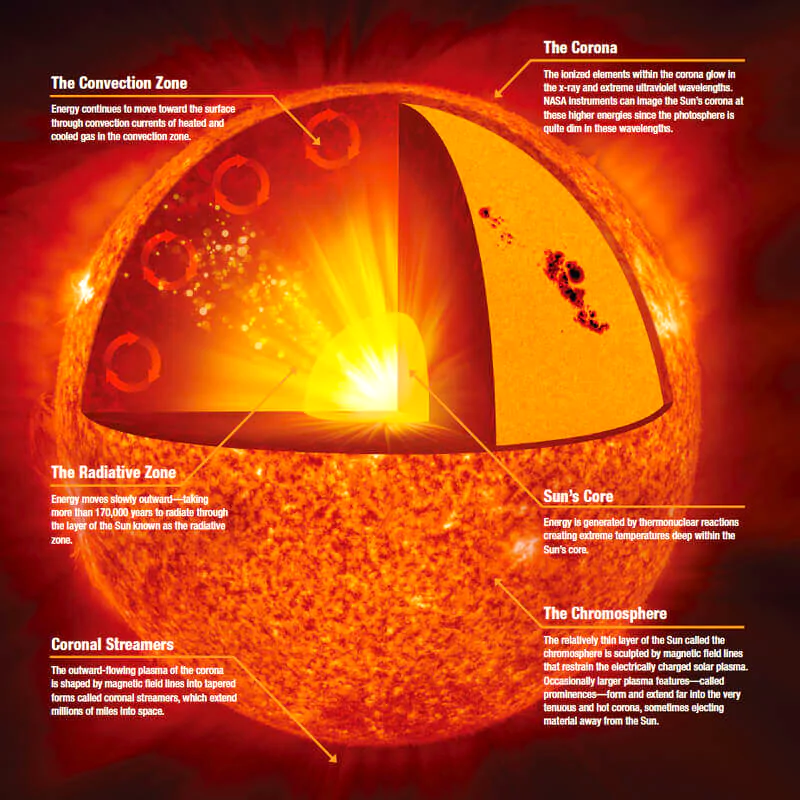
Aditya-L1, an ISRO spacecraft for solar atmosphere study, launched on September 2, 2023. India's Aditya-L1 mission has achieved its first significant solar observations.

Aditya L1- An Indian Solar Mission: In recent instances, the cosmos has grown to be a playground for human exploration, with India making widespread strides in unravelling the mysteries of our celestial neighbour. The Aditya L1 mission, spearheaded by the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), marks a historic moment as the state delves into area-primarily based solar statements. India’s Aditya-L1 mission has achieved a key milestone by capturing its first significant solar observations. Using the Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC), scientists have gained insights into the Sun’s coronal mass ejections (CMEs).
Recently, ISRO released Images of the Sun Captured by Aditya-L1 Payloads.
The images were taken by the remote sensing payloads Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) and Visible Emission Line Coronagraph (VELC) aboard the Aditya-L1 spacecraft.
Aditya L1 stands as India’s maiden foray into committed area-primarily based solar commentary. Conceptualised in 2008 through the Advisory Committee for Space Research, the mission seeks to examine the Sun from a near distance, providing unparalleled insights into its atmosphere and magnetic discipline.

Aditya L1 Image: Indian Solar Mission
Armed with seven present day payloads, Aditya L1 is equipped to look at various sun phenomena, inclusive of the Photosphere, Chromosphere, Solar Corona, sun emissions, solar winds, flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs). The spacecraft employs electromagnetic and particle detectors, as well as magnetic discipline detectors, for spherical-the-clock imaging of the Sun
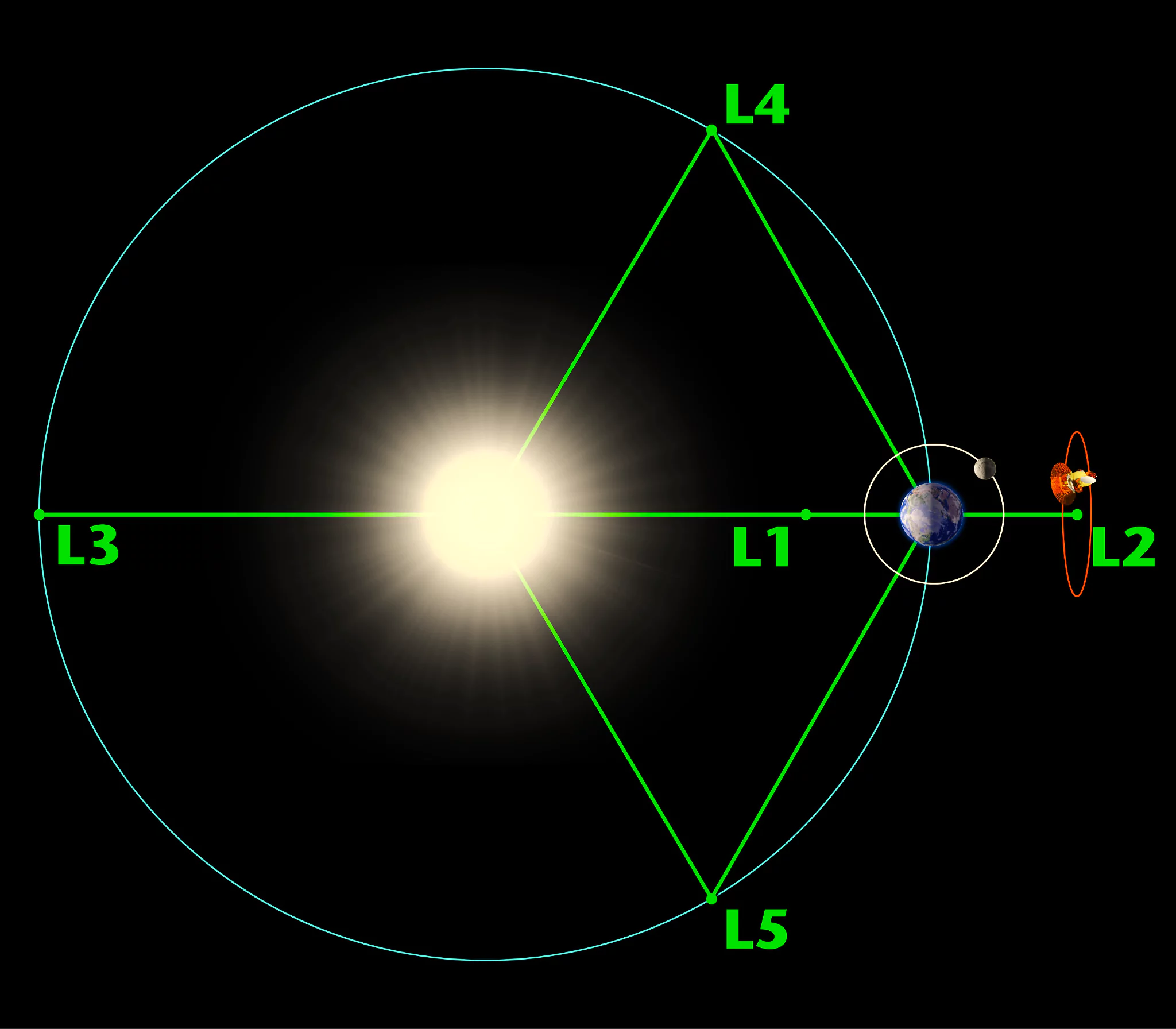
As Aditya L1 embarks on its celestial journey, it aims to dance along the gravitational chessboard, strategically positioning itself at Lagrange Point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth system. Here’s List of the distinctive Lagrange Points, where gravitational forces create celestial equilibrium, paving the way for unique observations:
| Lagrange Point | Position in the Sun-Earth System | Characteristics | Notable Satellites |
| L1 | Between the Sun and Earth |
|
|
| L2 | Directly ‘behind’ Earth from the Sun |
|
|
| L3 | Behind the Sun, opposite Earth |
|
|
| L4 and L5 | Forming an equilateral triangle with the two larger bodies |
|
|
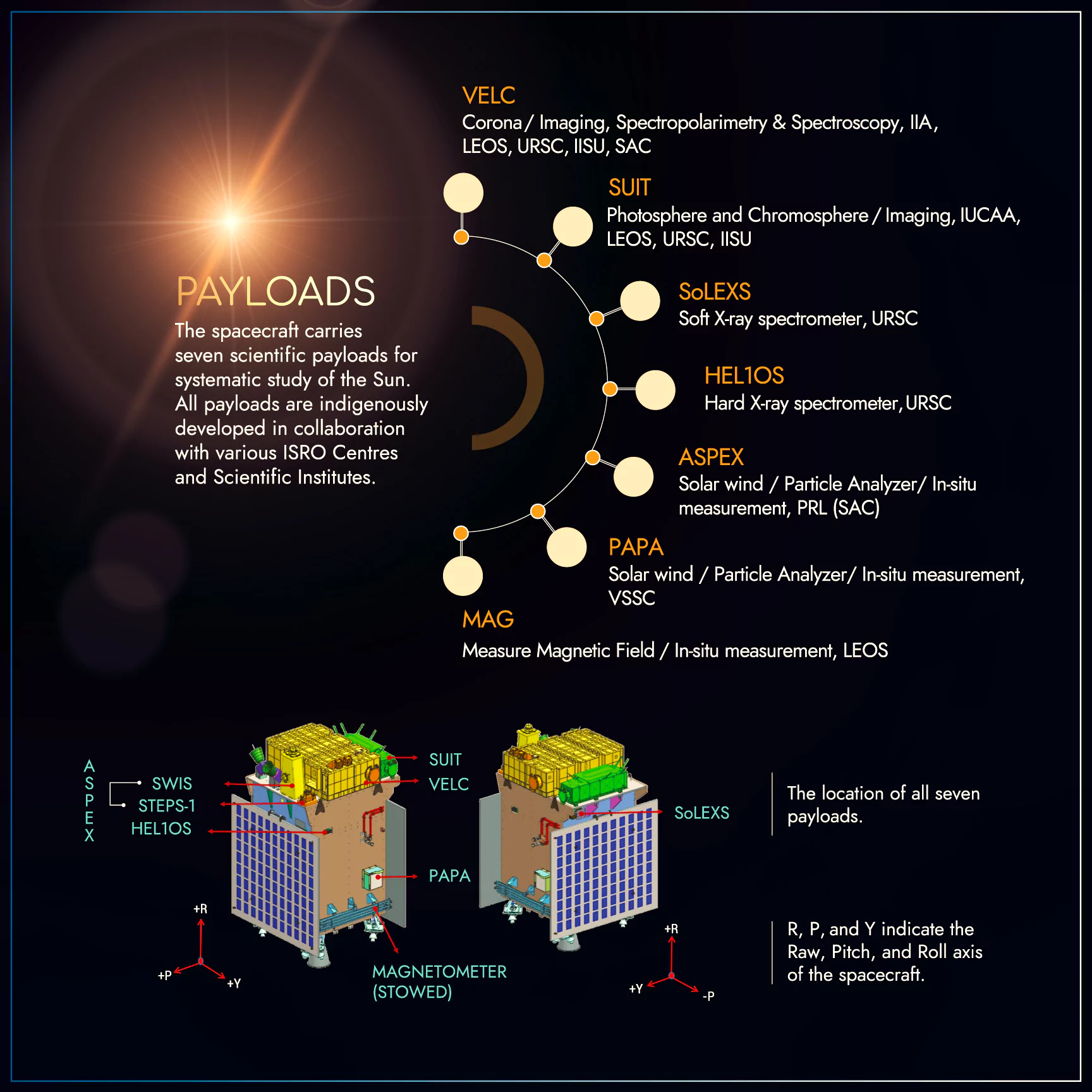
Aditya L1 Payloads |
Focus Area |
Observations |
| Visible Line Emission Coronagraph (VLEC) | Corona Imaging & Spectroscopy | Concentrates on capturing the intricate details of the Sun’s corona through advanced imaging techniques. |
| Solar Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (SUIT) | Photosphere and Chromosphere Imaging – Narrow & Broadband | Engages in photographing the Sun’s photosphere and chromosphere using both narrow and broadband spectra. |
| Solar Low Energy X-ray Spectrometer (SoLEXS) | Sun-as-a-star Soft X-ray observations | Devoted to observing soft X-ray emissions from the Sun, providing insights into its innermost dynamics. |
| Aditya Solar wind Particle Experiment (ASPEX) | Solar wind and Particle Analysis – Protons & Heavier Ions | Analyses solar wind and particles, including protons and heavier ions, unravelling their composition. |
| High Energy L1 Orbiting X-ray Spectrometer (HEL1OS) | Hard X-ray observations of the Sun | Specialised in capturing hard X-ray emissions from the Sun, offering a unique perspective on solar activities. |
| Plasma Analyser Package for Aditya (PAPA) | Solar wind and Particle Analysis – Electrons & Heavier Ions | Explores the solar wind and particles, with a specific focus on electrons and heavier ions. |
| Advanced Tri-axial High-Resolution Digital Magnetometers | In-situ magnetic field measurements (Bx, By, and Bz) | Conducts on-the-spot measurements of the solar magnetic field in three dimensions, enhancing our understanding. |
The Aditya L1 Mission is India's maiden committed space-based solar remark initiative led via the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO). It targets to examine the Sun's environment, magnetic discipline, and numerous solar phenomena.
The task was conceptualised in 2008 by using the Advisory Committee for Space Research, and it has advanced into an enormous milestone in India's area exploration endeavours.
Lagrange Points are positions in an area in which gravitational forces create equilibrium. Aditya L1 is strategically positioned at Lagrange Point 1 (L1) of the Sun-Earth device to achieve a continuous and stable statement of the Sun.
The primary objectives include analysing sun atmospheric dynamics, exploring coronal heating and mass ejections, conducting in-situ particle and plasma commentary, reading the physics of solar corona, and investigating the improvement, dynamics, and foundation of coronal mass ejections.
Aditya L1 is equipped with seven modern payloads that specialize in numerous components of solar observation, including the Photosphere, Chromosphere, Solar Corona, sun emissions, sun winds, flares, and Coronal Mass Ejections (CMEs).
The venture positions India as a trailblazer in solar exploration, complements its international medical status, contributes to strategic area diplomacy, propels technological innovation, aids in area weather prediction for countrywide security, gives an academic impetus, and evokes scientific interest.
Aditya L1's non-stop statement facilitates in forecasting space weather by way of tracking solar flares, coronal mass ejections, and sun winds, that may impact Earth's conversation, navigation, and energy grids.
Challenges encompass the tough space environment, precision in orbital insertion, device calibration and synchronisation, real-time statistics transmission, spacecraft autonomy, reaction time, budgetary and timeline constraints, and dynamics in worldwide collaboration.
Solar variability determined by Aditya L1 contributes to expertise its impact on Earth's climate styles, assisting weather technology studies.
Lagrange Points offer celestial equilibrium, efficient lengthy-duration observations, gasoline conservation, and strategic gateways for advancing cosmic knowledge.
<div class="new-fform">
</div>