The Delhi Air Quality Index (AQI) is a critical tool that is used to highlight and showcase real-time air quality levels and their potential impact on health.

The air quality in Delhi-NCR continues to remain severe, with the Air Quality Index (AQI) recorded at 420 at 7 am. Key locations reported extremely poor AQI levels:
The current levels, particularly in several areas of Delhi-NCR, exceed 401, marking them as severe, posing serious health risks to all individuals.
According to recent data, PM2.5 levels in Delhi are consistently well above the WHO’s recommended safe limit, often exceeding 300 µg/m³ on high-pollution days. Such raised levels are hazardous and can cause severe respiratory and cardiovascular health effects, especially for vulnerable groups like children and the elderly. The government of Delhi frequently advises residents to avoid outdoor activities, especially during early morning and evening hours when pollution levels peak.
Efforts like restricting construction activities, implementing the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP), and encouraging the use of public transport are ongoing to mitigate pollution levels. However, because of the high rise of this problem, these measures have shown limited and short-term success.
The Delhi Air Quality Index (AQI) is a critical tool that is used to highlight and showcase real-time air quality levels and their potential impact on health. The AQI in Delhi is calculated by measuring the concentrations of pollutants like PM2.5, PM10, nitrogen dioxide (NO2), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and ground-level ozone (O3). On average, Delhi’s AQI ranges between 300-400 in the winter months, categorizing it as “Very Poor” to “Severe.” At these levels, everyone may experience health effects, and sensitive groups may face more serious consequences.
Air pollution is a big menace for the society, especially in a city like Delhi, which faces this issue annually. It is therefore necessary to carry out steps that provide a long-term solution to this problem.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
UPSC Exam 2025 Related Articles
UPSC Prelims 2025 Exam
UPSC Notification 2025
UPSC Preparation 2025
UPSC Eligibility 2025
UPSC Exam Pattern
UPSC Syllabus
GRAP are the set measures that have to be taken only when the air quality in Delhi NCR deteriorates beyond a certain threshold.
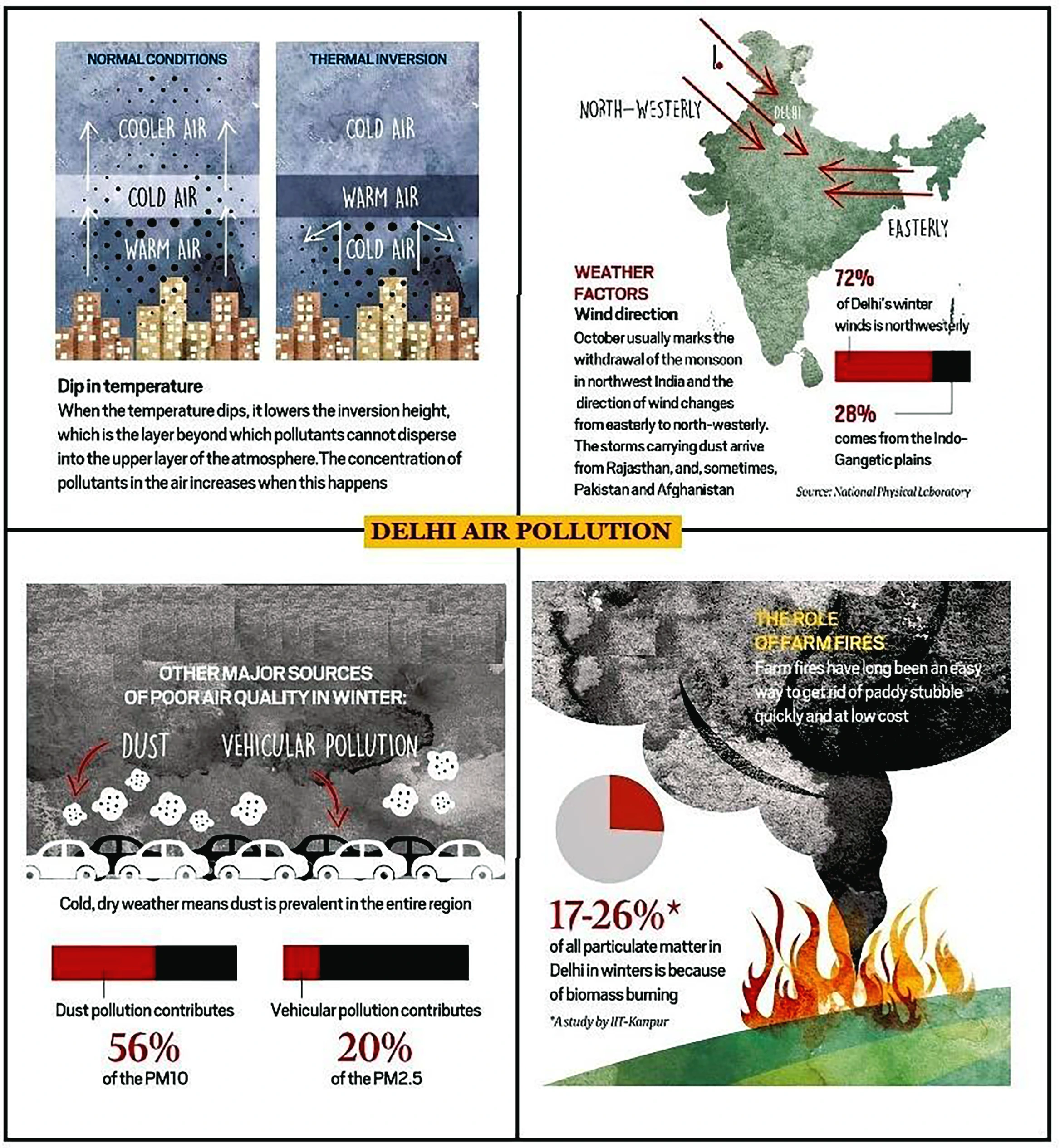
Vehicular emissions, dust, firecrackers, construction and demolition waste, stubble burning pollutants etc are some of the factors responsible for Delhi’s air pollution.
Delhi is land-locked from all sides. The north-westerly winds coming from Pakistan and Afghanistan bring in large amounts of dust particles to the region. Due to the presence of Himalayas, which block the escape route of the air, the dust and pollutants settle in the region.
CAQM was set up by the centre to coordinate and oversee diverse efforts to improve air quality in Delhi, Punjab, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
Introduction of GRAP, promoting public transport, odd-even scheme, ban on fossil fuel vehicles, ban on municipal waste burning, ban on coal fuel etc are some of the measures taken to address air pollution in Delhi.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>