Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO), based on data from the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), has classified Hepatitis D virus (HDV) as a Group 1 carcinogen, the same category as Hepatitis B (HBV) and Hepatitis C (HCV).
About Hepatitis D Virus (HDV)
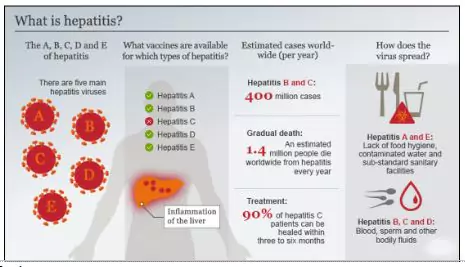
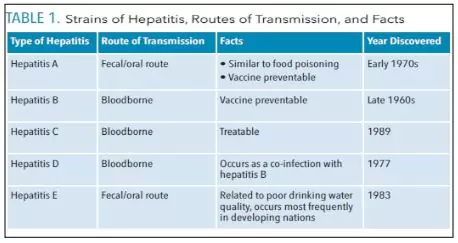
- Hepatitis D is a serious liver infection caused by the hepatitis D virus (HDV).
- Hepatitis refers to an inflammatory condition of the liver or swelling of the liver cells. It can be either acute or chronic and is believed to be caused by hepatotropic viruses (viruses that are directed to the liver).
 A Defective Virus: HDV is incomplete and requires HBV to replicate. It cannot infect on its own.
A Defective Virus: HDV is incomplete and requires HBV to replicate. It cannot infect on its own.- Dependent Infection: Only individuals already infected with HBV are vulnerable to HDV.
- Modes of Transmission: Same as HBV & HCV
- Infected blood and body fluids
- Unsafe injections or blood transfusions
- Mother-to-child transmission
- Unprotected sexual contact
- Sharing needles, especially among intravenous drug users
 Types of HDV Infections:
Types of HDV Infections:
- Co-infection: Simultaneous infection with HBV and HDV
- Superinfection: HDV infects someone already chronically infected with HBV, results in more severe disease, faster liver damage
- Why is hepatitis D considered carcinogenic?
- All types of hepatitis are associated with acute liver infection; however, only hepatitis B, C, and D can lead to chronic infections with a higher risk of liver cirrhosis, failure or cancer.
- Hepatitis D is associated with a two- to six-fold higher risk of liver cancer compared with hepatitis B.
- Concerning Scenario: 75 per cent of hepatitis D patients could develop liver cirrhosis within 15 years. People who have contracted hepatitis B alone are 50 per cent less likely to develop liver cancer as compared to people who have hepatitis B and D coinfection.
- WHO warning: One person dies every 30 seconds globally due to hepatitis-related liver disease or cancer
- Prevention & Control Measures:
- Hepatitis B Vaccination is the most effective tool, as HDV cannot exist without HBV
- India’s challenge: Only ~50% vaccine coverage, despite being part of Universal Immunisation Programme (UIP)
- Diagnosis: HDV-RNA blood test used for detecting infection
- Other Preventive Measures:
- Safe injection practices
- Proper screening of blood and organ donations
- Safe Sex
- Avoiding needle sharing
- Screening of high-risk groups
- Actions Required:
- Scale up Hepatitis B vaccination, especially in underserved areas
- Raise public awareness about HDV–HBV co-infection risks
- Expand access to new treatments like Bulevirtide
- Strengthen surveillance, research, and global partnerships
- Align with WHO’s Global Health Sector Strategy to eliminate viral hepatitis by 2030
- Key Initiatives:
- India: National Viral Hepatitis Control Program (2018), it aims to eliminate Hepatitis C by 2030 and reduce deaths from other types, in line with SDG 3.3.
- Global: WHO’s Global Health Sector Strategy on HIV, Viral Hepatitis and Sexually Transmitted Infections (2022–2030), it aims to eliminate viral hepatitis as a public health problem.
Comparison between Hepatitis D vs Hepatitis B
| Feature |
Hepatitis D (HDV) |
Hepatitis B (HBV) |
| Type of virus |
Defective virus |
Complete virus |
| Dependence |
Requires HBV to replicate |
Independent replication |
| Carcinogenic Status |
Newly classified as Group 1 carcinogen |
Already classified as Group 1 carcinogen |
| Cancer Risk |
2–6x higher risk in HBV-HDV co-infection |
Significant risk, even without cirrhosis |
| Prevention |
Indirectly prevented by HBV vaccination |
Directly prevented by HBV vaccination |
| Transmission |
Blood, fluids, unsafe sex/injection |
Same as HDV |
PWOnlyIAS Extra Edge:
About Carcinogenic Diseases
- Carcinogenic diseases are cancers caused by carcinogens – substances that damage DNA and trigger uncontrolled cell growth.
- Cancers from Chemical Carcinogens
- Lung, larynx, esophageal Cancers: Caused by tobacco smoke (rich in PAHs – polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons)
- Bladder Cancer: Linked to aniline dyes and industrial chemicals (e.g. in rubber industry)
- Mesothelioma, lung Cancer: Due to asbestos exposure – fibers get lodged in lungs causing chronic damage
- Leukemia: Caused by benzene (found in gasoline, industrial solvents)
- Cancers from Biological Carcinogens
- Liver cancer (Hepatocellular carcinoma): Caused by Hepatitis B & C viruses (lead to chronic liver inflammation)
- Cervical, oral, anal, throat cancers: Caused by HPV (Human Papillomavirus)
- Stomach cancer, gastric lymphoma: Linked to Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection
- Kaposi Sarcoma: From HHV-8 (Human Herpesvirus 8), especially in HIV-positive individuals
- Cancers from Physical Carcinogens
- Skin cancers (melanoma, BCC, SCC): Caused by UV radiation from sun or tanning beds
- Lung cancer: Due to exposure to radon gas (natural radioactive gas in buildings)
- Leukemia, other cancers: From ionizing radiation (e.g. nuclear accidents, medical imaging)
About International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC)
- The International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) is the specialized cancer research agency of the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Established: In 1965 by a resolution of the World Health Assembly (WHA).
- Objective: To promote international collaboration in cancer research and support evidence-based cancer prevention.
- Membership: Comprises 27 member countries, including India.
- Headquarters: Lyon, France
|
Read More About Global Hepatitis Report 2024
![]() 7 Aug 2025
7 Aug 2025

 A Defective Virus: HDV is incomplete and requires HBV to replicate. It cannot infect on its own.
A Defective Virus: HDV is incomplete and requires HBV to replicate. It cannot infect on its own. Types of HDV Infections:
Types of HDV Infections: