Guru Gobind Singh Jayanti or the Prakash Parv of the tenth Sikh Guru is celebrated on January 17, 2024.

Guru Gobind Singh Jayanti or the Prakash Parv of the tenth Sikh Guru is celebrated on January 17, 2024.
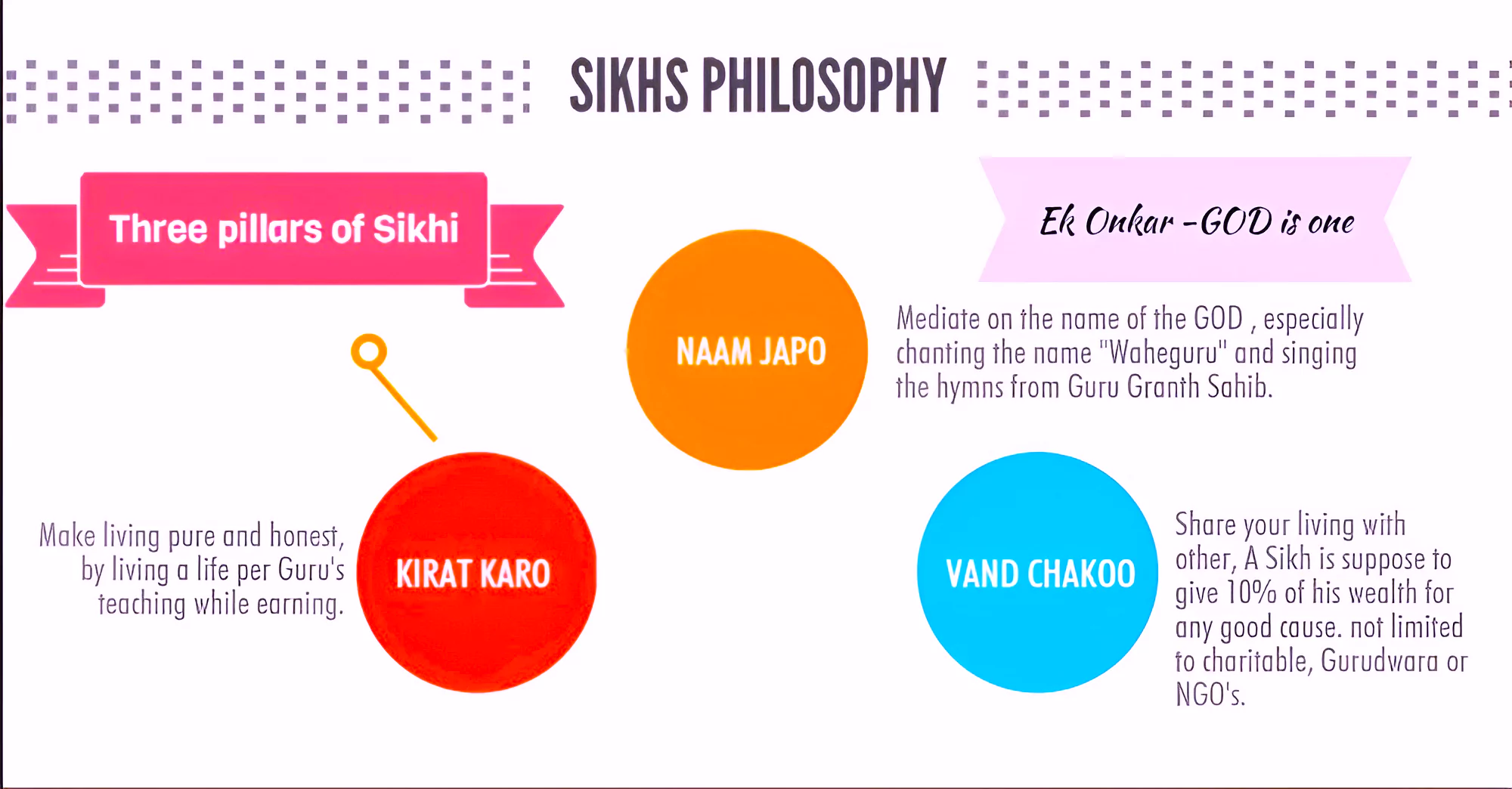
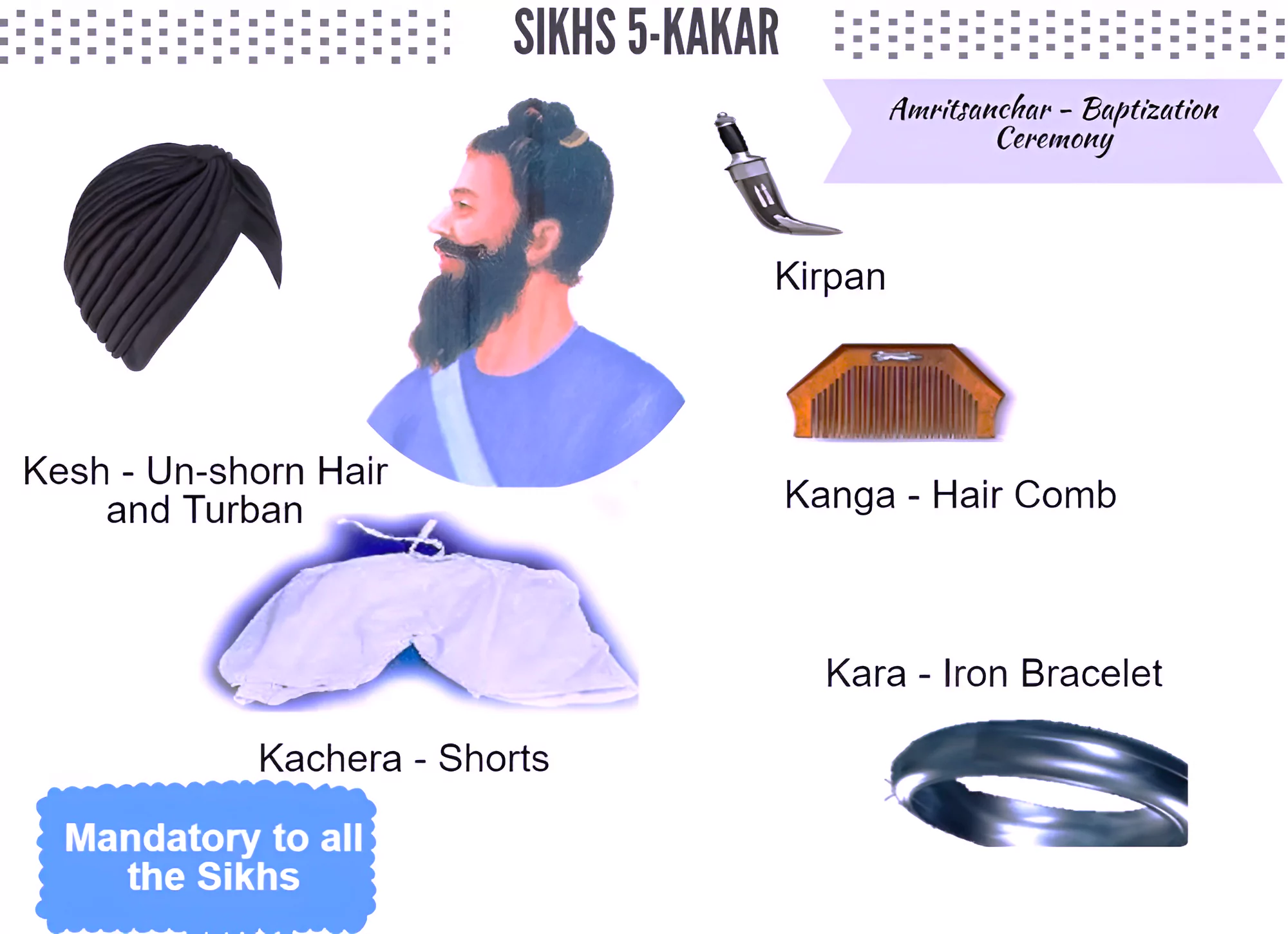
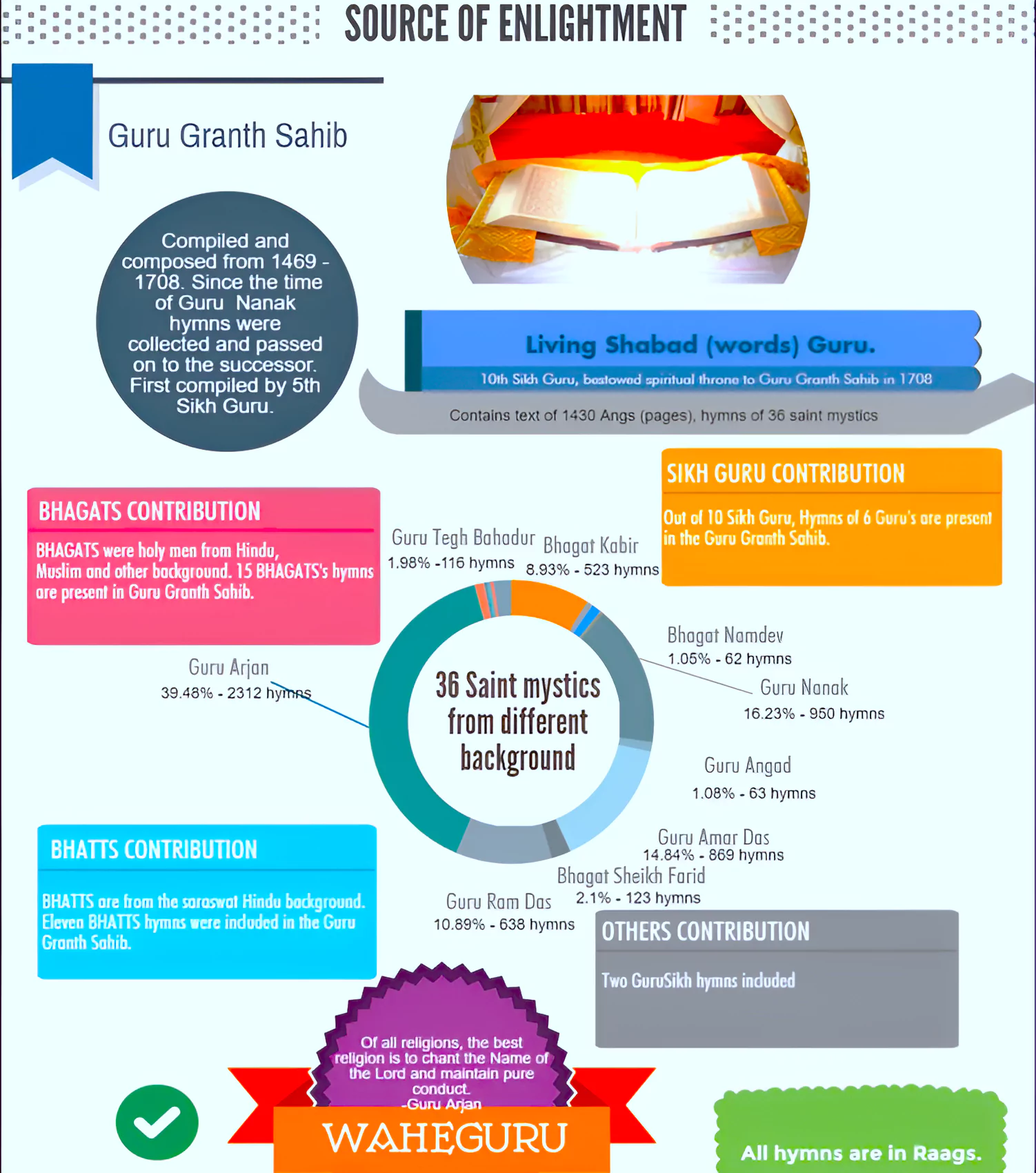
Panj Takht: There are five Takhts and these Takhts are five gurudwaras which have a very special significance for the Sikh community.
Important Gurudwara in Pakistan
|
|---|
| Sikh Guru | Contribution |
| 1. Guru Nanak (1469- 1539) |
|
| 2. Guru Angad Dev (1504-1552) |
|
| 3. Guru Amar Dass (1479-1574) |
|
| 4. Guru Ram Dass (1534-1581) |
|
| 5. Guru Arjun Dev (1563-1606) |
|
| 6. Guru Hargobind (1595-1644) |
|
| 7. Guru Har Rai (1630-1661) |
|
| 8. Guru Har Kishan (1656-1664) |
|
| 9. Guru Teg Bahadur (1621-1675) |
|
| Guru Govind Singh (1666-1708) |
|
| Guru Granth Sahib |
|

| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
Guru Gobind Singh Jayanti is celebrated on January 17.
Guru Gobind Singh Ji was born in Patna, Bihar, at Takhat Shri Harimander Ji Patna Sahib.
At the age of nine, Gobind Singh ji was proclaimed the tenth Guru of the Sikhs on Baisakhi in 1676.
Guru Gobind Singh created Khalsa in 1699 and codified Sikh law, producing literary works like the 'Dasam Granth.'
Guru Gobind Singh declared the Guru Granth Sahib to be the permanent Sikh Guru.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>