Indian National Science Day is celebrated in India on February 28 each year to mark the discovery of the Raman effect by Indian physicist Sir CV Raman on 28 February 1928.

India celebrates its National Science Day annually on 28 February.
Indian National Science Day is observed to highlight the importance of science in our daily lives and to encourage scientific temper among the masses. It celebrates the spirit of scientific inquiry and innovation, emphasizing the role of science in addressing societal challenges and fostering national development.

National Science Day is marked each year with a unique theme that reflects the focus of scientific endeavors in India. Table showcasing the themes over the years:
| Year | Theme |
| National Science Day 2024 theme |
|
| 2023 |
|
| 2022 |
|
| 2021 |
|
Indian National Science Day is celebrated across the country through various activities and events aimed at promoting scientific awareness and education. Some common ways of celebration include:
Several government and non-government organizations play a crucial role in organizing and promoting Indian National Science Day. The Ministry of Science and Technology, along with agencies like the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), and Indian National Science Academy (INSA), collaborate to coordinate nationwide celebrations and activities.
Sir Chandrasekhara Venkata Raman, commonly known as C.V. Raman, was an eminent Indian physicist born on November 7, 1888, in Tiruchirapalli, British India (now in Tamil Nadu, India). He made significant contributions to the field of physics, particularly in the study of light scattering, molecular spectroscopy, and the behavior of light in transparent materials.

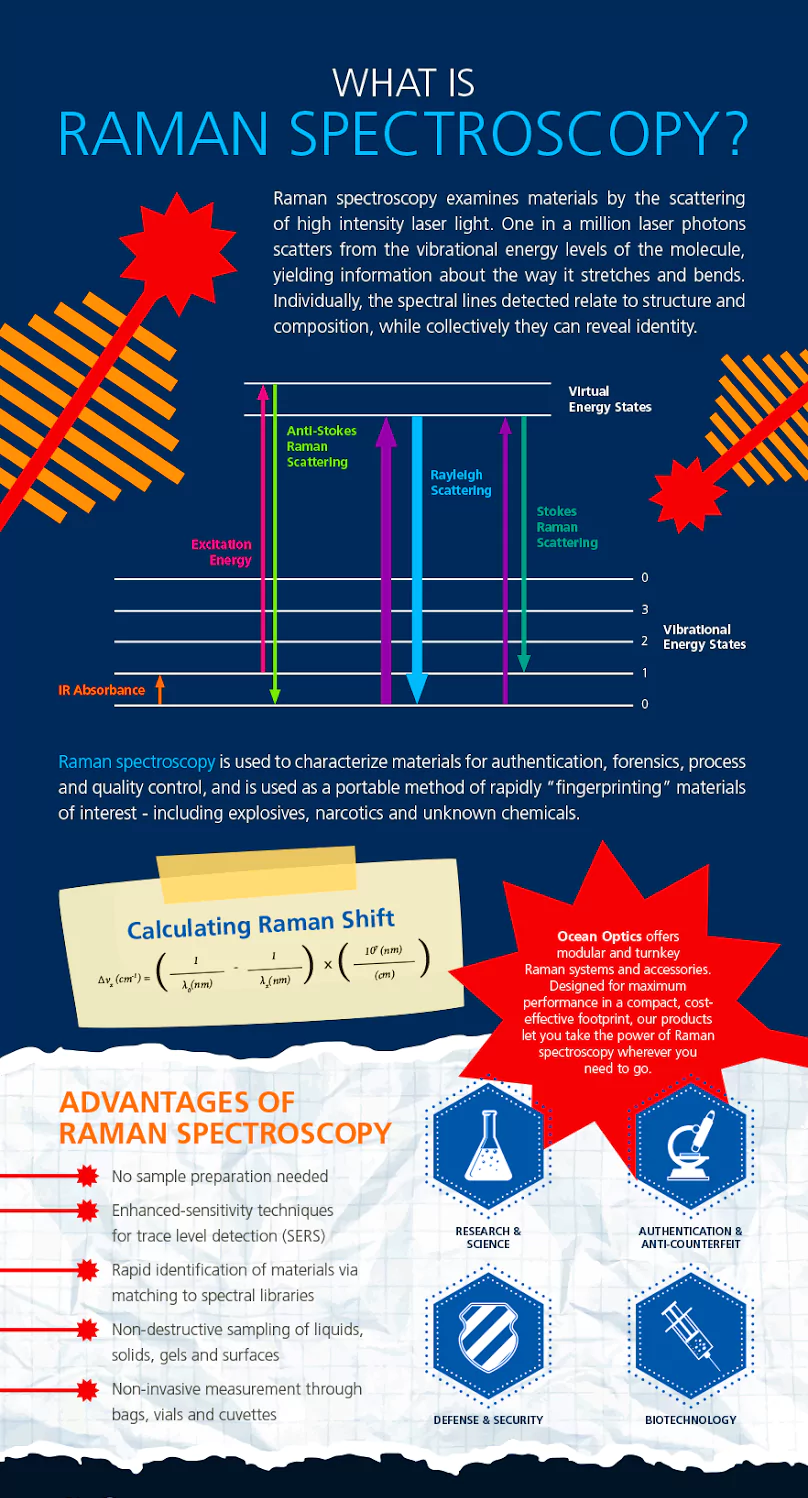
The Raman Effect, discovered by C.V. Raman in 1928, refers to the inelastic scattering of light by molecules, leading to changes in the energy and wavelength of the scattered photons. This phenomenon, based on the interaction between light and matter, provides valuable insights into the vibrational and rotational modes of molecules, thereby revolutionizing the field of spectroscopy and paving the way for numerous applications in chemistry, physics, and materials science.
| Scientist | Contribution |
| C.V. Raman |
|
| APJ Abdul Kalam |
|
| Homi J Bhabha |
|
| Srinivasa Ramanujan |
|
| Hargobind Khorana |
|
| Satyendra Nath Bose |
|
| Jagadish Chandra Bose |
|
| Important Science Days in India | Brief Description |
| National Innovation Day – January 30 |
|
| National Biotechnology Day – April 5 |
|
| World Environment Day – June 5 |
|
| National Mathematics Day – December 22 |
|
| National Technology Day – May 11 |
|
| National Science Day – February 28 |
|
| National Space Day – August 23 |
|
| World Science Day for Peace and Development – November 10 |
|
| World Space Week – October 4-10 |
|
Indian National Science Day serves as a tribute to the remarkable achievements of C.V. Raman and his groundbreaking discovery of the Raman Effect. It symbolizes India’s commitment to scientific excellence and innovation while promoting a culture of scientific inquiry and education nationwide. Through a diverse range of activities and initiatives, this day inspires and engages individuals of all ages to explore the wonders of science and contribute to the advancement of knowledge and technology for the betterment of society.
| Must Read | |
| NCERT Notes For UPSC | UPSC Daily Current Affairs |
| UPSC Blogs | UPSC Daily Editorials |
| Daily Current Affairs Quiz | Daily Main Answer Writing |
| UPSC Mains Previous Year Papers | UPSC Test Series 2024 |
It celebrates C.V. Raman's discovery and promotes scientific awareness and education.
Sir C.V. Raman and his assistant K.S. Krishnan discovered the Raman Effect in 1928.
Through workshops, exhibitions, lectures, competitions, and awareness campaigns nationwide.
Ministry of Science and Technology, DST, CSIR, Ministry of Education, NCSTC, and scientific institutions.
Nobel laureate C.V. Raman's work revolutionized physics and laid the foundation for scientific research in India.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>