France makes history by constitutionally guaranteeing abortion rights. Explore global perspectives, implications, and the contrasting Indian scenario under the MTP Act.

Recently, France has made history by enshrining the right to abortion in its constitution, becoming the first country in the world to explicitly guarantee a woman’s right to voluntarily terminate a pregnancy.
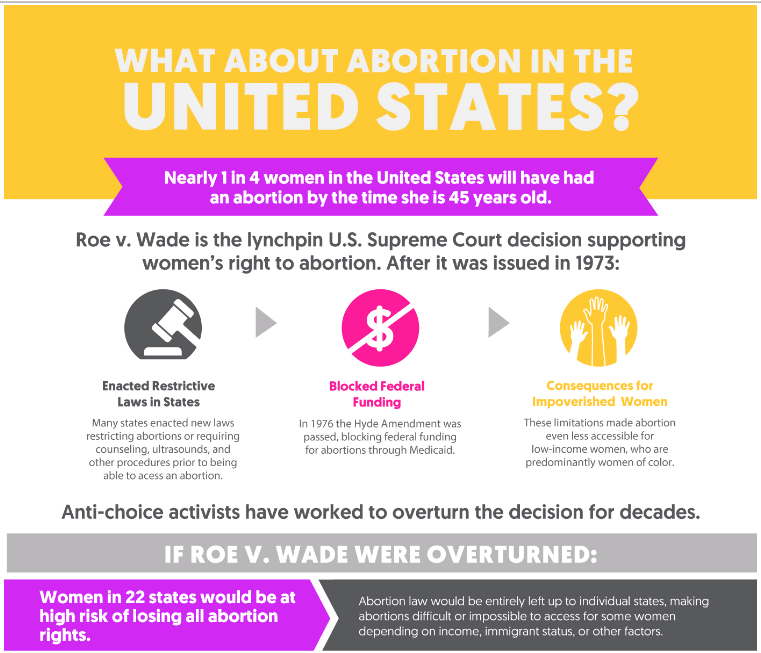
In 2022, the US Supreme Court made a controversial decision to reverse the landmark ruling of Roe v. Wade, which had previously recognized women’s constitutional right to abortion.
Abortion enjoys wide support in France across most of the political spectrum, and has been legal since 1975. Both houses of France Parliament, the National Assembly and the Senate, had separately adopted a bill — as required — to amend Article 34 of the French Constitution.
Article 34 of French Constitution
|
|---|
The bill was overwhelmingly backed by members of parliament, representing a significant victory for women’s rights advocates and a landmark moment in the ongoing battle for reproductive freedom.
The constitutional amendment, passed with a significant majority, solidifies the legal framework surrounding abortion and prevents future governments from rolling back these rights.
While the move has been celebrated by women’s rights activists, it has also faced criticism from anti-abortion groups and some political figures.
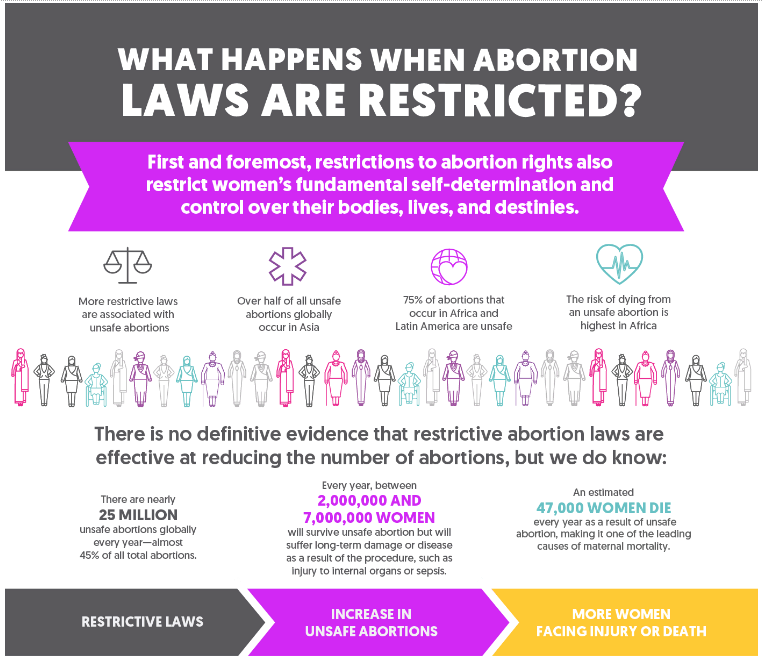
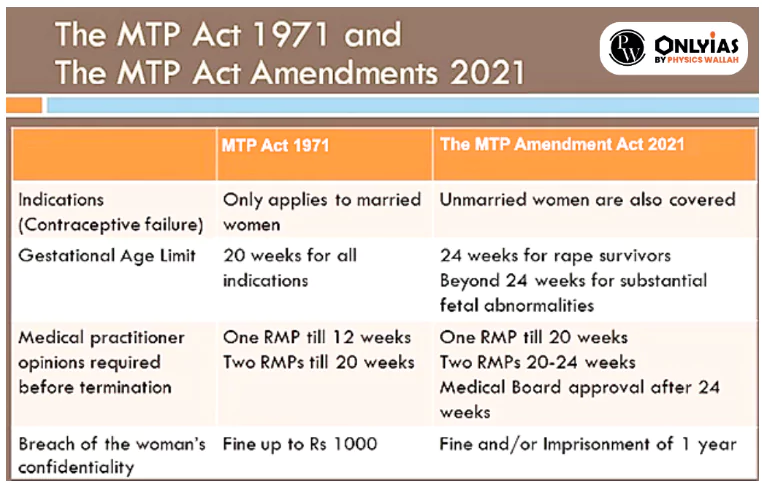
France has taken a historic step towards securing abortion rights, the situation in India presents a contrasting picture. In India, abortion is governed by the Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act, which allows for abortion under certain conditions.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
France becomes the first country to explicitly guarantee a woman's right to abortion.
The controversial 2022 US Supreme Court decision to reverse Roe v. Wade reignited debates on reproductive rights.
It grants Parliament authority to legislate on abortion, defining conditions and regulating healthcare facilities.
It was overwhelmingly backed by MPs and senators, securing significant public support.
India's Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP) Act has governed abortion under specific circumstances since 1971.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>