Explore the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) launched at G20 2023, connecting India to Europe through the Middle East, boosting trade, energy, and digital ties.

The India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor (IMEC) has recently garnered attention as it progresses with ambitions to strengthen trade and connectivity between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Launched during the G20 Summit in 2023, IMEC is positioned as a strategic counterbalance to China’s Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), highlighting India’s increasing role in global infrastructure projects. Keep on reading to understand what the IMEC corridor is and why it was proposed.
The IMEC Corridor, or the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor, is a proposed infrastructure network aimed at boosting economic links among participating regions. This project spans from India through the Middle East to Europe, involving vital transit and connectivity routes. The project intends to enhance economic cooperation, promote cross-border investments, and facilitate a smoother flow of goods and energy.
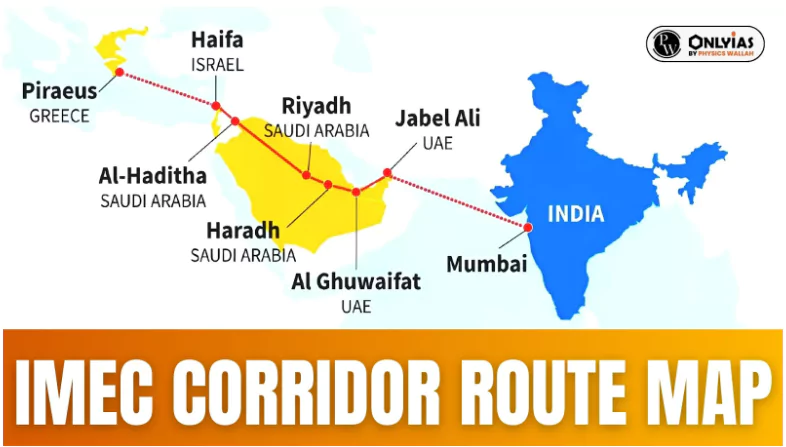
The IMEC (India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor) connects India, the Middle East, and Europe via a strategic route that promotes trade, energy, and digital connectivity. Here are the routes and key countries to create a major trade passage between Asia, the Middle East, and Europe.
IMEC’s main objective is to enhance regional connectivity and provide a reliable, efficient trade route. It seeks to diversify trade routes, reduce transit times, and offer an alternative to routes dominated by other major global powers. IMEC also emphasizes sustainable development, with potential for renewable energy transit and digital connectivity enhancements.
The IMEC Corridor, a strategic infrastructure initiative, aims to enhance connectivity and trade across key regions. Despite its potential, the corridor faces geopolitical tensions, funding constraints, and complex regulatory frameworks. Here is the current Status and Challenges of the IMEC Corridor:
| IMEC Corridor Component | Current Status/Progress | Challenges/Recommendations |
| Eastern Leg | India-UAE segment advancing, supported by CEPA (2022); Bilateral trade increased by 93% from 2020-21 to 2023-24. | Focus on Virtual Trade Corridor to improve trade processes, lower costs, and boost efficiency. |
| Western Leg | Slow progress due to Israel-Palestine conflict, affecting cooperation with Saudi Arabia and Jordan. | Cooperation delayed; geopolitical stability needed for effective partnership between Middle Eastern nations and Israel. |
| Broader Corridor Components | Energy, telecom, and fiber-optic projects were delayed due to West Asia conflicts. | Progress on clean energy and tech advancements is on hold until regional stability is achieved. |
| Digital Logistics & Supply Chain | Improve digital logistics to reduce costs and make India a supply chain hub. | Enhance trade and manufacturing competitiveness to position India as a leader in international supply chains, especially against competitors like China. |
| IMEC Secretariat | Proposed to aid coordination and implementation across regions. | Conduct empirical research, attract new partners, and establish frameworks for trade facilitation. |
| Geopolitical Stability Focus | Required to enable the full potential of IMEC, including energy and tech cooperation. | Diplomatic efforts to stabilize the Middle East situation will support broader IMEC objectives. |
The corridor’s map includes specific ports, rail networks, and transit hubs in each participating region, aiming to maximize efficiency in transporting goods and resources. Notably, ports in the UAE and Saudi Arabia play a critical role in linking Asia to Europe.
| IMEC Corridor Ports | |
| Region | Ports |
| India | Mundra (Gujarat), Kandla (Gujarat), Jawaharlal Nehru Port Trust (Navi Mumbai) |
| Middle East | Fujairah, Jebel Ali, Abu Dhabi (UAE), Dammam, Ras Al Khair (Saudi Arabia) |
| Railway Line | Links Fujairah (UAE) to Haifa (Israel), passing through Saudi Arabia (Ghuwaifat and Haradh) and Jordan |
| Israel | Haifa |
| Europe | Piraeus (Greece), Messina (Southern Italy), Marseille (France) |
UPSC candidates should understand the IMEC Corridor’s geopolitical implications, especially its role in India’s foreign policy and its economic impact. The corridor aligns with India’s vision of a multipolar global order and increased regional influence, which is essential knowledge for the UPSC Mains.
Ready to boost your UPSC 2025 preparation? Join PW’s UPSC online courses today!
UPSC Exam 2025 Related Articles
UPSC Prelims 2025 Exam
UPSC Notification 2025
UPSC Preparation 2025
UPSC Eligibility 2025
UPSC Exam Pattern
UPSC Syllabus
IMEC is a proposed trade corridor linking India, the Middle East, and Europe to improve connectivity and trade.
India, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Israel, and EU nations are involved in the corridor.
IMEC aims to facilitate economic cooperation, reduce transit times, and offer an alternative to existing trade routes.
IMEC enhances India's role in global trade, boosts economic ties, and supports regional connectivity initiatives.
IMEC provides an alternate trade route focusing on multilateral cooperation, whereas the BRI is largely China-centric.
IMEC was announced on September 2023 on the sidelines of the G20 summit in New Delhi.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>