Every year, July 26 is celebrated as the International Day for the Conservation of the Mangrove Ecosystem. The theme for 2025 is “Protecting Wetlands for our future.”
It was adopted during the 38th session of the general conference of UNESCO held in 2015.
What are Mangroves?
- Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees and shrubs found in coastal intertidal zones, where freshwater and seawater mix.
- They grow in tropical and subtropical climates with high rainfall (1,000–3,000 mm) and temperatures between 26–35°C.
- Characteristics of Mangrove:
-
- Vivipary: Seeds sprout while still on the parent tree, helping survival in salty, waterlogged conditions.
- Aerial roots: These breathing roots (pneumatophores) absorb oxygen from the air.
- Waxy and succulent leaves: Help reduce water loss and manage salt stress.
- Common Species: Red mangrove, Avicennia marina, grey mangrove, and Rhizophora are commonly found.
Importance of Mangroves
- Coastal Protection (Bio-shields): Their dense root systems reduce the force of storm surges and help prevent coastal erosion.
- Carbon Storage: Mangroves absorb carbon dioxide and store it in the soil for centuries, making them powerful carbon sinks.
- Livelihood Source: They support local communities through fishing, honey collection, aquaculture, and other eco-based livelihoods.
- Biodiversity Hotspots: Serve as breeding and nursery grounds for fish, birds, and reptiles. Their rich biodiversity supports complex food chains.
Threats to Mangrove Ecosystems
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels and increased storm frequency threaten mangrove survival and limit their natural landward migration.
- Human Encroachment: Rapid urbanisation, agriculture, aquaculture, and infrastructure development reduce mangrove habitats.
- Pollution and Dams: Industrial waste, oil spills, and damming of rivers disrupt natural water flow and degrade mangrove health.
- Limited Regeneration Space: Settlements and land use changes restrict their inland expansion, squeezing their natural range.
- UNESCO: Mangrove loss is occurring at 3–5 times the rate of global forest decline.
- IUCN: Over 50% of global mangrove ecosystems may collapse by 2050.
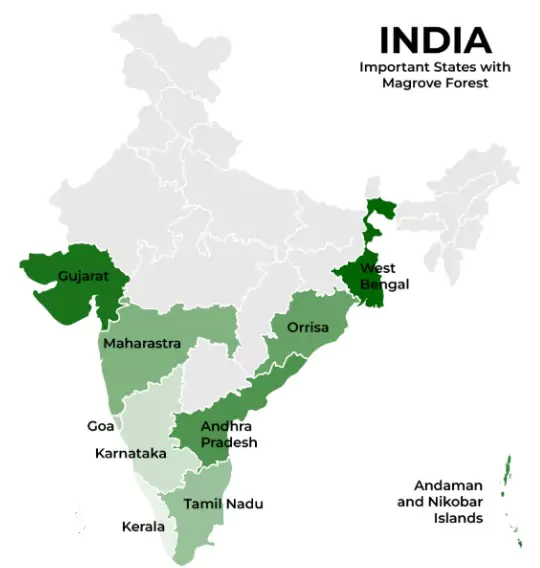
Mangroves in India
- India has a mangrove cover of 4,992 sq. km (ISFR 2023), which is 0.15% of the country’s land area.
- They are mostly found along the east and west coasts and on island territories.
Key Mangrove Forests
- Sundarbans: Largest contiguous mangrove forest globally, known for Royal Bengal Tigers and Gangetic dolphins.
- Bhitarkanika: Known for saltwater crocodiles and nesting Olive Ridley turtles.
|
State-wise Distribution
- West Bengal: Largest share, primarily in the Sundarbans.
- Gujarat: Second-largest, mainly around the Gulf of Kutch and Gulf of Khambhat.
- A&N Islands: Rich in coastal mangroves.
- Other Locations: Godavari–Krishna delta (Andhra Pradesh), Bhitarkanika (Odisha), Pichavaram (Tamil Nadu), and coastal Kerala.
Notable Restoration Efforts in India
Tamil Nadu
- Mangrove area doubled from 4,500 ha to over 9,000 ha (2021–2024).
- Green Tamil Nadu Mission aided revival in Thanjavur, Tiruvarur, Cuddalore.
- Pattuvanachi estuary (Muthupettai): 115 ha restored using 4.3 lakh Avicennia seeds, 6,000 Rhizophora propagules.
- Buckingham Canal (Chennai): 12,500 mangrove saplings planted after removing invasive Prosopis juliflora.
Mumbai (Maharashtra)
- Thane Creek restoration project (2025): Backed by Amazon’s Right Now Climate Fund.
- Target: 3.75 lakh mangrove saplings.
- 150 tonnes of plastic removed using trash booms.
- Support for women-led employment in planting & maintenance.
Gujarat
- Leading under the MISHTI scheme (launched June 5, 2023).
- 19,000+ ha mangroves restored in 2 years (out of a 5-year target of 54,000 ha).
- Focus areas: Kutch & Saurashtra coastlines.
- Gujarat holds 23.6% of India’s total mangrove cover.
Conservation Initiatives in India
- Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes (MISHTI): A central scheme aimed at restoring mangroves along coastlines and promoting eco-livelihoods.
- Sustainable Aquaculture In Mangrove Ecosystem (SAIME) (West Bengal): Promotes sustainable aquaculture that coexists with mangrove conservation.
- Vana Samrakshana Samitis (Andhra Pradesh): Community-led forest protection groups involved in coastal conservation.
- Green Tamil Nadu Mission: Includes mangrove plantation and protection efforts under broader environmental goals.
- CRZ Regulations: Prohibit destructive industrial activities and restrict construction near sensitive coastal zones.
International Initiatives
- Mangrove Alliance for Climate (MAC): Launched at COP27, it brings together countries including India to boost global mangrove restoration and protection efforts.
- Mangroves for the Future (MFF): An IUCN–UNDP initiative for sustainable coastal ecosystem management. It covers India and other tsunami-affected countries and includes coral reefs, lagoons, and wetlands.
![]() 31 Jul 2025
31 Jul 2025

