The Golden Triangle, a major opium production region in Southeast Asia, includes Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand. It remains a critical hub in the global Golden Triangle drug trade.
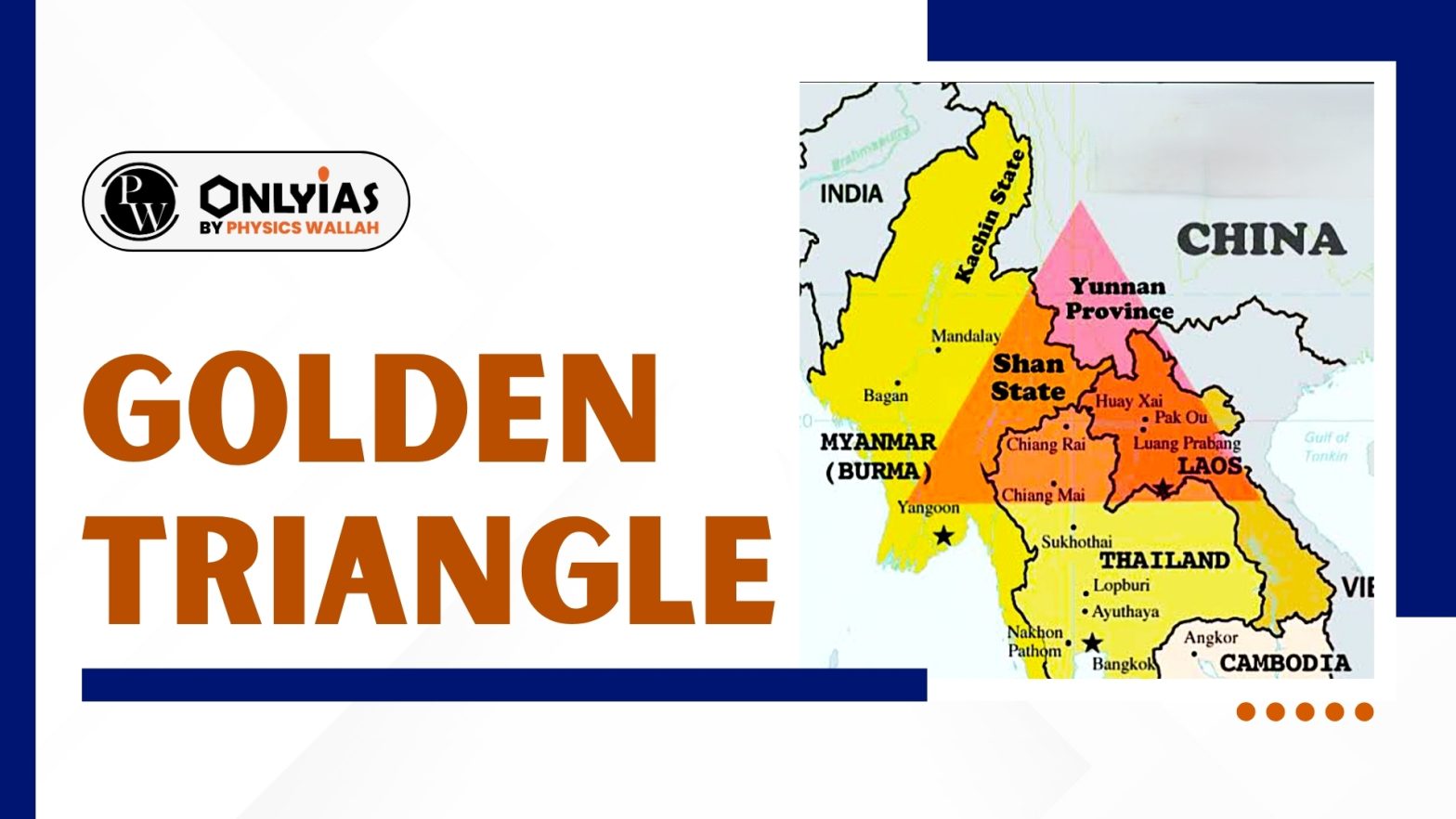
Golden Triangle: Golden Triangle is the most infamous region situated in Southeast Asia which is mostly known for its involvement in large-scale opium production. This area comprises the parts of Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand, these countries hold historical significance, by remaining the most significant opium-producing regions in the world. It became prominent in the illegal drug trade, specifically in the production and distribution of opium and heroin. Despite multiple efforts to restrain drug production, the Golden Triangle remains a focal point in the global narcotics industry.
The Golden Triangle refers to the interconnection of mountain regions where the borders of Thailand, Laos, and Myanmar meet. Its name symbolizes both the friendly geographical area for opium cultivation and the immense wealth generated through the illegal opium trade. The term Golden Triangle refers to one of the world’s two major opium-producing regions, the other being the Golden Crescent (which spans parts of Afghanistan, Iran, and Pakistan).
The term was popularized in the 1950s when it became clear that this region was a major centre for global opium production. In the past, the Golden Triangle was the world’s leading supplier of opium, with high production during the mid-20th century. Although Afghanistan has since surpassed it as the largest producer of opium in the world, the Golden Triangle continues to play a crucial role in the global drug trade.
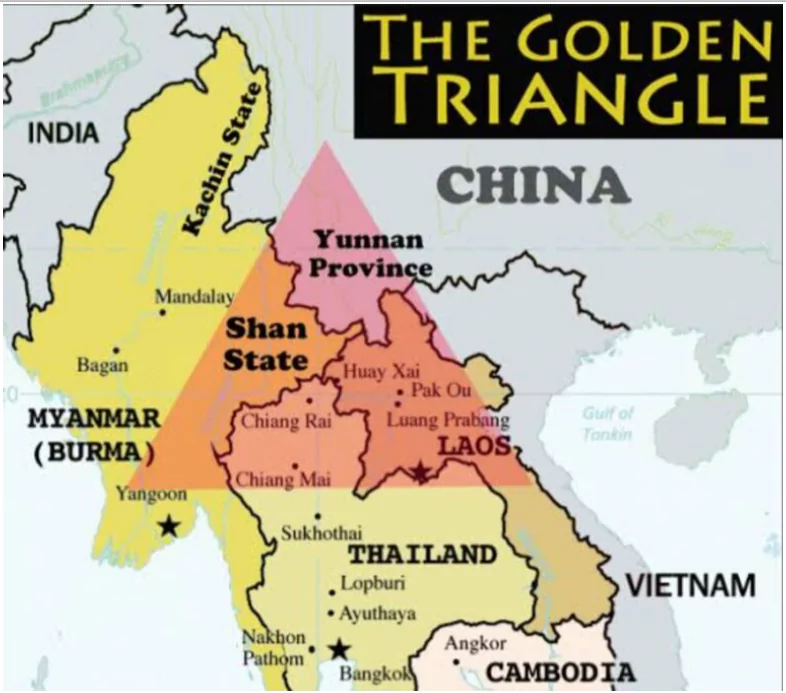
The Golden Triangle spans over the parts of Burma (Myanmar), China, Laos, and Thailand, while offering ideal conditions for opium cultivation. The history of opium production is rooted back to the 16th and 17th centuries. After World War II, heroin drug was a significant component of the opium trade, driven largely by demand from United States troops during the Vietnam War. The high demand for this drug transformed the opium economy into a highly profitable heroin industry.
Since 1964, continued efforts have been made to eradicate opium crops in the Golden Triangle but failed. The US government believes it, that equipment provided to the Burmese government for countering drug trafficking had been diverted to fight insurgencies, after such incidents US government restrained their assistance.
The Golden Triangle of opium production represents the huge illegal drug economy which is fueled by opium farming. Opium poppies (Papaver somniferum), which are processed into opium and heroin, are cultivated in remote areas of the region, predominantly in Myanmar’s Shan State, which has historically been the largest producer in the region. In recent years, cultivation has rapidly increased by 20%, followed by Chin and Kachin, where it increased by 10% and 6% respectively. The latest reports indicate significant opium cultivation in Myanmar’s Sagaing region near India. The average opium yield grew by 16% to 22.9 kg/ha due to improved farming techniques and investments in irrigation and fertilizers.
The Golden Triangle includes parts of three countries:
While the Golden Triangle holds a significant part of history, by standing alone as the leading producer. The largest producer of opium is Myanmar (Particularly Shan State), which is a major supplier of opium and heroin in East Asia, Southeast Asia, and Oceania. However, the Golden Triangle, particularly Myanmar, continues to play a vital role. The Taliban’s opium ban in Afghanistan, Myanmar is seeing a hike in production, with approx 47,100 hectares dedicated to opium cultivation in 2023 alone, as reported by the UNODC due to deteriorating governance and economic instability following the military takeover in 2021.
Myanmar has become the world’s top opium producer, surpassing Afghanistan. In 2023, Myanmar’s opium production is estimated to rise by 36%, reaching 1,080 tonnes, while Afghanistan’s output dropped by 95% after the Taliban’s 2022 drug ban, shifting global supply to Myanmar. In 2023, Myanmar’s opium farming surged, with land use increasing by 18%, from 40,100 to 47,000 hectares. The civil war in Myanmar has driven increased opium cultivation, particularly in Shan State, where insurgent groups rely on it for funding. Although this hasn’t reached the 2013 peak of 58,000 hectares, production has become more efficient. Farmers in Myanmar now earn 75% more, with average prices reaching $355 per kilogram. These shifts have made Myanmar the largest global producer, overtaking Afghanistan.
Aside from Afghanistan and Myanmar, smaller-scale opium cultivation exists in countries such as Mexico, where it is primarily grown for heroin production destined for the United States. In Southeast Asia, the revival of opium cultivation is seen as a response to economic desperation among farmers and the breakdown of state authority in parts of Myanmar.
In India, the Government announced an annual licensing policy for opium poppy cultivation, which details the minimum yield required for license renewal, the maximum area allowed per cultivator, and compensation for crop damage due to natural causes. Opium cultivation is restricted to specific areas in Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Uttar Pradesh, with districts like Mandsaur (Madhya Pradesh), Chittorgarh, and Jhalawar (Rajasthan) accounting for approximately 80% of the cultivation. These areas are strictly regulated to ensure controlled and legal production.
Opium poppy cultivation is only permitted in three states of India – Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh with the following 22 districts:
| Opium Cultivation in India | |||
| State | |||
| Districts | Madhya Pradesh | Rajasthan | Uttar Pradesh |
| Mandsaur | Kota | Barabanki | |
| Neemuch | Baran | Faizabad | |
| Ratlam | Jhalawar | Ghazipur | |
| Ujjain | Chittorgarh | Mau | |
| Jhabua | Udaipur | Lucknow | |
| Shajapur | Bhilwara | Raibareilly | |
| Rajgarh | Bareilly | ||
| Shahjahanpur | |||
| Budaun | |||
The efforts made to reduce opium production in the Golden Triangle are currently facing numerous challenges. These include:
The efforts made by governments and law enforcement authorities to control opium cultivation on a global level, by inducing several strategies:
The Golden Triangle remains an essential part of the global opium production chain, fueled by economic hardship, political instability, and the demand for heroin. With Myanmar now taking a leading role following Afghanistan’s restrictions on opium cultivation, the region’s influence in the illicit drug market is likely to grow. Addressing the root causes of this trade—poverty, conflict, and lack of enforcement—will be key to any future efforts to reduce the region’s role in global opium cultivation.
Sign up for the PWOnlyIAS Online Course by Physics Wallah and start your journey to IAS success today!
| Related Articles | |
| UPSC Syllabus | UPSC Exam Pattern |
| UPSC Interview Question | UPSC Interview Dates |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Mains GS Paper Exam Analysis |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
The Golden Triangle includes parts of Myanmar, Laos, and Thailand. These countries converge in Southeast Asia and are known for significant opium cultivation.
The Golden Triangle of opium production refers to a region infamous for producing opium, primarily used to manufacture heroin. It became a major hub for the illegal drug trade in the mid-20th century.
The region is called the Golden Triangle because of the vast profits generated by the opium trade, making it one of the most lucrative drug-producing regions in the world.
Myanmar is now the world's largest opium producer, according to the UN Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC). It producing some 25% of the world's opium, and forms part of the Golden Triangle.
Opium cultivation occurs primarily in the Golden Triangle (especially Myanmar), Afghanistan, and Mexico. These regions are key suppliers of the world's illegal opium.
Opium poppy cultivation in India has existed since the 10th century. Today it is prohibited under Section 8 of the NDPS Act, except for licensed cultivation in selected areas for medicinal purposes.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>
