Indian Defence Estates Service (IDES) oversees defence land management, cantonment administration, and estate planning. It ensures optimal use of defence properties while supporting cantonment governance and strengthening national security.

The Indian Defence Estates Service (IDES) is a premier Group ‘A’ Central Civil Service under the Ministry of Defence, dedicated to managing and safeguarding India’s vast defence land assets and cantonments. Established in 1926, the service plays a crucial role in land management, urban development, and infrastructure planning within defence areas. IDES officers oversee the administration of 62 Cantonment Boards, ensuring efficient governance and civic services for both military and civilian populations. By maintaining accountability and preventing encroachments, IDES significantly contributes to the nation’s security and strategic land management framework.
The Indian Defence Estates Service (IDES) operates as an organized Group A Central Service within the Government of India, under the Ministry of Defence. The selection process for Indian Defence Estates Service is based on the annual Civil Services Examination conducted by the UPSC. Established on December 16, 1926, the department has undergone a series of name changes, initially starting as the Military Lands and Cantonments Service, then evolving into the Defence Lands and Cantonments Service. In 1985, it officially adopted the name Indian Defence Estates Service. According to the Indian Defence Estates Service (Group ‘A’) Rules, 2013, IDES consists of 75% direct recruitment and 25% promotion. The history and development of IDES are closely intertwined with the recent history of the nation.
IDES stands for Indian Defence Estates Service, a Group ‘A’ Central Civil Service under the Ministry of Defence responsible for managing defence lands and cantonments across India. Established in 1926, IDES officers oversee land acquisition, administration of 62 Cantonment Boards, encroachment prevention, and urban development in defence areas. Recruited through UPSC Civil Services Examination, they ensure compliance with the Cantonments Act 2006 and advise on policy matters related to defence estates.
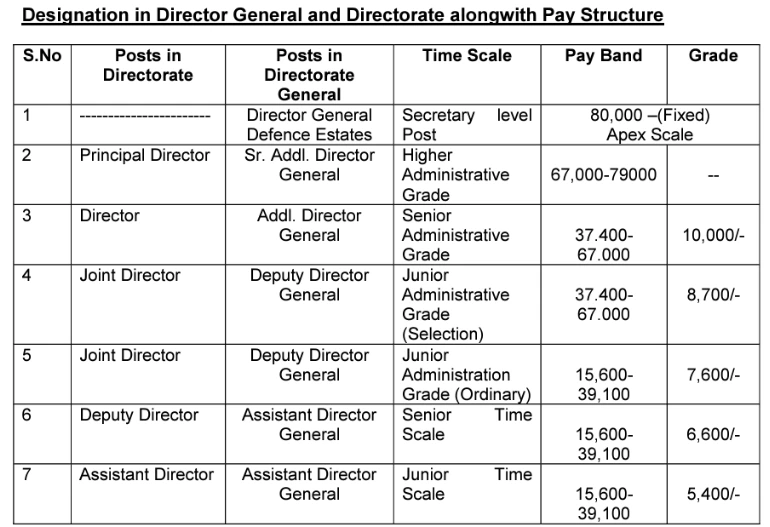
Organizational Framework of Indian Defence Estates Service: A Three-Tiered Structure
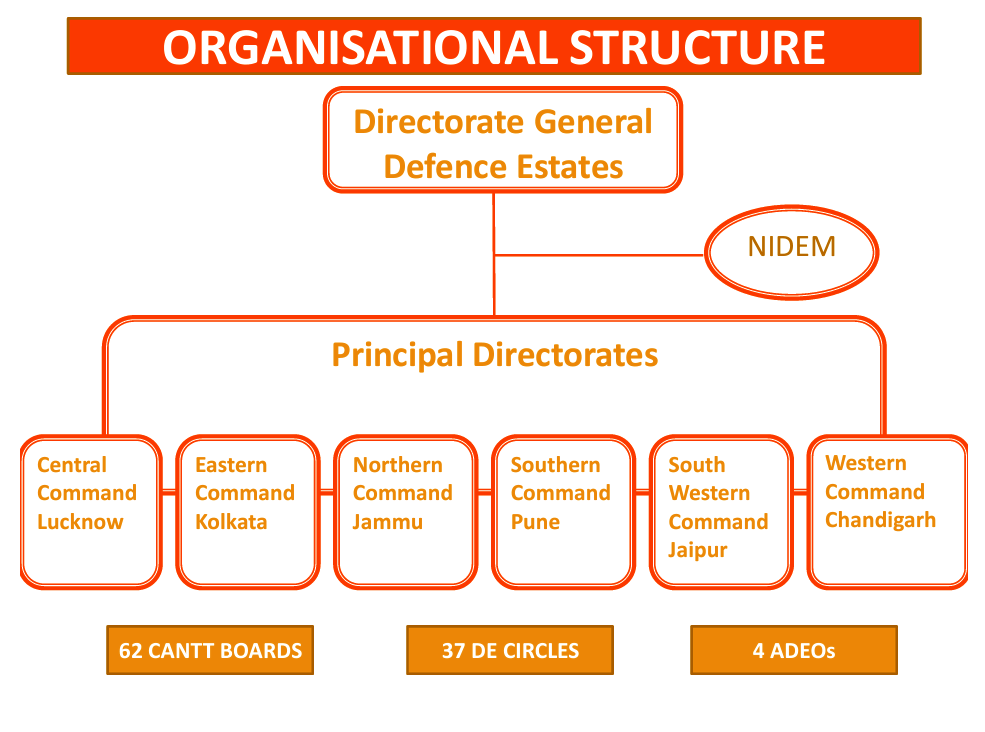
The structure of the Indian Defence Estates Service (IDES) is organized into three tiers.
IDES officers have the opportunity for deputation to various entities such as the Central Government, State Governments, Autonomous Organizations, Subordinate Organizations, PSUs, and participation in the Central Staffing Scheme.
The duties and responsibilities of IDES officers are diverse and undergo significant evolution across different stages of their careers, reflecting a dedication to effective land management, legal proficiency, and the well-being of cantonment residents.
In conclusion, the roles and responsibilities of IDES officers exemplify a trajectory marked by a commitment to efficient land management, legal expertise, and a dedication to the welfare of residents in cantonments. From their formative years as probationers to assuming the pinnacle position of Director General Defence Estates, IDES officers navigate a complex terrain, contributing significantly to the nation’s defense infrastructure and the well-being of communities within cantonments.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series |
Check Out UPSC CSE Books
Visit PW Store
IDES functions as a crucial Group A Central Service under the Ministry of Defence, responsible for overseeing defence lands, Cantonment Boards, and various land management functions.
Recruitment to IDES primarily occurs through the annual Civil Services Examination (CSE) conducted by the Union Public Service Commission (UPSC).
IDES follows a three-tier structure: The highest tier includes the Directorate General in Delhi Cantt., followed by six Directorates aligned with Army Commands at the middle tier. At the field level, Chief Executive Officers are stationed in 62 Cantonment Boards, along with Defence Estates Officers in 37 Defence Estates Circles.
IDES officers contribute significantly to policy formulation by offering counsel to the Ministry of Defence, overseeing law and regulation implementation, and addressing the land and building requirements of user services.
NIDEM serves as the dedicated training institute for IDES, delivering induction and in-service training. The institute plays a pivotal role in enhancing the skills of probationers and officers.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>