potential Impacts on Indian Economy
- Carry Trade Opportunities: As the US rate declines, the difference between US and Indian rates may widen.
- This creates attractive opportunities for currency carry trades in India, potentially increasing foreign investments in Indian bonds and equities.
- Boost to Global Growth Prospects: Lower rates in the US might stimulate its economy, which could have a positive ripple effect on global growth.
- India, alongside other emerging markets, may benefit from this potential economic uplift, especially as China contends with a real estate crisis.
- Investor Interest in Emerging Markets: With lower returns on US debt, investors may be drawn to emerging markets like India, seeking higher returns.
- This trend could bolster Indian equity markets and bring in increased foreign capital.
Domestic Monetary Policy Considerations in India
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has raised rates by 250 basis points since 2020, reaching 6.5% to control inflation.
- However, given the US Fed’s easing stance, the RBI may adopt a cautious approach in its upcoming Monetary Policy Committee meeting on December 4-6.
- Any delays by the Fed in further cuts could influence RBI’s decisions on its own rate adjustments.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Global Factors Impacting Indian Economy
- China’s Economic Stimulus: China is expected to launch a significant stimulus package, which may shift foreign portfolio investments (FPIs) away from India.
- Heightened tensions from Trump’s proposed tariffs on Chinese goods may further incentivize China to adopt aggressive fiscal measures, potentially decreasing India’s appeal to FPIs.
- Bank of Japan’s (BoJ) Expected Rate Hike: The BoJ is anticipated to raise rates in December, which could impact the yen carry trade and potentially increase market volatility.
- A rate hike could lead to a shift in global investment patterns, influencing India’s equity and currency markets.
![]() 9 Nov 2024
9 Nov 2024


