Recently, an avalanche hit a Border Roads Organisation (BRO) project site near Mana — India’s “first” village — in Uttarakhand’s Chamoli district, trapping several workers and prompting a rescue operation that involved multiple agencies.
About Avalanche
- Avalanche is a rapid descent of snow, ice, and debris down a mountain slope.
- It is triggered by natural or human-induced factors.
- It can cause widespread destruction, burying people, structures, and transport routes.
Snow avalanche zones
- Red Zone – The most dangerous zone where snow avalanches are most frequent and have an impact pressure of more than 3 tonnes per square metre.
- Blue Zone – Where the avalanche force is less than 3 tonnes per square metre and where living and other activities may be permitted with connection of safe design but such areas may have to be vacated on warning.
- Yellow Zone – Where snow avalanche occur only occasionally
|
Avalanches Prone Areas in India
- The Himalayas are well known for the occurrence of snow avalanches particularly Western Himalayas I .e. the snowy regions of Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh and Western Uttar Pradesh.
- Jammu and Kashmir – Higher reaches of Kashmir and Gurez valleys, Kargil and Ladakh and some of the major roads
- Himachal Pradesh – Chamba, Kullu- Spiti and Kinnaur vulnerable areas
- Uttarakhand – Parts of Tehri Garhwal and Chamoli districts are vulnerable areas.
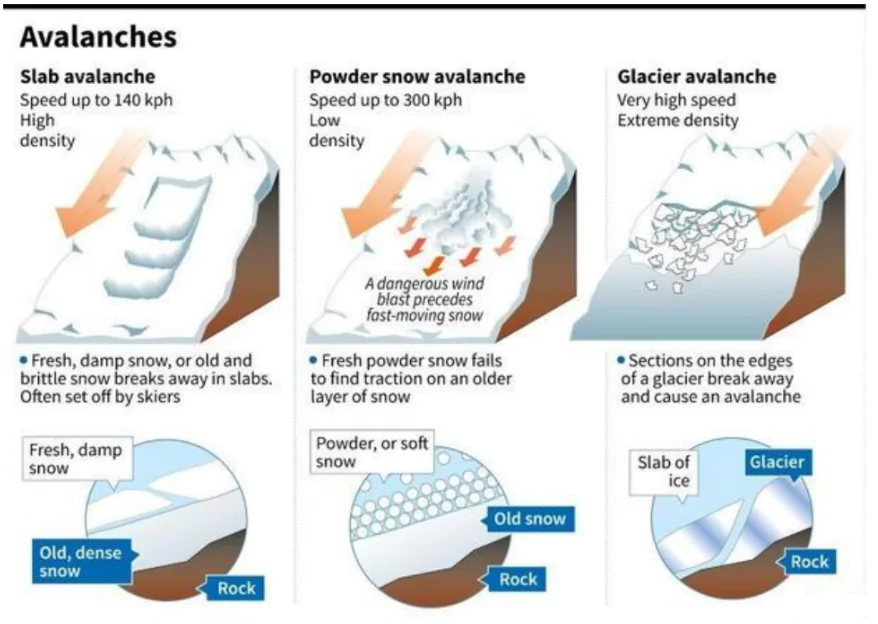
Types of Avalanches
- Loose Snow Avalanche:
- Occurs on steep slopes (>40°) with loosely bonded snow.
- Less deadly but disruptive.
 Slab Avalanche:
Slab Avalanche:-
- Large, cohesive snow layer fractures and slides.
- Most deadly, with speeds up to 100 km/h.
- Gliding Avalanche:
- The entire snowpack slides over smooth surfaces (e.g., rock).
- Common on slopes >15°.
- Powder Avalanche:
- High-speed avalanche with suspended snow particles in the air.
- Can reach speeds of 300 km/h, creating severe shockwaves.
- Wet Snow Avalanche:
- Triggered by melting snow due to temperature rise or rain.
- Slower but more destructive due to high density.
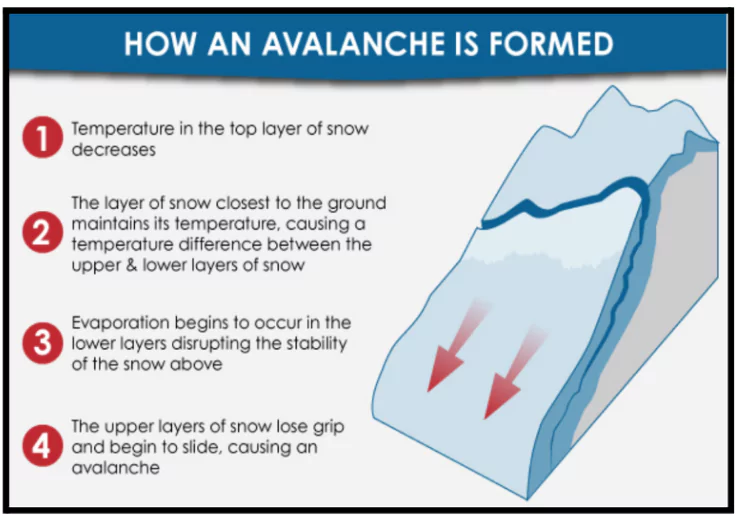
Causes of Avalanches
- Natural Causes:
- Heavy Snowfall & Wind: Uneven snow accumulation causes instability.
- Steep Slopes: Most likely on slopes between 30° and 45°.
- Temperature Fluctuations: Melting and refreezing weakens snow layers.
- Earthquakes & Vibrations: Can trigger avalanches.
- Human-Induced Causes:
- Winter Sports & Tourism: Disturb snow layers, increasing instability.
- Construction & Deforestation: Weakens slope stability.
- Military Operations: Explosions and heavy equipment can trigger avalanches.
Consequences & Impact
- Loss of Life & Injuries: Suffocation, trauma, hypothermia; survival chances drop after 15 minutes of burial.
- Destruction of Infrastructure: Bury roads, railways, buildings, and shelters.
- Disruptions in Communication & Utilities: Damages power lines, water supply, and communication networks.
- Environmental Hazards: Melting snow causes landslides and flash floods, harming ecosystems.
- Economic Impact: Disrupts tourism, damages infrastructure, and leads to recovery costs.
Precautionary Measures
- Avalanche Early Warning Systems:
- IMD Avalanche Forecasting: Tracks snowfall, slope stability, and temperature fluctuations to predict avalanches.
- Remote Sensing & AI-Based Prediction Models: Utilizes technology for real-time detection and forecasting of avalanches.
- Structural Protection Measures:
- Snow Barriers & Fences: Installed on avalanche-prone slopes to reduce snow buildup and block its path.
- Deflecting Structures: Redirect the avalanche away from populated areas to minimize damage.
- Artificial Avalanche Triggers:
- Controlled Explosions: Trigger smaller, controlled avalanches to prevent larger, uncontrollable ones from occurring.
- Zoning & Land Use Planning:
- Avoid Construction in Avalanche-Prone Areas: Ensure that buildings and infrastructure are not placed in high-risk zones.
- Ski Resorts & Highways Risk Assessments: Ski resorts and highways must follow detailed risk assessment reports to minimize exposure to avalanche hazards.
Needed Actions Required to be Taken
- Enhancing Real-Time Avalanche Forecasting: Strengthen satellite-based monitoring systems for early avalanche warnings.
- Improving Infrastructure Resilience: Build avalanche protection tunnels and snow-retention fences along highways to reduce risk.
- Stronger Coordination Between Agencies: Integrate efforts of IMD, BRO, NDMA, and ITBP for better disaster management and response.
- Community Training & Awareness Programs: Educate local residents, trekkers, and military personnel on avalanche survival skills and safety protocols.
- Encouraging Climate-Resilient Development: Prevent deforestation and unplanned construction in high-risk avalanche zones to reduce vulnerability.
Difference Between an Avalanche and a Landslide
| Aspect |
Avalanche |
Landslide |
|
|
- Sudden downhill movement of snow, ice, and debris
|
- Mass of rock, soil, or debris sliding down a hillside.
|
|
|
- Can reach speeds up to 320 km/h (200 mph).
|
- Varies, typically slower than avalanches.
|
|
|
- Heavy Snowfall, Weak snow layers, Earthquakes, Temperature Fluctuations Or human activity.
|
- Rainfall, Deforestation, Earthquakes, mining
- or human activity.
|
|
|
- Snow-covered mountains or slopes.
|
- Steep slopes in various terrains (forests, urban areas, hills).
|
About Mana Village
- Location: Situated in Chamoli district, Uttarakhand.
- Border: Shares a border with China.
- Formerly Known As: Referred to as the “Last Village” but now called the “First Indian Village”.
- Geographical Features: Located on the banks of the River Saraswati, just 3 km from Badrinath town.
- Renowned For: Famous for its woollen garments and materials made primarily from sheep wool.
![]() 3 Mar 2025
3 Mar 2025

 Slab Avalanche:
Slab Avalanche:
