The Election Commission of India has released granular data for the Lok Sabha elections 2024 and simultaneous assembly elections held in four states namely Andhra Pradesh, Arunachal Pradesh, Odisha and Sikkim
- Variables Covered: Details of electors, voter turnout, Party wise vote share, gender-based voting behaviour, state wise participation of women electors, regional variations etc.
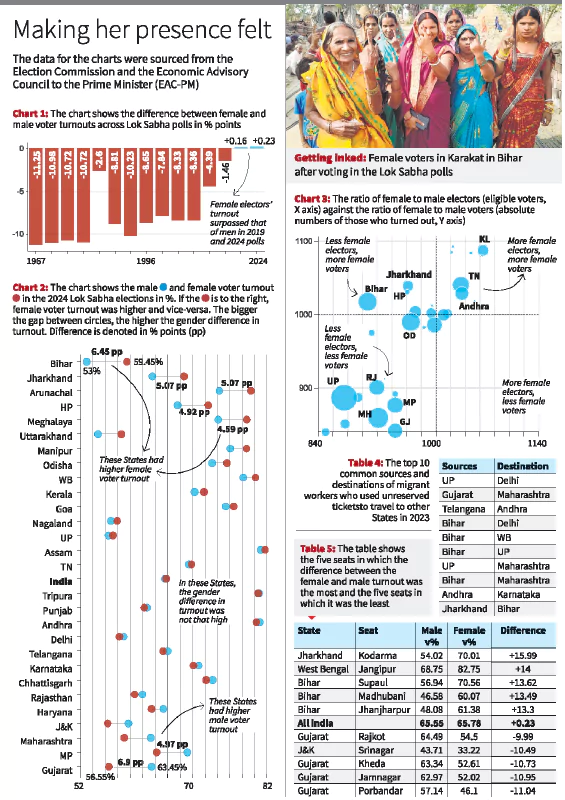
Women Participation
- Registered Electors:
- There are 47,63,11,240 registered women electors in 2024 out of 97,97,51,847 representing 48.62% as compared to 438537911 and 48.09% in 2019.
- Puducherry (53.03%) and Kerala (51.56%) had the highest percentage share of Female electors in 2024
- Per 1000 Male: Number of female electors per 1000 male electors was 946, as compared to 926 in 2019.
- Voting Behaviour:
- 65.78% of Female Electors voted in 2024 (excluding Surat) surpassing Male voters with 65.55% of voters.
- Females outnumbered men in voting numbers for the 2nd continuous time after the 2019 Lok Sabha elections with the difference in turnout increasing from 0.16 to 0.23 points
- Parliamentary Constituency wise Data: Dhubri (Assam) with 92.17% female voting, followed by Tamluk (West Bengal) with 87.57%.
- State wise Share: In 15 out of the 28 major states and U.T.s, female turnout surpassed that of men with the gender difference highest in Bihar, Jharkhand and Uttarakhand
- Male Voter Dominance: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Jammu & Kashmir, and Rajasthan however saw higher male voters turnout.
- Contesting Candidates:
- 800 female candidates contested for the elections in 2024 as compared to 726 female candidates in 2019.
- State Share: Maharashtra with 111 women candidates is followed by Uttar Pradesh [80] and Tamil Nadu [77].
- No Women Candidate: 152 parliamentary constituencies however saw no female candidates
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Election Commission of India
- It is an independent constitutional body responsible for administering the free and fair elections in order to uphold the true spirit of democracy.
- Article 324: It provides for an independent Election Commission for the ‘superintendence, direction and control of the electoral roll and conduct of the elections’ in India.
- Function: The Election Commission conducts the elections to
- Parliament; State Legislatures; Office of President and of Vice -President
- Composition: The Election Commission consists of the Chief Election Commissioner and 2 Election Commissioners
- Appointment: The President appoints Chief Election Commissioner and Election Commissioners.
- Removal: The Chief Election Commissioner can be removed from office only on the basis of a resolution passed to that effect by both the Houses of Parliament on grounds of ‘Proved misbehaviour or incapacity’.
- Powers and Functions:
-
- To determine the territorial area of the electoral constituencies in accordance with the Delimitation Commission Act.
- To prepare electoral rolls and revise them from time to time.
- To notify the schedule of the election
|
![]() 31 Dec 2024
31 Dec 2024

