Godavari River, known as the Dakshin Ganga, is peninsular India's longest river. It originates in Trimbakeshwar, Maharashtra, and flows east. This system supports agriculture, generates power, and holds cultural significance. It traverses several states and features extensive tributaries, dams, and a fertile delta region.

Godavari River, also called the Dakshin Ganga Godavari, is the longest river of peninsular India and one of the most important east flowing rivers of India. It originates at Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra, and travels about 1,465 km across the Deccan Plateau.
The river flows through Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha, forming a large delta before emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The Godavari River system includes numerous tributaries, dams, and Godavari irrigation projects that support agriculture, drinking water, and hydroelectric power.
Its fertile delta, cultural significance, and ecological role make it vital for millions of people and diverse ecosystems across central and southern India.
The Godavari River originates at Brahmagiri Mountain, Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra. It is about 1,465 kilometers long. It drains India’s third-largest basin, covering 312,812 square kilometers. This Godavari River basin extends through Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
Smaller parts are in Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Puducherry. The basin has black, red, and lateritic soils. The Godavari is called the Dakshin Ganga due to its size and importance.
Below is the map showing how the river flows from its source to the Bay of Bengal.
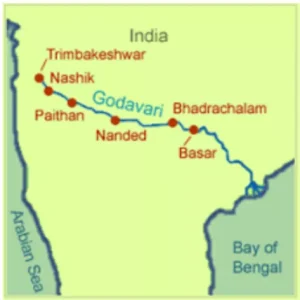
| Map Part | Details |
| Starting point | Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra |
| End point | Bay of Bengal near Rajahmundry |
| Main direction | Eastward |
| States touched | Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh and parts of Chhattisgarh, Odisha, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka |
Godavari River flows eastward across the Deccan Plateau. It turns southeast into Andhra Pradesh. Near Rajahmundry, it splits into two main streams: the Gautami Godavari and the Vashishta Godavari. These form a large delta before the Godavari River flows into the Bay of Bengal. The delta is rich with river deposits. Before the sea, the river forms seven mouths, collectively called Sapta Godavari.
The river basin divides into three sections: Upper, Middle, and Lower. The Upper section is from the source to the Manjira confluence. The Middle section is between the Manjira and Pranhita confluences. The Lower section is from the Pranahita confluence to the mouth.
The Godavari River length is about 1,465 km, making it one of the longest rivers in peninsular India. It is longer than many other rivers in the south.
The Godavari River has many tributaries. Left-bank tributaries are more numerous and larger.
These tributaries help drain the basin.
These are generally larger and more numerous.
This river system is large and complex. It includes the main river, many tributaries, and many dams or projects built across its path. This system gives water for irrigation, power, and other needs.
Godavari River in Maharashtra: In Maharashtra, the river flows swiftly across plains and hills. Many people worship the river here. The Godavari River source Trimbakeshwar Nashik marks the origin of this mighty river, making it an important pilgrimage and geographical point.
Godavari River in Telangana: The river enters Telangana next. Here it flows through broad valleys and helps farmers grow crops. It is also important for water storage and farming projects.
Godavari River in Andhra Pradesh: Finally, the Godavari river in Andhra Pradesh reaches the coastal plains and forms the Godavari delta region. This area is rich in soil and perfect for growing rice and other crops.
Many projects use the Godavari River and its tributaries.
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
The Godavari River has great importance:
Ready to boost your UPSC preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
The Godavari River originates at Trimbakeshwar, Nashik, Maharashtra.
The Godavari River is about 1,465 kilometers long.
The Godavari River is known as the "Dakshin Ganga."
The Pranahita River is the largest tributary of the Godavari River System.
The Godavari River flows through states are Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, and Odisha.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>