Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM) has taken steps to support women’s Self-Help Groups (SHGs) to improve their business, use of technology, and access to finances.
About Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Rural Livelihoods Mission (DAY-NRLM)

- It is the Flagship Program of the Ministry of Rural Development (MoRD).
- Objective: To reduce poverty by empowering the poor, especially women, through self-help groups (SHGs) and access to financial services and livelihoods.
- Origin: Restructured from Swarnajayanti Gram Swarojgar Yojana (SGSY) and renamed as DAY-NRLM in 2016.
- This initiative offers funds to strengthen community institutions and financial management capacity.
- The goal is to help SHG in building their track record to attract mainstream Bank finance.
- Financial support provided by DAY-NRLM
- Revolving Fund: SHGs receive Rs. 20,000 to Rs. 30,000.
- Community Investment Fund: SHGs can receive a Community Investment Fund of up to Rs. 2.50 lakh to improve their financial standing.
- Interest subvention: To reduce the cost of Bank loans, DAY-NRLM provides interest subvention to women SHGs, making credit more affordable.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Course
Online Marketing Platform for SHG Products
- There is an online marketing platform for SHG products i.e., www.esaras.in.
- Objective: The aim of this platform is to ensure better access of SHGs to online marketing.
|
- Key Sub-Schemes and Initiatives
- Start-up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP)
- A sub-scheme under DAY-NRLM that supports SHG women or their family members to set up small businesses.
- Key Statistics: 3.13 lakh rural enterprises were supported (as of October 2024).
- Banking Correspondent Sakhis/Digipay Sakhis
- SHG women are trained as Banking Correspondent Sakhis to improve access to banking services in rural areas.
- Current Deployment: 1,35,127 Banking Correspondent Sakhis working under DAY-NRLM.
About Self-Help Groups
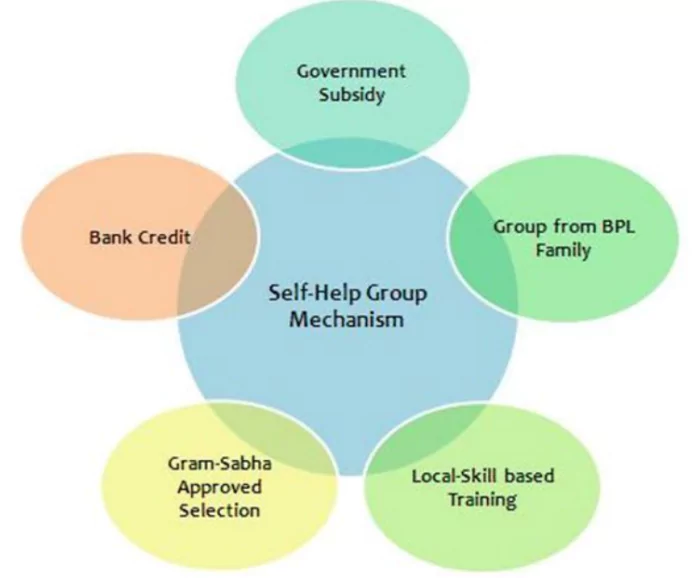
- SHGs are voluntary associations of economically disadvantaged individuals from similar socio-economic backgrounds.
- An SHG typically includes 5 (minimum) to 20 (maximum) members.
- Members collaborate to solve common problems through mutual support and community action.
- Origin of SHGs in India
- 1984: Inspired by Prof. Yunus’s Grameen Bank model, SHGs were introduced for social mobilization.
- NABARD’s Role: NABARD and NGOs initiated the SHG-Bank linkage program.
- 1990: RBI recognized SHGs as an alternative credit model.
Advantages of SHGs
- Low Transaction Costs: Beneficial for both lenders and borrowers.
- Women Empowerment: Encourages financial and social independence for women.
- Reduced Informal Borrowing: Decreases reliance on local moneylenders.
- Support by Corporates: Many companies promote SHGs for community development.
Check Out UPSC NCERT Textbooks From PW Store
Examples of Prominent SHGs in India
- Mahila Arthik Vikas Mahamandal (MAVIM): Empowers women in Maharashtra through training and credit facilities.
- Kudumbashree: Kerala-based program focused on women’s capacity building and income generation.
- Bandhan-Konnagar: Provides microfinance services and livelihood support.
- Bhagini Nivedita Gramin Vigyan Niketan (BNGVN): Promotes sustainable livelihoods through SHGs
|
- No Collateral Requirement: Overcomes barriers to formal credit access.
- Social Support: Platform for discussing and resolving common challenges.
Challenges Faced by SHGs
- Beneficiary Identification: Difficulty in identifying and including the poorest individuals.
- Training Gaps: Lack of quality training programs and expert trainers.
- Financial Literacy Issues: Limited access to formal financial services.
- Market Linkages: Poor integration with markets affects growth.
- Community Support: Inadequate business environment and value chain support.
Government Initiatives and Policies Supporting SHGs
- SHG-Bank Linkage Programme (SBLP): It is an initiative launched by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) in 1992.
 It aims to provide financial inclusion to rural poor, especially women, by linking Self-Help Groups (SHGs) with formal banking institutions.
It aims to provide financial inclusion to rural poor, especially women, by linking Self-Help Groups (SHGs) with formal banking institutions.
- Mission for Financial Inclusion (MFI): This initiative is a broader initiative to ensure access to financial services, namely, Banking/ Savings & Deposit Accounts, Remittance, Credit, Insurance, Pension in an affordable manner.
- Lakhpati Didi Initiative: This initiative was launched in 2023 which empowers women of self help groups to take multifaceted approaches to economic empowerment.
- It encourages them to adopt sustainable livelihood practices and have annual household income exceeding Rs. 1,00,000.
Enroll now for UPSC Online Classes
Way Forward
- Advanced Technology: SHG Should use better digital platforms for record-keeping, transactions, and communication
- Less reliance on informal lenders: This group, to reduce reliance on informal lenders and promote financial inclusion, should link it with financial institutions.
- Inclusive Approach: SHGs should adopt an inclusive approach to ensure fair participation and benefits of members from diverse socio-economic backgrounds.
- Community Resource Person (CRP): There should be a trained CRP to guide SHGs in identifying beneficiaries, managing finances, and scaling activities.
![]() 21 Dec 2024
21 Dec 2024



 It aims to provide financial inclusion to rural poor, especially women, by linking Self-Help Groups (SHGs) with formal banking institutions.
It aims to provide financial inclusion to rural poor, especially women, by linking Self-Help Groups (SHGs) with formal banking institutions. 